answers to part a of the national high school
... chlorates are also considered to be oxidising substances because they can release oxygen, nitrogen dioxide etc. when they are heated. The fuel indicated in the triangle could be any flammable substance, not just gasoline or oil etc. It could be wood or paper or absolutely anything that can burn. A ...
... chlorates are also considered to be oxidising substances because they can release oxygen, nitrogen dioxide etc. when they are heated. The fuel indicated in the triangle could be any flammable substance, not just gasoline or oil etc. It could be wood or paper or absolutely anything that can burn. A ...
chapter 21 chemistry of the main-group elements i
... Once we return to Mg(OH)2 from MgSO4, the other substances can be made by the indicated pathways. The return reaction is: MgSO 4 (aq) + 2 NaOH(aq) Mg(OH) 2 (s) + Na 2SO 4 (aq). Then the other reactions are ...
... Once we return to Mg(OH)2 from MgSO4, the other substances can be made by the indicated pathways. The return reaction is: MgSO 4 (aq) + 2 NaOH(aq) Mg(OH) 2 (s) + Na 2SO 4 (aq). Then the other reactions are ...
2009
... Salt A was crystallized from the water solution obtained by neutralization of 40 % solution of tetrafluoroboric acid with lithium hydroxide. Then, 11.25 g (m1) of A was heated to 350 °C, resulting in evolution of gas (compound B), which was absorbed in diethyl ether. The weight of the solid product ...
... Salt A was crystallized from the water solution obtained by neutralization of 40 % solution of tetrafluoroboric acid with lithium hydroxide. Then, 11.25 g (m1) of A was heated to 350 °C, resulting in evolution of gas (compound B), which was absorbed in diethyl ether. The weight of the solid product ...
Handout - UNT Chemistry
... has proceeded from reactants towards products. = 0: Reactants only = 1: Products only ...
... has proceeded from reactants towards products. = 0: Reactants only = 1: Products only ...
Problem 5. The Second Law of thermodynamics
... All these sites equally participate in catalytic formation of a single B on a single Au nanoparticle, rcat ...
... All these sites equally participate in catalytic formation of a single B on a single Au nanoparticle, rcat ...
Problem 5. The Second Law of thermodynamics
... All these sites equally participate in catalytic formation of a single B on a single Au nanoparticle, rcat ...
... All these sites equally participate in catalytic formation of a single B on a single Au nanoparticle, rcat ...
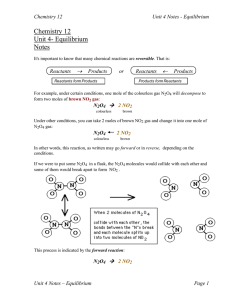
Chemical Equilibrium is reached when
... However, in 1 L of water we have 55.5 M of water which is very large compared with the concentrations of other species in solution, and we assume that it doesn’t change during the course of a reaction. Kc = [CH3COO-][H3O+]/[CH3COOH] Kc = Kc`[H2O] Note that it is general practice not to include units ...
... However, in 1 L of water we have 55.5 M of water which is very large compared with the concentrations of other species in solution, and we assume that it doesn’t change during the course of a reaction. Kc = [CH3COO-][H3O+]/[CH3COOH] Kc = Kc`[H2O] Note that it is general practice not to include units ...
Werner Mormann Mohamed Al
... In an attempt to investigate the applicability of this method to other acids, vinyl laurate (dodecanoate) was used under otherwise identical conditions. In this case a DS of only 0.2 was achieved after 48 h. This may be attributed to the low solubility of vinyl laurate in water and of starch in viny ...
... In an attempt to investigate the applicability of this method to other acids, vinyl laurate (dodecanoate) was used under otherwise identical conditions. In this case a DS of only 0.2 was achieved after 48 h. This may be attributed to the low solubility of vinyl laurate in water and of starch in viny ...
Chemistry HSC - The Bored of Studies Community
... 1. Thermal cracking – requires very high temps and generally not used. End products hard to control since many places where bonds could break, early method. Accelerates reaction and drives equilibrium to reactants. 2. Catalytic cracking of fractions separated from petroleum. – material is passed ove ...
... 1. Thermal cracking – requires very high temps and generally not used. End products hard to control since many places where bonds could break, early method. Accelerates reaction and drives equilibrium to reactants. 2. Catalytic cracking of fractions separated from petroleum. – material is passed ove ...
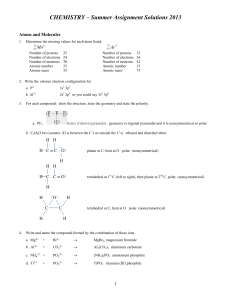
CHEMISTRY – Summer Assignment Solutions 2013
... Calculate the amount of heat needed to heat 40.0 g of water, specific heat of 4.184 J/g C, from 25.0 C to 60.0 C. Treat this one of two ways. Either as a specific heat problem, use q=mTCp, where q is heat and Cp is the specific heat, T = Tfinal - Tinitial. Or, as a conversion problem, multiply ...
... Calculate the amount of heat needed to heat 40.0 g of water, specific heat of 4.184 J/g C, from 25.0 C to 60.0 C. Treat this one of two ways. Either as a specific heat problem, use q=mTCp, where q is heat and Cp is the specific heat, T = Tfinal - Tinitial. Or, as a conversion problem, multiply ...
Document
... more surface area for contact with other reactants certain types of chemicals are more reactive than others e.g., the activity series of metals ions react faster than molecules no bonds need to be broken ...
... more surface area for contact with other reactants certain types of chemicals are more reactive than others e.g., the activity series of metals ions react faster than molecules no bonds need to be broken ...
Solutions (DOC format, upgraded July 20)
... All these sites equally participate in catalytic formation of a single B on a single Au nanoparticle, rcat ...
... All these sites equally participate in catalytic formation of a single B on a single Au nanoparticle, rcat ...
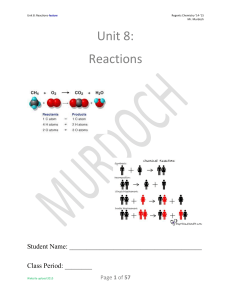
Unit 8: Reactions
... 3. Double Replacement: A solution reaction in which the positive ion of one compound combines with the negative ion of the other compound to form a precipitate, and the other ions remain dissolved in solution. 4. Law of Conservation of Charge: Charge may not be created or destroyed by physical or ch ...
... 3. Double Replacement: A solution reaction in which the positive ion of one compound combines with the negative ion of the other compound to form a precipitate, and the other ions remain dissolved in solution. 4. Law of Conservation of Charge: Charge may not be created or destroyed by physical or ch ...
Unit 5 - Chemical Reactions - Student
... A chemical reaction is the process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances. The original substances are called REACTANTS and the resulting substances are called PRODUCTS. According to the Law of CONSERVATION OF MASS, the total mass of the reactants are equal ...
... A chemical reaction is the process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances. The original substances are called REACTANTS and the resulting substances are called PRODUCTS. According to the Law of CONSERVATION OF MASS, the total mass of the reactants are equal ...
(+1) + - Edublogs
... Oxidation numbers and the periodic table Some observed trends in compounds. Metals have positive oxidation numbers. Transition metals typically have more than one oxidation number. Nonmetals and semimetals have both positive and negative oxidation numbers. No element exists in a compound with an ox ...
... Oxidation numbers and the periodic table Some observed trends in compounds. Metals have positive oxidation numbers. Transition metals typically have more than one oxidation number. Nonmetals and semimetals have both positive and negative oxidation numbers. No element exists in a compound with an ox ...
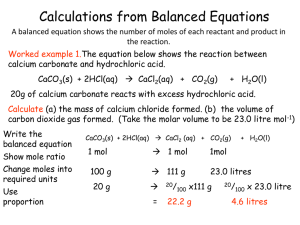
Calculations from Balanced Equations
... balanced equations, to calculate the amounts of reactants needed or the amounts of products produced. A limiting reactant is the substance that is fully used up and thereby limits the possible extent of the reaction. Other reactants are said to be in excess. ...
... balanced equations, to calculate the amounts of reactants needed or the amounts of products produced. A limiting reactant is the substance that is fully used up and thereby limits the possible extent of the reaction. Other reactants are said to be in excess. ...
SUPPORT MATERIAL CLASS – X(science) FIRST TERM
... 1) Chemical reaction— Chemical changes or chemical reactions are the changes in which one or more new substances are formed. 2 )Chemical Equations – Representation of a chemical reaction in terms of symbols and formulae of the reactants and products is known as chemical equation. 3) Balanced Chemica ...
... 1) Chemical reaction— Chemical changes or chemical reactions are the changes in which one or more new substances are formed. 2 )Chemical Equations – Representation of a chemical reaction in terms of symbols and formulae of the reactants and products is known as chemical equation. 3) Balanced Chemica ...
Descriptive Chemistry for Midterm Exam #2
... Oxidation states: 0 in H2, +1 in compounds with other non-metals, −1 in metal hydrides. Industrial Preparation of H2: This is carried out through the reduction of +1 oxidation state in H2O using electrolysis or at high temperature where C(s), CO(g), and hydrocarbons act as strong reducing agents, co ...
... Oxidation states: 0 in H2, +1 in compounds with other non-metals, −1 in metal hydrides. Industrial Preparation of H2: This is carried out through the reduction of +1 oxidation state in H2O using electrolysis or at high temperature where C(s), CO(g), and hydrocarbons act as strong reducing agents, co ...
Objective (Local, State, National – College Board)
... Because of the organization of the College Board outline, several topics which are treated together in our AP course are fragmented in different sections of this outline. So here is a course calendar to replace the “time range” box on the objective descriptions. Mid Aug – 1st week of Sept. Review st ...
... Because of the organization of the College Board outline, several topics which are treated together in our AP course are fragmented in different sections of this outline. So here is a course calendar to replace the “time range” box on the objective descriptions. Mid Aug – 1st week of Sept. Review st ...
Catalysis

Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required.