Torque
... Torque is a twist or turn that tends to produce rotation. * * * Applications are found in many common tools around the home or industry where it is necessary to turn, tighten or loosen devices. ...
... Torque is a twist or turn that tends to produce rotation. * * * Applications are found in many common tools around the home or industry where it is necessary to turn, tighten or loosen devices. ...
force
... 1) Objects moving in a circle always have a component of acceleration, called centripetal, which is toward the center of the circle.* 2) Centripetal acceleration must be caused by a force: ...
... 1) Objects moving in a circle always have a component of acceleration, called centripetal, which is toward the center of the circle.* 2) Centripetal acceleration must be caused by a force: ...
Motion and Speed Classwork Name
... of an entire trip. Instantaneous speed is the speed at any one moment during the trip. 25. Yes. If travelling at a constant speed inst speed = avg speed. 26. 100 m/ 30 s = 3.33 m/s ...
... of an entire trip. Instantaneous speed is the speed at any one moment during the trip. 25. Yes. If travelling at a constant speed inst speed = avg speed. 26. 100 m/ 30 s = 3.33 m/s ...
location latitude elevation (m) g (m/s2) north pole 0 9.8322
... Let’s study the example of the rising and falling ball. In the example of the person falling from a bridge, I assumed positive velocity values without calling attention to it, which meant I was assuming a coordinate system whose x axis pointed down. In this example, where the ball is reversing direc ...
... Let’s study the example of the rising and falling ball. In the example of the person falling from a bridge, I assumed positive velocity values without calling attention to it, which meant I was assuming a coordinate system whose x axis pointed down. In this example, where the ball is reversing direc ...
Structure of Neutron Stars
... However, then in 2007 at a conference the authors announced that the result was incorrect. Actually, the initial value was 2.1+/-0.2 (1 sigma error). New result: 1.26 +/- 0.14 solar [Nice et al. 2008, Proc. of the conf. “40 Years of pulsars”] 3. PSR B1516+02B in a globular cluster. M~2 solar (M>1.72 ...
... However, then in 2007 at a conference the authors announced that the result was incorrect. Actually, the initial value was 2.1+/-0.2 (1 sigma error). New result: 1.26 +/- 0.14 solar [Nice et al. 2008, Proc. of the conf. “40 Years of pulsars”] 3. PSR B1516+02B in a globular cluster. M~2 solar (M>1.72 ...
Newton’s First Law - Miss Gray's Superb Science Site
... Inclined Planes: a tilted surface • An object placed on a tilted surface will often slide down the surface. • The rate at which the object slides down the surface is dependent upon how tilted the surface is; the greater the tilt of the surface, the faster the rate at which the object will slide dow ...
... Inclined Planes: a tilted surface • An object placed on a tilted surface will often slide down the surface. • The rate at which the object slides down the surface is dependent upon how tilted the surface is; the greater the tilt of the surface, the faster the rate at which the object will slide dow ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion Review
... f. An object can experience two or more forces and not accelerate. g. A contact force results from the physical contact between two objects. h. A field force results from the action of two objects which are positioned some distance away. i. Spring and tension forces are examples of field forces. j. ...
... f. An object can experience two or more forces and not accelerate. g. A contact force results from the physical contact between two objects. h. A field force results from the action of two objects which are positioned some distance away. i. Spring and tension forces are examples of field forces. j. ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... The ratio of weight to mass is the same for all falling objects in the same locality; hence, their accelerations are the same in the absence of air ...
... The ratio of weight to mass is the same for all falling objects in the same locality; hence, their accelerations are the same in the absence of air ...
The Formation and Evolution of Massive Black Holes - Ira-Inaf
... massive star is to collapse into a black hole with a mass similar to that of its progenitor. However, this is not the case when the content of heavy elements increases. In today’s universe, a very massive star would lose most of its mass in powerful winds before collapsing into a stellar mass black ...
... massive star is to collapse into a black hole with a mass similar to that of its progenitor. However, this is not the case when the content of heavy elements increases. In today’s universe, a very massive star would lose most of its mass in powerful winds before collapsing into a stellar mass black ...
ƒ A S ƒ ƒ B
... in an inertial frame of reference—that is, either at rest or moving with constant velocity—the vector sum of forces acting on it must be zero (Newton’s first law). Free-body diagrams are essential in identifying the forces that act on the body being considered. Newton’s third law (action and reactio ...
... in an inertial frame of reference—that is, either at rest or moving with constant velocity—the vector sum of forces acting on it must be zero (Newton’s first law). Free-body diagrams are essential in identifying the forces that act on the body being considered. Newton’s third law (action and reactio ...
8 - PUE
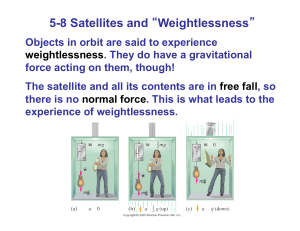
... 20. The period of geostationary satellite T is 24 hrs. 21. The group of the geostationary satellites sent up by India is INSAT group of satellites. 22. Geostationary satellites are widely used for telecommunications in India. 23. The dimensional formula for G is [M-1 L3 T -2]. 24. Orbital speed of a ...
... 20. The period of geostationary satellite T is 24 hrs. 21. The group of the geostationary satellites sent up by India is INSAT group of satellites. 22. Geostationary satellites are widely used for telecommunications in India. 23. The dimensional formula for G is [M-1 L3 T -2]. 24. Orbital speed of a ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.