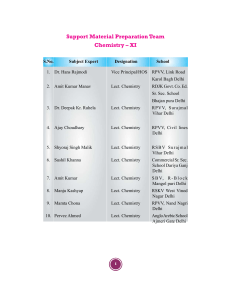
Support Material
... in it while weight is the force exerted by gravity on an object. The mass of a substance is constant whereas its weight may vary from one place to another due to change in gravity. ...
... in it while weight is the force exerted by gravity on an object. The mass of a substance is constant whereas its weight may vary from one place to another due to change in gravity. ...
Rotational−Vibrational Levels of Diatomic Molecules Represented
... potential). Thus, the degree of the overall agreement between the exact potentials and the potentials 1 and 3 is measured here by the ratios ∆Ui (see Tables 1 and 2; the corresponding values of ch are given in Table 3). The ratios are much smaller than 1 (typically, they are smaller than 0.05). Howe ...
... potential). Thus, the degree of the overall agreement between the exact potentials and the potentials 1 and 3 is measured here by the ratios ∆Ui (see Tables 1 and 2; the corresponding values of ch are given in Table 3). The ratios are much smaller than 1 (typically, they are smaller than 0.05). Howe ...
IUPAC Provisional Recommendations
... Consider a di- or a polyatomic molecule AB in the gas phase, at T = 0 K. By means of an electron or a photon, this molecule can be ionized and excited to a state AB+*, which subsequently decomposes into the fragments A+ and B: AB(g) → AB+*(g) + e−(g) → A+(g) + B(g) + e−(g) ...
... Consider a di- or a polyatomic molecule AB in the gas phase, at T = 0 K. By means of an electron or a photon, this molecule can be ionized and excited to a state AB+*, which subsequently decomposes into the fragments A+ and B: AB(g) → AB+*(g) + e−(g) → A+(g) + B(g) + e−(g) ...
5 SURFACE CHEMISTRY CATEGORY
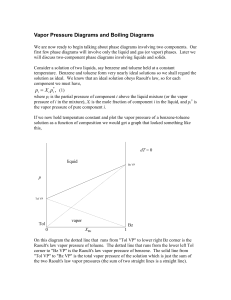
... 1. State Henry’s law correlating the pressure of a gas and its solubility in a solvent and mention two applications of the law. 2. State Raoult’s law for solutions of volatile liquids. Taking suitable examples explain the meaning of positive and negative deviations from Raoult’s law. 3.Define the te ...
... 1. State Henry’s law correlating the pressure of a gas and its solubility in a solvent and mention two applications of the law. 2. State Raoult’s law for solutions of volatile liquids. Taking suitable examples explain the meaning of positive and negative deviations from Raoult’s law. 3.Define the te ...
Worked out problems
... reduction process (electrons on the reactant side of the equation). By definition, the reduction process occurs at the cathode. The second half-reaction is the oxidation process (electrons on the product side of the equation), which occurs at the anode. The I– ions are the source of electrons, and t ...
... reduction process (electrons on the reactant side of the equation). By definition, the reduction process occurs at the cathode. The second half-reaction is the oxidation process (electrons on the product side of the equation), which occurs at the anode. The I– ions are the source of electrons, and t ...
Answer
... • Henry's law relates the solubility of a gas to its pressure. i.e. c = kp The Henry’s law constant for N2(g) at 298 K is 6.8 × 10–4 mol L–1 atm–1. A diver descends to a depth where the pressure is 5 atm. If the diver’s body contains about 5 L of blood, calculate the maximum amount of nitrogen gas d ...
... • Henry's law relates the solubility of a gas to its pressure. i.e. c = kp The Henry’s law constant for N2(g) at 298 K is 6.8 × 10–4 mol L–1 atm–1. A diver descends to a depth where the pressure is 5 atm. If the diver’s body contains about 5 L of blood, calculate the maximum amount of nitrogen gas d ...
الشريحة 1
... Regardless of the particular solute being considered, separation of the solute particles from one another requires an input of energy to overcome their attractive interactions. The process is therefore endothermic (H1 > 0). Separation of solvent molecules to accommodate the solute also always requ ...
... Regardless of the particular solute being considered, separation of the solute particles from one another requires an input of energy to overcome their attractive interactions. The process is therefore endothermic (H1 > 0). Separation of solvent molecules to accommodate the solute also always requ ...
Chapter 4. Hard and Soft Acid/Base Theory based on Lewis Acids
... acid-base reaction A(sol) + B(sol) → AB(sol) can be made to look like an exchange process by writing it as follows. A(S) n + B(S) m → A-B + [(n+m)/2]S-S The second product here is an adduct of solvent with solvent. Example: Ni(H2O)62+ (BA-HB) + H3N-HOH (HA-BB) → Ni(NH3)62+ (BA-BB) + HOH-OH2 (HA-HB) ...
... acid-base reaction A(sol) + B(sol) → AB(sol) can be made to look like an exchange process by writing it as follows. A(S) n + B(S) m → A-B + [(n+m)/2]S-S The second product here is an adduct of solvent with solvent. Example: Ni(H2O)62+ (BA-HB) + H3N-HOH (HA-BB) → Ni(NH3)62+ (BA-BB) + HOH-OH2 (HA-HB) ...
Chemical Reactivity of Ti+ within Water, Dimethyl Ether, and
... provided a detailed theoretical examination of the energies and possible structures of these oxides.24 We propose that the production of TiO3+ ions is due to the effective insertion capability of Ti+ ion into H2O molecules, as reflected by the large exothermicity of this reaction. Figure 2 displays ...
... provided a detailed theoretical examination of the energies and possible structures of these oxides.24 We propose that the production of TiO3+ ions is due to the effective insertion capability of Ti+ ion into H2O molecules, as reflected by the large exothermicity of this reaction. Figure 2 displays ...
- Mendeley Data
... (Table 6). Different quantity of Schiff base complex (0.005, 0.01 and 0.02 mmol) were used in the epoxidation of cyclooctene in the CHCl3 and in the presence of TBHP However, the maximum epoxidation yield was made by 0.01 mmol of complex. Our further investigation concerned the oxidation of cyclohex ...
... (Table 6). Different quantity of Schiff base complex (0.005, 0.01 and 0.02 mmol) were used in the epoxidation of cyclooctene in the CHCl3 and in the presence of TBHP However, the maximum epoxidation yield was made by 0.01 mmol of complex. Our further investigation concerned the oxidation of cyclohex ...
Solidification in heat packs: I. Nucleation rate
... requires the calculation of the free energy of forming one incipient nucleus, ⌬⍀ nU . We can represent the energy of forming a cluster of n molecules, ⌬⍀ n , as a sum of three contributions, from volume effects ⌬G® Žmelting., surface effects ⌬Gs Žwetting., and mixing effects ⌬Gm. A detailed derivati ...
... requires the calculation of the free energy of forming one incipient nucleus, ⌬⍀ nU . We can represent the energy of forming a cluster of n molecules, ⌬⍀ n , as a sum of three contributions, from volume effects ⌬G® Žmelting., surface effects ⌬Gs Žwetting., and mixing effects ⌬Gm. A detailed derivati ...
6 theoretical problems 2 practical problems
... was officially opened. It consists of a tunnel from Copenhagen to an artificial island, and a bridge from the island to Malmö in Sweden. The major construction materials employed are concrete and steel. This problem deals with chemical reactions relating to production and degradation of such materia ...
... was officially opened. It consists of a tunnel from Copenhagen to an artificial island, and a bridge from the island to Malmö in Sweden. The major construction materials employed are concrete and steel. This problem deals with chemical reactions relating to production and degradation of such materia ...
Class 1
... Multiple-charged ions are formed if there are many ionizable sites in the molecule, as in peptides and proteins, so that the formula masses of large molecules can be determined by ESI – another big advantage over EI. Most analyzers have limits on the size of m/z that can be measured with acceptable ...
... Multiple-charged ions are formed if there are many ionizable sites in the molecule, as in peptides and proteins, so that the formula masses of large molecules can be determined by ESI – another big advantage over EI. Most analyzers have limits on the size of m/z that can be measured with acceptable ...
Density functional theory of solvation in a polar solvent
... tions can be proposed. The rigorous definition of the excess functional involves the direct correlation function 共the c function兲 of the inhomogeneous fluid, which is connected to the pair correlation function 共the h function兲 through the Ornstein-Zernike 共OZ兲 equation. A tempting approximation is t ...
... tions can be proposed. The rigorous definition of the excess functional involves the direct correlation function 共the c function兲 of the inhomogeneous fluid, which is connected to the pair correlation function 共the h function兲 through the Ornstein-Zernike 共OZ兲 equation. A tempting approximation is t ...
Equilibrium chemistry
Equilibrium chemistry is a concerned with systems in chemical equilibrium. The unifying principle is that the free energy of a system at equilibrium is the minimum possible, so that the slope of the free energy with respect to the reaction coordinate is zero. This principle, applied to mixtures at equilibrium provides a definition of an equilibrium constant. Applications include acid-base, host-guest, metal-complex, solubility, partition, chromatography and redox equilibria.