13AP General Equilibrium FR worksheet (missing 1988)
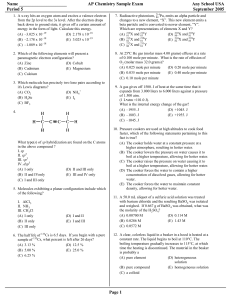
... Sulfuryl chloride, SO2Cl2, is a highly reactive gaseous compound. When heated, it decomposes as follows: SO2Cl2(g) ↔ SO2(g)+ Cl2(g) This decomposition is endothermic. A sample of 3.509 grams of SO2Cl2 is placed in an evacuated 1.00 liter bulb and the temperature is raised to 375 K. (a) What would be ...
... Sulfuryl chloride, SO2Cl2, is a highly reactive gaseous compound. When heated, it decomposes as follows: SO2Cl2(g) ↔ SO2(g)+ Cl2(g) This decomposition is endothermic. A sample of 3.509 grams of SO2Cl2 is placed in an evacuated 1.00 liter bulb and the temperature is raised to 375 K. (a) What would be ...
Document
... 12. What is the percent yield for the reaction shown if 1 mole of O2 produces 9.0 grams of water? 2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O 1 mole of O2 can at most produce 2 moles of water (theoretical yield is 36 g since molar mass of water is about 18 g/mol. So %yield = (9g/36g)x100=25% a) 400% ...
... 12. What is the percent yield for the reaction shown if 1 mole of O2 produces 9.0 grams of water? 2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O 1 mole of O2 can at most produce 2 moles of water (theoretical yield is 36 g since molar mass of water is about 18 g/mol. So %yield = (9g/36g)x100=25% a) 400% ...
The Wizard Test Maker
... An experiment is set up to determine the molecular mass of a water-soluble, nonvolatile, non-electrolyte. The equipment listed above is availeable to use. No other equipment is available. (a) Briefly list the steps needed to carry out this experiment. (b) What experimental data needs to be collected ...
... An experiment is set up to determine the molecular mass of a water-soluble, nonvolatile, non-electrolyte. The equipment listed above is availeable to use. No other equipment is available. (a) Briefly list the steps needed to carry out this experiment. (b) What experimental data needs to be collected ...
IB Chemistry HL Topic5 Questions 1. Which combination of ionic
... Two values of the lattice enthalpies for each of the silver halides are quoted in the Data Booklet. Discuss the bonding in silver fluoride and in silver iodide, with reference to ...
... Two values of the lattice enthalpies for each of the silver halides are quoted in the Data Booklet. Discuss the bonding in silver fluoride and in silver iodide, with reference to ...
A STUDY OF THE RATE OF THE REACTION OF CHLORINE
... • The blue dye (FD & C #1) has an absorbance maximum at 630 nm. • We will supply you with a solution of the food dye. (We use 18 drops of “Club House” Brand blue food colouring per litre of solution. The blue colouring comes in a set of four different food colours, available at the supermarket.) • T ...
... • The blue dye (FD & C #1) has an absorbance maximum at 630 nm. • We will supply you with a solution of the food dye. (We use 18 drops of “Club House” Brand blue food colouring per litre of solution. The blue colouring comes in a set of four different food colours, available at the supermarket.) • T ...
fahad h. ahmad - Fahad`s Academy
... chlorine molecule has formula Cl2, where Cl is chlorine symbol and the subscript number (2) shows that there are 2 atoms in a chlorine gas molecule. ...
... chlorine molecule has formula Cl2, where Cl is chlorine symbol and the subscript number (2) shows that there are 2 atoms in a chlorine gas molecule. ...
1.8 M - Thierry Karsenti
... and the energy laws that govern them. Most chemical reactions and virtually all biological processes take place not between pure solids, liquids or gases, but rather among ions and molecules dissolved in water or other solvents (i.e. in solution). In this module we will therefore examine the various ...
... and the energy laws that govern them. Most chemical reactions and virtually all biological processes take place not between pure solids, liquids or gases, but rather among ions and molecules dissolved in water or other solvents (i.e. in solution). In this module we will therefore examine the various ...
Slides
... • Gibbs free energy (G) or free energy can be used to express spontaneity from the perspective of the system. • ΔG (kJ/mol) is the maximum amount of energy available to do work on the surroundings and takes into account both enthalpy and entropy. • In a spontaneous process at constant temperature ...
... • Gibbs free energy (G) or free energy can be used to express spontaneity from the perspective of the system. • ΔG (kJ/mol) is the maximum amount of energy available to do work on the surroundings and takes into account both enthalpy and entropy. • In a spontaneous process at constant temperature ...
Document
... its heat capacity. • Molar Heat Capacity – The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one mole of a substance by 1 Kelvin. ...
... its heat capacity. • Molar Heat Capacity – The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one mole of a substance by 1 Kelvin. ...
Kinetics of Mesophase Formation from Petroleum and Coal Derived
... transformation in petroleum pitches is slower due to the aliphatic carbon in mesophase which causes looseness of molecular planarity and increases the mesophase mobility. This behavior results in the narrowing of the characteristic peak for mesophase. In another study, it was shown (3) that the reac ...
... transformation in petroleum pitches is slower due to the aliphatic carbon in mesophase which causes looseness of molecular planarity and increases the mesophase mobility. This behavior results in the narrowing of the characteristic peak for mesophase. In another study, it was shown (3) that the reac ...
Redox Biocatalysis. Fundamentals and Applications Brochure
... Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2174326/ ...
... Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2174326/ ...
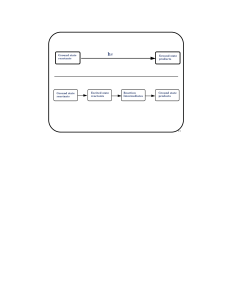
Ground state reactants Ground state products Ground state
... a triplet sensitizer to molecular oxygen • It cannot occur if the sensitizer energy is significantly below 22 kcal/mol. • It can only populate the 1∆g level of molecular oxygen if the sensitizer energy is between 22 and 37 kcal/mol, since population of the 1Σg level would be energetically unfavorabl ...
... a triplet sensitizer to molecular oxygen • It cannot occur if the sensitizer energy is significantly below 22 kcal/mol. • It can only populate the 1∆g level of molecular oxygen if the sensitizer energy is between 22 and 37 kcal/mol, since population of the 1Σg level would be energetically unfavorabl ...
Chapter 14: Chemical Kinetics
... For example, compare the reaction between a solid and a gas with the reaction between two gases. The solid–gas reaction (for example, iron and oxygen reacting to form rust) will generally occur at a much slower rate than the gas–gas reaction (for example, oxygen and methane burning in a Bunsen burne ...
... For example, compare the reaction between a solid and a gas with the reaction between two gases. The solid–gas reaction (for example, iron and oxygen reacting to form rust) will generally occur at a much slower rate than the gas–gas reaction (for example, oxygen and methane burning in a Bunsen burne ...
Reactions Balancing Chemical Equations uses Law of conservation
... Solution reactions Gas phase reactions ...
... Solution reactions Gas phase reactions ...
Deans Community High School Intermediate 2 Revision Notes www
... if the reactions require a large amount of energy (usually in the form of heat). Also some reactants and products actually begin to decompose or react in different ways if the temperature is too high; so although the temperature gives the collisions enough energy to cause a chemical reaction, the pr ...
... if the reactions require a large amount of energy (usually in the form of heat). Also some reactants and products actually begin to decompose or react in different ways if the temperature is too high; so although the temperature gives the collisions enough energy to cause a chemical reaction, the pr ...
Catalysis

Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required.