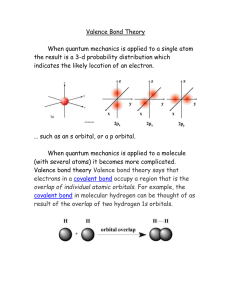
Review 2nd KEY
... ____ 2. A spherical electron cloud surrounding an atomic nucleus would best represent a. an s orbital. c. a combination of px and py orbitals. b. a px orbital. d. a combination of an s and a px orbital. ____ 3. For an electron in an atom to change from the ground state to an excited state, a. energy ...
... ____ 2. A spherical electron cloud surrounding an atomic nucleus would best represent a. an s orbital. c. a combination of px and py orbitals. b. a px orbital. d. a combination of an s and a px orbital. ____ 3. For an electron in an atom to change from the ground state to an excited state, a. energy ...
Slide 1
... oElectromagnetic spectrum Energy quantization oPlanck oE=h. (h≈6.6260755x10-34 J.s) Photoelectric effect oWhen light strikes the surface of a metal and e- are ejected oE=h.c/ Bohr model oRadius of the circular orbits increase as n increases oAn atom with its e- in the lowest possible energy lev ...
... oElectromagnetic spectrum Energy quantization oPlanck oE=h. (h≈6.6260755x10-34 J.s) Photoelectric effect oWhen light strikes the surface of a metal and e- are ejected oE=h.c/ Bohr model oRadius of the circular orbits increase as n increases oAn atom with its e- in the lowest possible energy lev ...
PS7 - Bergen.org
... (a) Write the ground state electron configuration for an arsenic atom, showing the number of electrons in each subshell. You may start with the previous noble gas. ...
... (a) Write the ground state electron configuration for an arsenic atom, showing the number of electrons in each subshell. You may start with the previous noble gas. ...
honors-chapter6-reading
... 1. Define electronmagnetic radiation and list its properties. 2. Define properties and “parts” of a wave. 3. What is the speed of light? Include a formula, numerical value, units and relationship of wavelength and frequency in your definition. 4. Review metric prefixes identified in Table 6.1 and re ...
... 1. Define electronmagnetic radiation and list its properties. 2. Define properties and “parts” of a wave. 3. What is the speed of light? Include a formula, numerical value, units and relationship of wavelength and frequency in your definition. 4. Review metric prefixes identified in Table 6.1 and re ...
final2012
... a) What orbitals are filled for the protons and neutrons in these two nuclei? List how many neutrons or protons are in each energy level. Use the notation that lists energy levels by primary quantum number, orbital shell type and total angular momentum, rather than shell number. (Hint – all of the l ...
... a) What orbitals are filled for the protons and neutrons in these two nuclei? List how many neutrons or protons are in each energy level. Use the notation that lists energy levels by primary quantum number, orbital shell type and total angular momentum, rather than shell number. (Hint – all of the l ...
ELECTRONS IN ATOMS
... 6. What is the difference between the previous models of the atom and the modern Previous models described the motion of electrons the quantum mechanical model? ______________________________________________)____ same way as the motion of large objects.The quantum mechanical model is not based on th ...
... 6. What is the difference between the previous models of the atom and the modern Previous models described the motion of electrons the quantum mechanical model? ______________________________________________)____ same way as the motion of large objects.The quantum mechanical model is not based on th ...
Ch 11 WS Orbitals and Electron Arrangement
... Atomic Orbitals 7. A(n) is often thought of as a region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron. 8. Circle the letter of the term that is used to label the energy levels of electrons. a. atomic orbitals c. quantum b. quantum mechanical numbers d. principal quantum number ...
... Atomic Orbitals 7. A(n) is often thought of as a region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron. 8. Circle the letter of the term that is used to label the energy levels of electrons. a. atomic orbitals c. quantum b. quantum mechanical numbers d. principal quantum number ...
Particle-like Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation
... de Broglie postulated that matter can behave in some respects like light. Both light and matter (at the atomic level) are wavelike as well as particlelike. This wave/ particle description of light and matter is a mathematical model that accounts for atomic properties and behavior (math of quantum me ...
... de Broglie postulated that matter can behave in some respects like light. Both light and matter (at the atomic level) are wavelike as well as particlelike. This wave/ particle description of light and matter is a mathematical model that accounts for atomic properties and behavior (math of quantum me ...
Chapter 5 Sec. 2 Bohr`s Model and the Quantum Mechanical Model
... correctly predicted the frequencies of the lines in hydrogen’s atomic emission spectra. o Energy States of Hydrogen Bohr proposed the following: ...
... correctly predicted the frequencies of the lines in hydrogen’s atomic emission spectra. o Energy States of Hydrogen Bohr proposed the following: ...
Orbitals and energy levels
... In the quantum mechanical model, the probability of finding an electron within a certain volume of space surrounding the nucleus can be represented as a fuzzy cloud. The cloud is more dense where the probability of finding the electron is ...
... In the quantum mechanical model, the probability of finding an electron within a certain volume of space surrounding the nucleus can be represented as a fuzzy cloud. The cloud is more dense where the probability of finding the electron is ...
Details
... Structure of the atom, the early atomic theories, theories of electromagnetic radiation, Plank theory, Bohr theory. Quantum theory, Schrodinger wave equation, quantum numbers, shapes of orbitals and electronic configuration. Periodic classification of the elements and periodic relationship among the ...
... Structure of the atom, the early atomic theories, theories of electromagnetic radiation, Plank theory, Bohr theory. Quantum theory, Schrodinger wave equation, quantum numbers, shapes of orbitals and electronic configuration. Periodic classification of the elements and periodic relationship among the ...
Quantum Mechanics
... and neutrons) and from this made his own model of the atom The Bohr model of the atom explains the equations for the atomic spectrum of hydrogen, but does not work for any other element Even though his theory was wrong, it provided an excellent starting point for quantum mechanics ...
... and neutrons) and from this made his own model of the atom The Bohr model of the atom explains the equations for the atomic spectrum of hydrogen, but does not work for any other element Even though his theory was wrong, it provided an excellent starting point for quantum mechanics ...
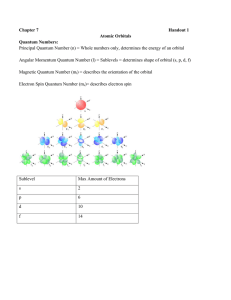
Chapter 7 Handout 1 Atomic Orbitals Quantum Numbers: Principal
... Rules for filling orbitals: 1. Aufbau Principle: a. Electrons fill up orbitals of lowest energy first b. Orbitals in the same sublevel are equal in energy c. Sometimes energy levels overlap 2. Pauli Exculsion Principle a. There is a max of 2 electrons in any one orbital b. These 2 electrons must ha ...
... Rules for filling orbitals: 1. Aufbau Principle: a. Electrons fill up orbitals of lowest energy first b. Orbitals in the same sublevel are equal in energy c. Sometimes energy levels overlap 2. Pauli Exculsion Principle a. There is a max of 2 electrons in any one orbital b. These 2 electrons must ha ...