FREE Sample Here
... Ans: The inflection point, which occurs when the weak acid has been exactly one half titrated with NaOH, occurs at a pH equal to the pKa of the weak acid. The region of greatest buffering capacity (where the titration curve is flattest) occurs at pH values of pKa ±1. (See Fig. 2-17, p. 59.) 33. Buff ...
... Ans: The inflection point, which occurs when the weak acid has been exactly one half titrated with NaOH, occurs at a pH equal to the pKa of the weak acid. The region of greatest buffering capacity (where the titration curve is flattest) occurs at pH values of pKa ±1. (See Fig. 2-17, p. 59.) 33. Buff ...
Document
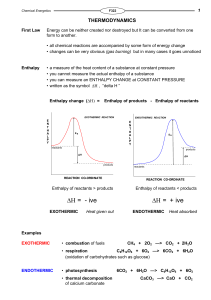
... Fig.2 The direction of spontaneous change for a gas is toward filling its container. A gas that already fills its container does not collect spontaneously in a small region of the container. A glass cylinder containing a brown gas (upper piece of glassware in the left illustration) is attached to a ...
... Fig.2 The direction of spontaneous change for a gas is toward filling its container. A gas that already fills its container does not collect spontaneously in a small region of the container. A glass cylinder containing a brown gas (upper piece of glassware in the left illustration) is attached to a ...
Chemistry - Tumkur University
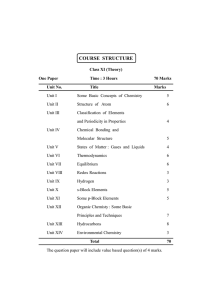
... Review of I law of thermodynamics, need for II law of thermodynamics and different ways of stating II law of thermodynamics with respect to its spontaneity, spontaneous and nonspontaneous processes. Concept of entropy and its significance-illustrations for order, disorder, physical, chemical process ...
... Review of I law of thermodynamics, need for II law of thermodynamics and different ways of stating II law of thermodynamics with respect to its spontaneity, spontaneous and nonspontaneous processes. Concept of entropy and its significance-illustrations for order, disorder, physical, chemical process ...
A Few Things You Might Want To Know
... Mixtures can be heterogeneous or homogeneous (= solutions). They consist of substances that can be separated by physical changes (distillation, crystallization, chromatography). Substances can be either elements or compounds. Compounds can be separated into elements by chemical changes (redox reacti ...
... Mixtures can be heterogeneous or homogeneous (= solutions). They consist of substances that can be separated by physical changes (distillation, crystallization, chromatography). Substances can be either elements or compounds. Compounds can be separated into elements by chemical changes (redox reacti ...
Acid + Base Class # 1
... 51. First, the pH scale is a logarithm scale. That means small changes in numbers are really changes in EXPONENTS. Just like the Richter scale you learned about in Earth Science. An earthquake of 2.0 will shake you and might make you feel dizzy. A quake of 3.0 is TEN TIMES as strong, and will shake ...
... 51. First, the pH scale is a logarithm scale. That means small changes in numbers are really changes in EXPONENTS. Just like the Richter scale you learned about in Earth Science. An earthquake of 2.0 will shake you and might make you feel dizzy. A quake of 3.0 is TEN TIMES as strong, and will shake ...
A STUDY OF THE RATE OF THE REACTION OF CHLORINE
... the ∆Hfusion questions overleaf will be very useful in completing this assignment. The molar enthalpy of fusion, ∆Hfusion, of water is defined as the amount of energy required to change 1 mol of ice at 0oC to 1 mol of water at 0oC. H2O(s) + enthalpy of fusion → H2O(l) Your job, should you choose to ...
... the ∆Hfusion questions overleaf will be very useful in completing this assignment. The molar enthalpy of fusion, ∆Hfusion, of water is defined as the amount of energy required to change 1 mol of ice at 0oC to 1 mol of water at 0oC. H2O(s) + enthalpy of fusion → H2O(l) Your job, should you choose to ...
Kinetics of Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol with Dilute Nitric Acid
... Table 2 shows that the ratio of alcohol consumed to HNO3 at different reaction conditions is ∼2.0. This is consistent with the stoichiometric requirement indicated by eq 7. In addition, the gas-phase analysis (Suchak et al., 1989) was performed in an operating plant, using the HNO3 oxidation of benz ...
... Table 2 shows that the ratio of alcohol consumed to HNO3 at different reaction conditions is ∼2.0. This is consistent with the stoichiometric requirement indicated by eq 7. In addition, the gas-phase analysis (Suchak et al., 1989) was performed in an operating plant, using the HNO3 oxidation of benz ...
Chapter Ten
... weak acid and its conjugate base. ► Rearranging the Ka equation shows that the value of [H3O+] depends on the ratio [HA]/[A-]. [H3O+] = Ka [HA]/[A-] ► Most H3O+ added is removed by reaction with A- ,so [HA] increases and [A-] decreases. As long as these changes are small, the ratio [HA]/[A-] changes ...
... weak acid and its conjugate base. ► Rearranging the Ka equation shows that the value of [H3O+] depends on the ratio [HA]/[A-]. [H3O+] = Ka [HA]/[A-] ► Most H3O+ added is removed by reaction with A- ,so [HA] increases and [A-] decreases. As long as these changes are small, the ratio [HA]/[A-] changes ...
1 Chemistry 222
... acid is the same as the NaOH, we expect equivalence points to occur at 20, 40, and 60 mL of titrant added. From our pKa values, we can estimate the pH at the first two equivalence points because the primary species that are present are the amphiprotic forms. Midway to each equivalence point, pH is d ...
... acid is the same as the NaOH, we expect equivalence points to occur at 20, 40, and 60 mL of titrant added. From our pKa values, we can estimate the pH at the first two equivalence points because the primary species that are present are the amphiprotic forms. Midway to each equivalence point, pH is d ...
5.2 Calculations of Enthalpy Changes (SL/HL)
... The enthalpy change during a chemical reaction depends on 3 factors. (H or q) 1. The temperature change. 2. The mass that changes temperature. 3. The specific heat capacity of the material that changes temperature. H = m C T H in kJ, m in Kg (in aqueous solutions it will be the mass of water w ...
... The enthalpy change during a chemical reaction depends on 3 factors. (H or q) 1. The temperature change. 2. The mass that changes temperature. 3. The specific heat capacity of the material that changes temperature. H = m C T H in kJ, m in Kg (in aqueous solutions it will be the mass of water w ...
Equilibrium chemistry
Equilibrium chemistry is a concerned with systems in chemical equilibrium. The unifying principle is that the free energy of a system at equilibrium is the minimum possible, so that the slope of the free energy with respect to the reaction coordinate is zero. This principle, applied to mixtures at equilibrium provides a definition of an equilibrium constant. Applications include acid-base, host-guest, metal-complex, solubility, partition, chromatography and redox equilibria.