Chapter 9 Stoichiometry
... Enthalpy is the amount of heat that a substance has at a given temperature and pressure (see Table 8.1 pg 190) The heat of a reaction is the heat that is released or absorbed during a chemical reaction. Heat of Reaction is represented by The symbol H ...
... Enthalpy is the amount of heat that a substance has at a given temperature and pressure (see Table 8.1 pg 190) The heat of a reaction is the heat that is released or absorbed during a chemical reaction. Heat of Reaction is represented by The symbol H ...
Spring Exam 2 - Chemistry
... This is VERY IMPORTANT! Under IDENTIFICATION NUMBER, put in your 8 DIGIT STUDENT ID NUMBER (do not use the 9 at the beginning of your number) beginning in column A and continuing through column H, column I will be blank, (do NOT use column J at this time); be sure to fill in the correct circles (a c ...
... This is VERY IMPORTANT! Under IDENTIFICATION NUMBER, put in your 8 DIGIT STUDENT ID NUMBER (do not use the 9 at the beginning of your number) beginning in column A and continuing through column H, column I will be blank, (do NOT use column J at this time); be sure to fill in the correct circles (a c ...
Activity C14: Rate of a Chemical Reaction 1
... In this activity you will determine the effect of changes in concentration of the reactants on the rate of the chemical reaction. The reaction for this activity is the acidic reduction of the thiosulfate ion to sulfur and sulfur dioxide. The equation for the reaction is: S2O32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) ====== ...
... In this activity you will determine the effect of changes in concentration of the reactants on the rate of the chemical reaction. The reaction for this activity is the acidic reduction of the thiosulfate ion to sulfur and sulfur dioxide. The equation for the reaction is: S2O32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) ====== ...
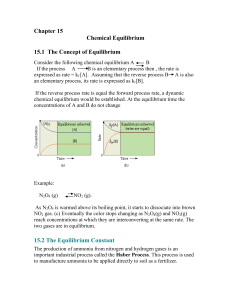
Consider the following chemical equilibrium A B
... Adding H2 will cause the system to shift as to reduce the concentration of H2 to its original value. This will caus the system to produce more of NH3 b. Effect of volume and pressure If a system at equilibrium is disturbed by decreasing the volume (increasing the total pressure), the system respond ...
... Adding H2 will cause the system to shift as to reduce the concentration of H2 to its original value. This will caus the system to produce more of NH3 b. Effect of volume and pressure If a system at equilibrium is disturbed by decreasing the volume (increasing the total pressure), the system respond ...
Electrochemistry
... Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers (In order of priority): 1. The oxidation number of any pure element is _________. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is __________ to its charge. 3. The ______ of the oxidation numbers in a compound is zero if ____________, or equal to the ___________ if ...
... Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers (In order of priority): 1. The oxidation number of any pure element is _________. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is __________ to its charge. 3. The ______ of the oxidation numbers in a compound is zero if ____________, or equal to the ___________ if ...
H - JMap
... If you wish to change an answer, erase your first penciled circle and then circle with pencil the number of the answer you want. After you have completed the examination and you have decided that all of the circled answers represent your best judgment, signal a proctor and turn in all examination ma ...
... If you wish to change an answer, erase your first penciled circle and then circle with pencil the number of the answer you want. After you have completed the examination and you have decided that all of the circled answers represent your best judgment, signal a proctor and turn in all examination ma ...
THERMODYNAMICS. Elements of Physical Chemistry. By P. Atkins
... CONSERVATION OF ENERGY – states that: ...
... CONSERVATION OF ENERGY – states that: ...
THERMODYNAMICS. Elements of Physical Chemistry. By P. Atkins
... CONSERVATION OF ENERGY – states that: ...
... CONSERVATION OF ENERGY – states that: ...
Analyze
... (b) Because two moles of CO are produced from CO 2 (which is not an element) and C, this reaction does not represent H f° . (c) Because two substances are produced and one of the reactants (CO 2) is not an element, this reaction does not represent H f° . (d) One mole of CH4 is produced from elemen ...
... (b) Because two moles of CO are produced from CO 2 (which is not an element) and C, this reaction does not represent H f° . (c) Because two substances are produced and one of the reactants (CO 2) is not an element, this reaction does not represent H f° . (d) One mole of CH4 is produced from elemen ...
File - Chem with Appleby
... reactions are proceeding _____________ ___________________________ Once equilibrium is achieved, the _______________ of each reactant and product remains ________________. ...
... reactions are proceeding _____________ ___________________________ Once equilibrium is achieved, the _______________ of each reactant and product remains ________________. ...
Triple Award - Cheltenham College
... marks are given for chemical equations: 1 for correct formulae, 1 for correct balancing; the second mark will not be given if the equation is balanced but the formulae are incorrect. ...
... marks are given for chemical equations: 1 for correct formulae, 1 for correct balancing; the second mark will not be given if the equation is balanced but the formulae are incorrect. ...
Chemical Reaction
... Strong acids must be handled with care. They are dangerous because they can react easily with materials such as skin, wood and cloth. You need to know about the chemical reactions of acids with metals and carbonates. ...
... Strong acids must be handled with care. They are dangerous because they can react easily with materials such as skin, wood and cloth. You need to know about the chemical reactions of acids with metals and carbonates. ...
O 2 (g) - Valdosta State University
... Summary: Matter and Energy Dispersal • A final state of a system can be more probable than the initial state if: – The atoms and molecules can be more ____________ and/or – ___________ can be dispersed over a greater number of atoms and molecules. ...
... Summary: Matter and Energy Dispersal • A final state of a system can be more probable than the initial state if: – The atoms and molecules can be more ____________ and/or – ___________ can be dispersed over a greater number of atoms and molecules. ...
Unit 6 Study Guide - Dorman High School
... have the gases A, B, C, and D at equilibrium. Upon adding gas A, the value of K A) increases because when A is added, more products are made, increasing the product-to-reactant ratio B) decreases because A is a reactant, so the product-toreactant ratio decreases C) does not change because A does not ...
... have the gases A, B, C, and D at equilibrium. Upon adding gas A, the value of K A) increases because when A is added, more products are made, increasing the product-to-reactant ratio B) decreases because A is a reactant, so the product-toreactant ratio decreases C) does not change because A does not ...
L2S08b
... A state function is a property of a system that can be determined by specifying its final and initial conditions (in terms of temperatue, pressure, etc). The value of a state function does not depend on the particular history of the sample, only its ...
... A state function is a property of a system that can be determined by specifying its final and initial conditions (in terms of temperatue, pressure, etc). The value of a state function does not depend on the particular history of the sample, only its ...
Thermochemical Approaches to Neutralization Reactions between
... neutralization between weak acid and strong base. The practical usefulness of the present laboratory activity as an advanced thermochemical experiment at high school and as an introductory experiment to chemical thermodynamics at college was discussed. Introduction In the high school chemistry, the ...
... neutralization between weak acid and strong base. The practical usefulness of the present laboratory activity as an advanced thermochemical experiment at high school and as an introductory experiment to chemical thermodynamics at college was discussed. Introduction In the high school chemistry, the ...
Section II - School District 27J
... Copper metal reacts with nitric acid to produce copper (II) nitrate, nitrogen monoxide and water. a. Write the balanced chemical equation. b. Identify the oxidizing agent. c. If a 0.300 mol sample of copper reacts with 10.0 mL of 12.0 M nitric acid, how many moles of nitrogen monoxide gas will form? ...
... Copper metal reacts with nitric acid to produce copper (II) nitrate, nitrogen monoxide and water. a. Write the balanced chemical equation. b. Identify the oxidizing agent. c. If a 0.300 mol sample of copper reacts with 10.0 mL of 12.0 M nitric acid, how many moles of nitrogen monoxide gas will form? ...
CHAPTER 17
... = K1/2 [A]1/2(1- ) = K1/2 [A]1/2 - K1/2 [A]1/2 + K1/2 [A]1/2 = K1/2 [A]1/ (1 + K1/2 [A]1/2) (1 + K1/2 [A]1/2) = K1/2 [A]1/2 ...
... = K1/2 [A]1/2(1- ) = K1/2 [A]1/2 - K1/2 [A]1/2 + K1/2 [A]1/2 = K1/2 [A]1/ (1 + K1/2 [A]1/2) (1 + K1/2 [A]1/2) = K1/2 [A]1/2 ...
LESSON 23: Exploding Bags
... the structure or composition of the materials change. Chemical reactions occur around us all the time. When a chemical change is complete, the resulting substance(s) is/are different from the original substance(s). The substance or substances that start a chemical reaction are called reactants. The ...
... the structure or composition of the materials change. Chemical reactions occur around us all the time. When a chemical change is complete, the resulting substance(s) is/are different from the original substance(s). The substance or substances that start a chemical reaction are called reactants. The ...
Catalysis

Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required.