Exam 2 Review - Iowa State University
... 12. Consider the sine waves representing light or electromagnetic radiation. Which one corresponds to photons with the largest energy? ...
... 12. Consider the sine waves representing light or electromagnetic radiation. Which one corresponds to photons with the largest energy? ...
WORKSHEET 36: ATOMIC PROPERTIES
... Explain your answer. (2) _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 7. Define electron affinity. (2) ________ ...
... Explain your answer. (2) _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 7. Define electron affinity. (2) ________ ...
CH7 handout is here.
... 8. Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that we cannot know exactly the position and velocity of an electron both at the same instant. Explain what we studied under ‘position’ and under ‘velocity’. What were the assumptions when studying ‘position’? “velocity”? ...
... 8. Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that we cannot know exactly the position and velocity of an electron both at the same instant. Explain what we studied under ‘position’ and under ‘velocity’. What were the assumptions when studying ‘position’? “velocity”? ...
Quantum numbers
... The size of an atom The definition of the size of a hydrogen atom 1s orbital is the radius of the sphere that encloses 90% of the total electron probability. ...
... The size of an atom The definition of the size of a hydrogen atom 1s orbital is the radius of the sphere that encloses 90% of the total electron probability. ...
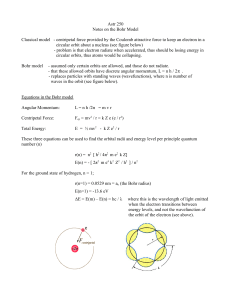
Astr 250 Notes on the Bohr Model Classical model
... circular orbit about a nucleus (see figure below) - problem is that electron radiate when accelerated, thus should be losing energy in circular orbits, thus atoms would be collapsing. Bohr model ...
... circular orbit about a nucleus (see figure below) - problem is that electron radiate when accelerated, thus should be losing energy in circular orbits, thus atoms would be collapsing. Bohr model ...
Units 1-6
... I can calculate conversions of all types (metric prefix, energy, temperature, density, etc.) including set up, sig figs and units I understand that energy takes different forms, and I can classify energy as potential (chemical, positional, gravitational), kinetic (including temperature) or radiant. ...
... I can calculate conversions of all types (metric prefix, energy, temperature, density, etc.) including set up, sig figs and units I understand that energy takes different forms, and I can classify energy as potential (chemical, positional, gravitational), kinetic (including temperature) or radiant. ...
Name
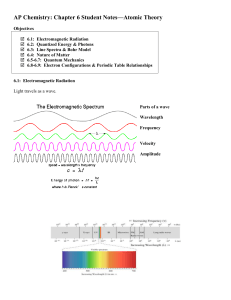
... 12. Look at Figure 5.8. The electromagnetic spectrum consists of radiation over a broad band of wavelengths. What type of radiation has the lowest frequency? The highest frequency? 13. What happens when an electric current is passed through the gas or vapor of an element? 14. Passing the light emitt ...
... 12. Look at Figure 5.8. The electromagnetic spectrum consists of radiation over a broad band of wavelengths. What type of radiation has the lowest frequency? The highest frequency? 13. What happens when an electric current is passed through the gas or vapor of an element? 14. Passing the light emitt ...
Atomic Structure
... – Principal quantum number (n) = main energy level/shell (n=1,2,3,….) – Angular momentum quantum number (l) = shape = block/subshell (s=0; p=1; d=2; f=3) – Magnetic quantum number (ml) = orientation (-l to +l) – Spin quantum number (ms) = +1/2 or -1/2 ...
... – Principal quantum number (n) = main energy level/shell (n=1,2,3,….) – Angular momentum quantum number (l) = shape = block/subshell (s=0; p=1; d=2; f=3) – Magnetic quantum number (ml) = orientation (-l to +l) – Spin quantum number (ms) = +1/2 or -1/2 ...
Quantum Chemical Simulations and Descriptors
... electronic wave function with the electronic density as the basic quantity. Whereas the many-body wavefunction is dependent on 3N variables, three spatial variables for each of the N electrons, the density is only a function of three variables and is a simpler quantity to deal with both conceptually ...
... electronic wave function with the electronic density as the basic quantity. Whereas the many-body wavefunction is dependent on 3N variables, three spatial variables for each of the N electrons, the density is only a function of three variables and is a simpler quantity to deal with both conceptually ...
CHEMISTRY 1A
... 1. A sample of gas occupies 2.85 L at -23C and a pressure of 575 torr. Calculate the new pressure, in atm., if the temperature is raised to 92C and the new volume is 745 mL. (760 torr = 760 mmHg = 1 atm) ...
... 1. A sample of gas occupies 2.85 L at -23C and a pressure of 575 torr. Calculate the new pressure, in atm., if the temperature is raised to 92C and the new volume is 745 mL. (760 torr = 760 mmHg = 1 atm) ...
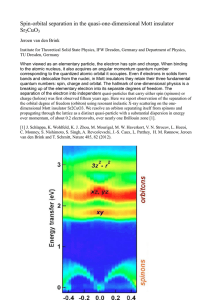
Spin-orbital separation in the quasi-one
... Institute for Theoretical Solid State Physics, IFW Dresden, Germany and Department of Physics, TU Dresden, Germany When viewed as an elementary particle, the electron has spin and charge. When binding to the atomic nucleus, it also acquires an angular momentum quantum number corresponding to the qua ...
... Institute for Theoretical Solid State Physics, IFW Dresden, Germany and Department of Physics, TU Dresden, Germany When viewed as an elementary particle, the electron has spin and charge. When binding to the atomic nucleus, it also acquires an angular momentum quantum number corresponding to the qua ...
4. Structure of the Atom
... Never express yourself more clearly than you are able to think. Prediction is very difficult, especially about the future. - Niels Bohr ...
... Never express yourself more clearly than you are able to think. Prediction is very difficult, especially about the future. - Niels Bohr ...