A STUDY OF THE RATE OF THE REACTION OF CHLORINE
... • The blue dye (FD & C #1) has an absorbance maximum at 630 nm. • We will supply you with a solution of the food dye. (We use 18 drops of “Club House” Brand blue food colouring per litre of solution. The blue colouring comes in a set of four different food colours, available at the supermarket.) • T ...
... • The blue dye (FD & C #1) has an absorbance maximum at 630 nm. • We will supply you with a solution of the food dye. (We use 18 drops of “Club House” Brand blue food colouring per litre of solution. The blue colouring comes in a set of four different food colours, available at the supermarket.) • T ...
unit iii kinetics and mechanism of reactions in metal complexes
... According to Taube, the degree of lability or inertness of a transition metal complex can be correlated with the d electronic configuration of the metal ion. If a complex contains electrons in the antibonding eg* orbitals, the electrons are expected to be weakly bound and easily displaced; it is lab ...
... According to Taube, the degree of lability or inertness of a transition metal complex can be correlated with the d electronic configuration of the metal ion. If a complex contains electrons in the antibonding eg* orbitals, the electrons are expected to be weakly bound and easily displaced; it is lab ...
chem 111 practice exam
... Tear off this top page (pg. 1)-It is your scratch paper The following are molar masses you may or may not need: H2O = 18.02 ...
... Tear off this top page (pg. 1)-It is your scratch paper The following are molar masses you may or may not need: H2O = 18.02 ...
Lecture 4
... Al(OH)3 and hydrogen sulfide gas, H2S according to the following chemical equation: Al2S3 (s) + 6 H2O (l) 2 Al(OH)3 (s) + 3 H2S (g) Calculate the percent yield when 45.7 g of Al(OH)3 are recuperated after 50.0 g of Al2S3 are completely reacted. ...
... Al(OH)3 and hydrogen sulfide gas, H2S according to the following chemical equation: Al2S3 (s) + 6 H2O (l) 2 Al(OH)3 (s) + 3 H2S (g) Calculate the percent yield when 45.7 g of Al(OH)3 are recuperated after 50.0 g of Al2S3 are completely reacted. ...
153KB PDF - Clydeview Academy
... The reaction was carried out at several temperatures between 40 °C and 60 °C. The end of the reaction was indicated by a colour change from purple to colourless. (a) ...
... The reaction was carried out at several temperatures between 40 °C and 60 °C. The end of the reaction was indicated by a colour change from purple to colourless. (a) ...
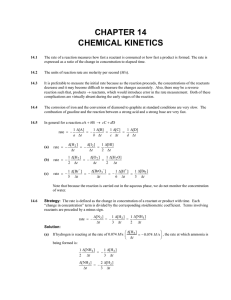
CHAPTER 14 CHEMICAL KINETICS
... Strategy: The rate law, determined in part (a), shows that the slow step involves reaction of a molecule of X2 with a molecule of Y. Since Z is not present in the rate law, it does not take part in the slow step and must appear in a fast step at a later time. (If the fast step involving Z happened b ...
... Strategy: The rate law, determined in part (a), shows that the slow step involves reaction of a molecule of X2 with a molecule of Y. Since Z is not present in the rate law, it does not take part in the slow step and must appear in a fast step at a later time. (If the fast step involving Z happened b ...
6.5 Half-reactions and electrodes
... equilibrium can do electrical work as the reaction drives electrons through an external circuit • With a large potential difference, a given number of electrons travelling can do a larger amount of electrical work. • A cell in which the overall reaction is at equilibrium can do no work with zero p ...
... equilibrium can do electrical work as the reaction drives electrons through an external circuit • With a large potential difference, a given number of electrons travelling can do a larger amount of electrical work. • A cell in which the overall reaction is at equilibrium can do no work with zero p ...
Dr David`s Chemistry Revision Themes
... (a) The concentration of the thiosulphate solution was varied and the time taken for a given amount of sulphur to be deposited was recorded. The temperature and the concentration of hydrogen ion were kept constant. A graph was plotted of rate (reciprocal of time) against concentration. Draw the best ...
... (a) The concentration of the thiosulphate solution was varied and the time taken for a given amount of sulphur to be deposited was recorded. The temperature and the concentration of hydrogen ion were kept constant. A graph was plotted of rate (reciprocal of time) against concentration. Draw the best ...
PowerPoint - Balancing Equations
... indicate numbers of atoms. E.g. Ca(OH)2 • Notice that the OH is a group O Ca O H • The 2 refers to both H and O H • How many of each atom are in the following? a) NaOH Na = 1, O = 1, H = 1 b) Ca(OH)2 Ca = 1, O = 2, H = 2 c) 3Ca(OH)2 Ca = 3, O = 6, H = 6 ...
... indicate numbers of atoms. E.g. Ca(OH)2 • Notice that the OH is a group O Ca O H • The 2 refers to both H and O H • How many of each atom are in the following? a) NaOH Na = 1, O = 1, H = 1 b) Ca(OH)2 Ca = 1, O = 2, H = 2 c) 3Ca(OH)2 Ca = 3, O = 6, H = 6 ...
Kinetic study on carbonation of crude Li2CO3 with CO2
... atmospheric pressure. The experiments were carried out in a slurry bubble column reactor with 0.05 m inner diameter and 1.0 m height. Parameters that may affect the dissolution of Li2CO3 in the CO2-water solutions such as CO2-bubble perforation diameter, CO2 partial pressure, CO2 gas flow rate, Li2C ...
... atmospheric pressure. The experiments were carried out in a slurry bubble column reactor with 0.05 m inner diameter and 1.0 m height. Parameters that may affect the dissolution of Li2CO3 in the CO2-water solutions such as CO2-bubble perforation diameter, CO2 partial pressure, CO2 gas flow rate, Li2C ...
Atomic Theory (2
... 1.) Who were the early contributors to the atomic theory, and what was their view of the atom? 2.) Who discovered the electron? 3.) Who discovered the charge of an electron? 4.) Who discovered the nucleus? 5.) Who discovered the proton? 6.) Describe the composition of the atom and the experiments th ...
... 1.) Who were the early contributors to the atomic theory, and what was their view of the atom? 2.) Who discovered the electron? 3.) Who discovered the charge of an electron? 4.) Who discovered the nucleus? 5.) Who discovered the proton? 6.) Describe the composition of the atom and the experiments th ...
0.08206 L atm/K mol - Arizona State University
... Potential energy increases and kinetic energy increases. Potential energy increases and kinetic energy decreases. Potential energy decreases and kinetic energy increases. Potential energy decreases and kinetic energy decreases. There is no change at all. ...
... Potential energy increases and kinetic energy increases. Potential energy increases and kinetic energy decreases. Potential energy decreases and kinetic energy increases. Potential energy decreases and kinetic energy decreases. There is no change at all. ...
ENZYMES
... – Lipase works only on __________ – Sucrase works only on ____________ – Protease works only on ____________ – __________ works only on fructose ...
... – Lipase works only on __________ – Sucrase works only on ____________ – Protease works only on ____________ – __________ works only on fructose ...
Name AP Chemistry Take Home Quiz – Due Thursday, 1/9/2014
... a. CN-(aq) is a stronger base than C2H3O2-(aq) b. HCN(aq) is a stronger acid than HC2H3O2(aq) c. The conjugate base of CN-(aq) is C2H3O2-(aq) d. The equilibrium constant will increase with an increase in temperature. e. The pH of a solution containing equimolar amounts of CN-(aq) and HC2H3O2(aq) is ...
... a. CN-(aq) is a stronger base than C2H3O2-(aq) b. HCN(aq) is a stronger acid than HC2H3O2(aq) c. The conjugate base of CN-(aq) is C2H3O2-(aq) d. The equilibrium constant will increase with an increase in temperature. e. The pH of a solution containing equimolar amounts of CN-(aq) and HC2H3O2(aq) is ...
4.1 Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations
... balancing a chemical equation. Consider as an example the reaction between one methane molecule (CH4) and two diatomic oxygen molecules (O2) to produce one carbon dioxide molecule (CO2) and two water molecules (H2O). The chemical equation representing this process is provided in the upper half of Fi ...
... balancing a chemical equation. Consider as an example the reaction between one methane molecule (CH4) and two diatomic oxygen molecules (O2) to produce one carbon dioxide molecule (CO2) and two water molecules (H2O). The chemical equation representing this process is provided in the upper half of Fi ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.