class xii – preparatory examination - 1
... than water.The gas is also soluble in CCl4.Its solution in alcohol is used as an antiseptic.Identify ‘A’ and ‘B’ and explain the observations. 12. Which is more acidic-phenol or p-nitrophenol ? Explain. 13. How will you distinguish between : ...
... than water.The gas is also soluble in CCl4.Its solution in alcohol is used as an antiseptic.Identify ‘A’ and ‘B’ and explain the observations. 12. Which is more acidic-phenol or p-nitrophenol ? Explain. 13. How will you distinguish between : ...
Chemical Reactions Q3U3
... Experimentation has proved that, in some cases, not all of the reactants are converted to the product, no matter how much time is given. These reactions are reversible! ...
... Experimentation has proved that, in some cases, not all of the reactants are converted to the product, no matter how much time is given. These reactions are reversible! ...
Calculating molar volume
... Step 3: Using the number of moles in step 1, choose one reactant and work out the number of moles of the other reactant needed to react with it: ...
... Step 3: Using the number of moles in step 1, choose one reactant and work out the number of moles of the other reactant needed to react with it: ...
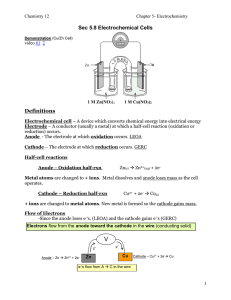
Unit 13: Electrochemistry (Link to Prentice Hall Text: Chapters 22
... Why would you ever want to force a nonspontaneous reaction? (a) To obtain pure metals Many metals are only found as compounds in nature. Electrolysis can lead to a deposit of the pure metal on the cathode. (b) To recharge a battery A car battery powers the car through a spontaneous reaction, but wha ...
... Why would you ever want to force a nonspontaneous reaction? (a) To obtain pure metals Many metals are only found as compounds in nature. Electrolysis can lead to a deposit of the pure metal on the cathode. (b) To recharge a battery A car battery powers the car through a spontaneous reaction, but wha ...
couverture these PRES Toulouse M ESCARCEGA 2011
... several times through this cycle; in this sense, the catalyst remains unaltered but dynamic. The number of moles of substrate that a mole of catalyst can convert into product molecules through this cycle before becoming inactivated is called the turnover number (TON) and is a measure of the catalys ...
... several times through this cycle; in this sense, the catalyst remains unaltered but dynamic. The number of moles of substrate that a mole of catalyst can convert into product molecules through this cycle before becoming inactivated is called the turnover number (TON) and is a measure of the catalys ...
LABORATORY MANUAL CHEMISTRY 121
... You should now have two pairs of solutions that are gun metal gray, or some other color. The exact color is not important as long as you have a color representing the half-way point in the reaction. Keep these tubes in an ice bath so that they do not undergo additional reaction during the laboratory ...
... You should now have two pairs of solutions that are gun metal gray, or some other color. The exact color is not important as long as you have a color representing the half-way point in the reaction. Keep these tubes in an ice bath so that they do not undergo additional reaction during the laboratory ...
Ch 4 Student
... consumed and limits amount of product • Reactant in excess – reactant present in greater quantity than limiting reactant • Theoretical Yield – amount of product made based on consumption of all the limiting reactant • Actual Yield – amount of product actually produced • Percent Yield – (actual/theor ...
... consumed and limits amount of product • Reactant in excess – reactant present in greater quantity than limiting reactant • Theoretical Yield – amount of product made based on consumption of all the limiting reactant • Actual Yield – amount of product actually produced • Percent Yield – (actual/theor ...
PDF File
... of E‚*S (or E‚*∆P). Reaction was initiated by addition of UCG ([UCG] ) 100 µM; KdUCG ) 7 µM) (or UCGA: [UCGA] ) 950 µM, KdUCGA ) 88 µM) to rapidly form the E‚*S‚UCG (or E‚*∆P‚UCGA) complex, along with a large excess (1 µM) of unlabeled P to prevent rebinding of dissociated *S (or *∆P). The observed ...
... of E‚*S (or E‚*∆P). Reaction was initiated by addition of UCG ([UCG] ) 100 µM; KdUCG ) 7 µM) (or UCGA: [UCGA] ) 950 µM, KdUCGA ) 88 µM) to rapidly form the E‚*S‚UCG (or E‚*∆P‚UCGA) complex, along with a large excess (1 µM) of unlabeled P to prevent rebinding of dissociated *S (or *∆P). The observed ...
base hydrolysis of cobalt(iii)
... Methanol was chosen as a solvent because it has much less tendency to coordinate to cobalt than does water, ...
... Methanol was chosen as a solvent because it has much less tendency to coordinate to cobalt than does water, ...
Chem 1202 - LSU Department of Chemistry
... TDS is the energy associated with entropy; TDS is waste energy which cannot be used for any purpose! But the total amount of energy in the universe is constant (First Law)! Every spontaneous process that occurs at T > 0 converts some of the energy of the universe into waste energy. Once all of the e ...
... TDS is the energy associated with entropy; TDS is waste energy which cannot be used for any purpose! But the total amount of energy in the universe is constant (First Law)! Every spontaneous process that occurs at T > 0 converts some of the energy of the universe into waste energy. Once all of the e ...
Chemistry IGCSE
... Chromatography is a process used to separate and identify two or more substances from a mixture. This method depends on the solubility of the tested substances. Chromatography, for instance, is also used to find out the number of components in a drink. Let’s say we want to find the number o ...
... Chromatography is a process used to separate and identify two or more substances from a mixture. This method depends on the solubility of the tested substances. Chromatography, for instance, is also used to find out the number of components in a drink. Let’s say we want to find the number o ...
Practice problems
... the cathode. The second half-reaction is the oxidation (electrons shown on the product side of the equation), which occurs at the anode. The I– ions are the source of electrons, and the Cr2O72– ions accept the electrons. Hence, the electrons flow through the external circuit from the electrode immer ...
... the cathode. The second half-reaction is the oxidation (electrons shown on the product side of the equation), which occurs at the anode. The I– ions are the source of electrons, and the Cr2O72– ions accept the electrons. Hence, the electrons flow through the external circuit from the electrode immer ...
Equilibrium
... Kp = 6.8 x 10-9 If COCl2(g) at an initial pressure of 1.00 atm decomposes, calculate the equilibrium pressures of all species? ...
... Kp = 6.8 x 10-9 If COCl2(g) at an initial pressure of 1.00 atm decomposes, calculate the equilibrium pressures of all species? ...
Catalysis

Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required.