Oxidation and Reduction
... 14. Recall that the same number of electrons that are lost by atoms during oxidation must be gained by atoms during reduction. Show how the half-reactions for Reactions C and D in Model 2 can be added together to give the overall redox reactions shown. ...
... 14. Recall that the same number of electrons that are lost by atoms during oxidation must be gained by atoms during reduction. Show how the half-reactions for Reactions C and D in Model 2 can be added together to give the overall redox reactions shown. ...
Document
... Products • The resulting substances produced in a chemical reaction. • written on the right hand side of the chemical equation ...
... Products • The resulting substances produced in a chemical reaction. • written on the right hand side of the chemical equation ...
File
... Species react as a result of collisions of sufficient energy and proper orientation The rate of reaction is expressed as the change in concentration of a particular reactant/product per unit time Concentration changes in a reaction can be followed indirectly by monitoring changes in mass, volume, co ...
... Species react as a result of collisions of sufficient energy and proper orientation The rate of reaction is expressed as the change in concentration of a particular reactant/product per unit time Concentration changes in a reaction can be followed indirectly by monitoring changes in mass, volume, co ...
chapter15-burno.1348..
... Significance of the Equilibrium Constant The significance of the equilibrium constant lies in the fact that for a chemical reaction taking place at a particular temperature T, the equilibrium constant (KC or Kp) has a particular numerical value. This means that no matter what the starting concentra ...
... Significance of the Equilibrium Constant The significance of the equilibrium constant lies in the fact that for a chemical reaction taking place at a particular temperature T, the equilibrium constant (KC or Kp) has a particular numerical value. This means that no matter what the starting concentra ...
134_2010_1897_MOESM1_ESM - Springer Static Content Server
... reaction in the expanded volume (2 L), there is an equivalent net consumption of H+-ions (-1.55E-07 mol/L) and OH-- ions (-1.55E-07 mol/L) – incorrect sign, used in Table S1 – to form 1.55E-07 mol/L H2O. Therefore, at initial state before chemical reaction, the concentrations of 0.140 mol/L NaOH an ...
... reaction in the expanded volume (2 L), there is an equivalent net consumption of H+-ions (-1.55E-07 mol/L) and OH-- ions (-1.55E-07 mol/L) – incorrect sign, used in Table S1 – to form 1.55E-07 mol/L H2O. Therefore, at initial state before chemical reaction, the concentrations of 0.140 mol/L NaOH an ...
Full answers
... reaction coordinate Calculate the factor by which the reaction speeds up due to the presence of each of these two catalysts at a temperature of 37 C. Assume that the pre-exponential Arrhenius factor remains constant. Using the Arrhenius equation, k = A exp(-Ea / RT). Assuming that A is constant, the ...
... reaction coordinate Calculate the factor by which the reaction speeds up due to the presence of each of these two catalysts at a temperature of 37 C. Assume that the pre-exponential Arrhenius factor remains constant. Using the Arrhenius equation, k = A exp(-Ea / RT). Assuming that A is constant, the ...
Chapter 15 PPT
... Thermodynamics is the study of the changes in energy and transfers of energy that accompany chemical and physical processes. In this chapter we will address 3 fundamental questions. Will two (or more) substances react when they are mixed under specified conditions? If they do react, what energy chan ...
... Thermodynamics is the study of the changes in energy and transfers of energy that accompany chemical and physical processes. In this chapter we will address 3 fundamental questions. Will two (or more) substances react when they are mixed under specified conditions? If they do react, what energy chan ...
Prelab Assignment: The lodination of Acetone
... the reaction will give you information about the order of the reaction with respect to H+. Repeat the experiment with this mixture to establish the time of reaction to within 15 seconds, again making sure that the temperature is within about a degree of that observed previously. From the rate you de ...
... the reaction will give you information about the order of the reaction with respect to H+. Repeat the experiment with this mixture to establish the time of reaction to within 15 seconds, again making sure that the temperature is within about a degree of that observed previously. From the rate you de ...
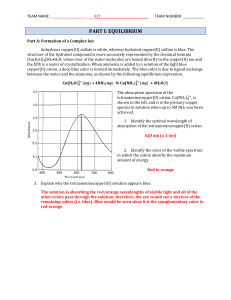
C. Adding acid shifts the equilibrium to the right
... Atoms of an element that are chemically alike but differ in mass are called isotopes of the element. Isotopes of an element have different mass numbers because they have different numbers of neutrons, but they all have the same atomic number. Electron configurations represent the way electrons are a ...
... Atoms of an element that are chemically alike but differ in mass are called isotopes of the element. Isotopes of an element have different mass numbers because they have different numbers of neutrons, but they all have the same atomic number. Electron configurations represent the way electrons are a ...
Chem Stoichiometry Study Guide
... 9. Solid carbon disulfide burns in oxygen to yield carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide gases. 10. Iron metal reacts with aqueous silver nitrate to produce aqueous iron(III) nitrate and silver metal. IDENTIFY THE TYPE OF REACTION, PREDICT THE PRODUCTS (STATES NOT REQUIRED), AND BALANCE THE EQUATION: ...
... 9. Solid carbon disulfide burns in oxygen to yield carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide gases. 10. Iron metal reacts with aqueous silver nitrate to produce aqueous iron(III) nitrate and silver metal. IDENTIFY THE TYPE OF REACTION, PREDICT THE PRODUCTS (STATES NOT REQUIRED), AND BALANCE THE EQUATION: ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... Chemical kinetics is the branch of chemistry that measures rates of chemical reactions, studies the factors that influence them, designs and prepares new catalysts, and interprets the results at the molecular level. The independent variable of chemical kinetics, from the chemical reaction starting m ...
... Chemical kinetics is the branch of chemistry that measures rates of chemical reactions, studies the factors that influence them, designs and prepares new catalysts, and interprets the results at the molecular level. The independent variable of chemical kinetics, from the chemical reaction starting m ...
Answers - Scioly.org
... 20. The student concludes that she has synthesized ethyl butanoate. Use evidence from the two experiments to support or to refute her claim. The peak of highest mass to charge ratio is approximately 116; therefore, the unknown molecule would have a molecular mass of 116. Ethyl butanoate has the chem ...
... 20. The student concludes that she has synthesized ethyl butanoate. Use evidence from the two experiments to support or to refute her claim. The peak of highest mass to charge ratio is approximately 116; therefore, the unknown molecule would have a molecular mass of 116. Ethyl butanoate has the chem ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... substances can combine during a chemical reaction to produce new substances. The substances that undergo change are called reactants. The new substances are products. Sometimes during a chemical reaction, one type of reactant will be used up before the other reactants. This reactant is the limiting ...
... substances can combine during a chemical reaction to produce new substances. The substances that undergo change are called reactants. The new substances are products. Sometimes during a chemical reaction, one type of reactant will be used up before the other reactants. This reactant is the limiting ...
Catalysis

Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required.