Section 2 Types of Chemical Reactions
... Characteristics of Chemical Equations • The following 3 requirements will aid you in writing and reading chemical equations correctly: 1. The equation must represent known facts. 2. The equation must contain the correct formulas for the reactants and products. 3. The Law of conservation of mass must ...
... Characteristics of Chemical Equations • The following 3 requirements will aid you in writing and reading chemical equations correctly: 1. The equation must represent known facts. 2. The equation must contain the correct formulas for the reactants and products. 3. The Law of conservation of mass must ...
Unit 5: Chemical Equations and Reactions
... Physical Change: - the change of a substance that alter its physical appearance but does not alter its chemical composition. (It is easily reversible.) Examples: freezing water into ice (phase change – freezing), breaking a large clump of sugar into powder form using a mortar and pestle. Chemical Pr ...
... Physical Change: - the change of a substance that alter its physical appearance but does not alter its chemical composition. (It is easily reversible.) Examples: freezing water into ice (phase change – freezing), breaking a large clump of sugar into powder form using a mortar and pestle. Chemical Pr ...
Chapter_4_Reactions_in_Aqueous_Solution
... Check AgCl is about 25 percent chloride by mass, so the roughly 1 g of AgCl precipitate that formed corresponds to about 0.25 g of chloride, which is a little less than half of the mass of the original sample. Therefore, the calculated percent chloride of 47.51 percent is reasonable. ...
... Check AgCl is about 25 percent chloride by mass, so the roughly 1 g of AgCl precipitate that formed corresponds to about 0.25 g of chloride, which is a little less than half of the mass of the original sample. Therefore, the calculated percent chloride of 47.51 percent is reasonable. ...
Rhenium- and molybdenum-catalyzed dehydration reactions
... ratio close to one and are highly functionalized with hydroxyl groups. Therefore a completely different type of chemistry is required to acquire building blocks from lignocellulosic biomass suitable for the chemical industry: while in the case of fossil feedstocks functionality must be added, functi ...
... ratio close to one and are highly functionalized with hydroxyl groups. Therefore a completely different type of chemistry is required to acquire building blocks from lignocellulosic biomass suitable for the chemical industry: while in the case of fossil feedstocks functionality must be added, functi ...
6 Thermodynamics
... The cis- structure has a smaller C−C bond energy because its ∆Hf is more positive, and it has a higher potential energy. (b) Find the values for ∆G° for this reaction at 298 K. ∆H°rxn = (−11.2 kJ/mol) – (−7.0 kJ/mol) = −4.2 kJ/mol ∆S°rxn = (+296 J/mol·K) – (+301 J/mol·K) = −5 J/mol·K ∆G°rxn = ∆H° − ...
... The cis- structure has a smaller C−C bond energy because its ∆Hf is more positive, and it has a higher potential energy. (b) Find the values for ∆G° for this reaction at 298 K. ∆H°rxn = (−11.2 kJ/mol) – (−7.0 kJ/mol) = −4.2 kJ/mol ∆S°rxn = (+296 J/mol·K) – (+301 J/mol·K) = −5 J/mol·K ∆G°rxn = ∆H° − ...
SCH 4U REVIEW Notes
... polymer – a molecule of large molar mass that consists of many repeating subunits called monomers; two types: addition and condensation monomer – a molecule or compound usually containing carbon and of relatively low molecular weight and simple structure which is capable of conversion to polymers by ...
... polymer – a molecule of large molar mass that consists of many repeating subunits called monomers; two types: addition and condensation monomer – a molecule or compound usually containing carbon and of relatively low molecular weight and simple structure which is capable of conversion to polymers by ...
Study guide for final
... 38) Dipole-dipole forces are weaker than dispersion forces. 39) Ionic solids tend to have higher melting points than molecular solids. 40) Ice can float in a glass of liquid water because the solid form of water is more dense than the liquid form. 41) A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or mo ...
... 38) Dipole-dipole forces are weaker than dispersion forces. 39) Ionic solids tend to have higher melting points than molecular solids. 40) Ice can float in a glass of liquid water because the solid form of water is more dense than the liquid form. 41) A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or mo ...
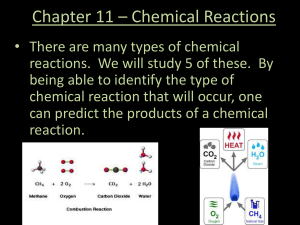
Chapter 11 * Chemical Reactions
... participate in the formation of the nonaqueous product are written. General Equation: Na2SO4 (aq) + Ba(NO3)2 (aq 2NaNO3 (aq) + BaSO4 (s) Ionic Equation: 2Na+1 (aq) + SO4-2 (aq) + Ba+2 (aq) + 2NO3-1 (aq) 2Na+1 (aq) + 2 NO3-1 (aq) + BaSO4 (s) Net Ionic Equation: Ba+2 (aq) + SO4-2 (aq) BaSO4 (s) ...
... participate in the formation of the nonaqueous product are written. General Equation: Na2SO4 (aq) + Ba(NO3)2 (aq 2NaNO3 (aq) + BaSO4 (s) Ionic Equation: 2Na+1 (aq) + SO4-2 (aq) + Ba+2 (aq) + 2NO3-1 (aq) 2Na+1 (aq) + 2 NO3-1 (aq) + BaSO4 (s) Net Ionic Equation: Ba+2 (aq) + SO4-2 (aq) BaSO4 (s) ...
equilibrium questions - Southington Public Schools
... (iii) Hypoiodous acid has the formula HOI. Predict whether HOI is a stronger acid or a weaker acid than the acid that you identified in part (a)(i). Justify your prediction in terms of chemical bonding. (b) Write the equation for the reaction that occurs between hypochlorous acid and water. (c) A 1. ...
... (iii) Hypoiodous acid has the formula HOI. Predict whether HOI is a stronger acid or a weaker acid than the acid that you identified in part (a)(i). Justify your prediction in terms of chemical bonding. (b) Write the equation for the reaction that occurs between hypochlorous acid and water. (c) A 1. ...
Quiroga Franco - J. Electrochem. Soc.
... Because of the global warming and the fossil fuels depletion, zeroemission electrochemical devices for energy conversion and storage, such as fuel cells and secondary batteries, are called to play a significant role in the sustainable development of the Humanity. The operation principles of these de ...
... Because of the global warming and the fossil fuels depletion, zeroemission electrochemical devices for energy conversion and storage, such as fuel cells and secondary batteries, are called to play a significant role in the sustainable development of the Humanity. The operation principles of these de ...
Untitled
... All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without either the prior written permission of the publisher or a licence permitting restricted ...
... All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without either the prior written permission of the publisher or a licence permitting restricted ...
Course : Chem 401F
... sedimentation velocity and sedimentation equilibrium methods (M z), viscosity and molecular weight (Mv); natural and synthetic polymers; polymerization and functionality principle; linear, branched and crosslinked (network) polymers; thermoplastics and thermosets; elastomers, fibres and plastics; co ...
... sedimentation velocity and sedimentation equilibrium methods (M z), viscosity and molecular weight (Mv); natural and synthetic polymers; polymerization and functionality principle; linear, branched and crosslinked (network) polymers; thermoplastics and thermosets; elastomers, fibres and plastics; co ...
Problem 1: A brief history of life in the universe
... Elemental hydrogen and helium are rare on Earth, because they escaped from the early Earth. Escape velocity is the minimum velocity of a particle or object (e.g., a gas molecule or a rocket) needed to become free from the gravitational attraction of a planet. Escape velocity of an object with mass m ...
... Elemental hydrogen and helium are rare on Earth, because they escaped from the early Earth. Escape velocity is the minimum velocity of a particle or object (e.g., a gas molecule or a rocket) needed to become free from the gravitational attraction of a planet. Escape velocity of an object with mass m ...
sch4ureview
... polymer – a molecule of large molar mass that consists of many repeating subunits called monomers; two types: addition and condensation monomer – a molecule or compound usually containing carbon and of relatively low molecular weight and simple structure which is capable of conversion to polymers by ...
... polymer – a molecule of large molar mass that consists of many repeating subunits called monomers; two types: addition and condensation monomer – a molecule or compound usually containing carbon and of relatively low molecular weight and simple structure which is capable of conversion to polymers by ...
12 U Chem Review
... polymer – a molecule of large molar mass that consists of many repeating subunits called monomers; two types: addition and condensation monomer – a molecule or compound usually containing carbon and of relatively low molecular weight and simple structure which is capable of conversion to polymers by ...
... polymer – a molecule of large molar mass that consists of many repeating subunits called monomers; two types: addition and condensation monomer – a molecule or compound usually containing carbon and of relatively low molecular weight and simple structure which is capable of conversion to polymers by ...
11.1 Enthalpy PowerPoint
... consists of an insulated container made of three nested polystyrene cups, a measured quantity of water, and a thermometer. The chemical is placed in or dissolved in the water of the calorimeter. Energy transfers between the chemical system and the surrounding water is monitored by measuring changes ...
... consists of an insulated container made of three nested polystyrene cups, a measured quantity of water, and a thermometer. The chemical is placed in or dissolved in the water of the calorimeter. Energy transfers between the chemical system and the surrounding water is monitored by measuring changes ...
Branham
... The following study deals with the characteristics of the reaction to form BaSO4 and BaCO3 from Na2SO4 and Na2CO3, respectively, using BaS as the other reactant. These reactions would theoretically increase the efficiency of the chemical recovery process in papermaking to near 100% by completely con ...
... The following study deals with the characteristics of the reaction to form BaSO4 and BaCO3 from Na2SO4 and Na2CO3, respectively, using BaS as the other reactant. These reactions would theoretically increase the efficiency of the chemical recovery process in papermaking to near 100% by completely con ...
Catalysis

Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required.