Lecture 25 Notes
... Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases A Brønsted-Lowry acid is any substance that is able to give hydrogen ions (H+) to another molecule or ion ...
... Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases A Brønsted-Lowry acid is any substance that is able to give hydrogen ions (H+) to another molecule or ion ...
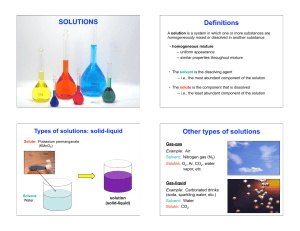
Types of Solutions
... point where you cannot dissolve any more sugar. • This is called saturated solution. • However, if you heat this solution, more sugar will dissolve • When the solution is cooled, the sugar will remain in solution • This is called a supersaturated solution. ...
... point where you cannot dissolve any more sugar. • This is called saturated solution. • However, if you heat this solution, more sugar will dissolve • When the solution is cooled, the sugar will remain in solution • This is called a supersaturated solution. ...
10.3 Ligand Field Theory 10.3 Ligand Field Theory
... e- from the ligands → all six bonding MO e- from M ion → t2g & eg* - strong-field ligands: strong interaction b/w ligands & M ions : large t2g & eg* split : ∆o large - weak-field ligands: weak interaction b/w ligands & M ions : smaller t2g & eg* split : ∆o small - d0-d3 ...
... e- from the ligands → all six bonding MO e- from M ion → t2g & eg* - strong-field ligands: strong interaction b/w ligands & M ions : large t2g & eg* split : ∆o large - weak-field ligands: weak interaction b/w ligands & M ions : smaller t2g & eg* split : ∆o small - d0-d3 ...
Chemical Equations
... solution, these can also be balanced in acidic solution or basic solution. They are part of the general topic of oxidation and reduction, oxidation numbers, half-reactions, and electrochemistry which we won't go into here, except to outline the steps. In the method of half-reactions, you first break ...
... solution, these can also be balanced in acidic solution or basic solution. They are part of the general topic of oxidation and reduction, oxidation numbers, half-reactions, and electrochemistry which we won't go into here, except to outline the steps. In the method of half-reactions, you first break ...
print
... Based on trials 1 & 2, determine the order for NO. Considering the order of NO, and the change in the [NO] concentration between trials 1 & 3, determine the expected change in the rate (based solely on the [NO] change). Determine the change in rate between trials 1 & 3. Factor out the change in rate ...
... Based on trials 1 & 2, determine the order for NO. Considering the order of NO, and the change in the [NO] concentration between trials 1 & 3, determine the expected change in the rate (based solely on the [NO] change). Determine the change in rate between trials 1 & 3. Factor out the change in rate ...
5 Energetics/thermochemistry
... When an exothermic reaction transfers heat energy to the surroundings the chemical reactants lose potential energy. The products have less potential energy than the reactants. This potential energy stored in the chemical bonds is known as enthalpy and is given the symbol H. The transfer of heat ener ...
... When an exothermic reaction transfers heat energy to the surroundings the chemical reactants lose potential energy. The products have less potential energy than the reactants. This potential energy stored in the chemical bonds is known as enthalpy and is given the symbol H. The transfer of heat ener ...
chemistry (9189)
... industrial and laboratory visits relevant to the content of the options chosen. In order to specify the syllabus as precisely as possible and also to emphasise the importance of skills other than recall, learning Outcomes have been used throughout. Each part of the syllabus is specified by a Content ...
... industrial and laboratory visits relevant to the content of the options chosen. In order to specify the syllabus as precisely as possible and also to emphasise the importance of skills other than recall, learning Outcomes have been used throughout. Each part of the syllabus is specified by a Content ...
Thermal and Statistical Physics
... intelligence/information technology, finance, philosophy, etc. Indeed one of the central reasons why a physics degree is an ideal preparation for doing interdisciplinary research (not to mention investment banking, or theology) is that physicists are trained to quantitatively understand probability, ...
... intelligence/information technology, finance, philosophy, etc. Indeed one of the central reasons why a physics degree is an ideal preparation for doing interdisciplinary research (not to mention investment banking, or theology) is that physicists are trained to quantitatively understand probability, ...
(a) From , 2013 General Chemistry I
... by two different paths. (a) Path A is an isothermal, reversible expansion. (b) Path B has two parts. In step 1, the gas is cooled at constant volume until its pressure has fallen to 1.20 atm. In step 2, it is heated and allowed to expand against a constant pressure of 1.20 atm until its volume is 20 ...
... by two different paths. (a) Path A is an isothermal, reversible expansion. (b) Path B has two parts. In step 1, the gas is cooled at constant volume until its pressure has fallen to 1.20 atm. In step 2, it is heated and allowed to expand against a constant pressure of 1.20 atm until its volume is 20 ...
Thermodynamics: Entropy and Free Energy
... standard molar entropy, J/mol K. Table 19.1.1 shows standard molar entropy values for water at various temperatures. Interactive Figure 19.1.11 shows a generalized plot of the entropy of a substance at each temperature from 0 K to above its boiling point. Note in Table 19.1.1 and Interactive Figur ...
... standard molar entropy, J/mol K. Table 19.1.1 shows standard molar entropy values for water at various temperatures. Interactive Figure 19.1.11 shows a generalized plot of the entropy of a substance at each temperature from 0 K to above its boiling point. Note in Table 19.1.1 and Interactive Figur ...
Equilibrium chemistry
Equilibrium chemistry is a concerned with systems in chemical equilibrium. The unifying principle is that the free energy of a system at equilibrium is the minimum possible, so that the slope of the free energy with respect to the reaction coordinate is zero. This principle, applied to mixtures at equilibrium provides a definition of an equilibrium constant. Applications include acid-base, host-guest, metal-complex, solubility, partition, chromatography and redox equilibria.