Chapter 5 : Electrons in Atoms
... measurement of an object without disturbing it. The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is fundamentally impossible to know precisely both the velocity and position of a particle at the same time. The only quantity that can be known is the probability for an electron to occupy a certain ...
... measurement of an object without disturbing it. The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is fundamentally impossible to know precisely both the velocity and position of a particle at the same time. The only quantity that can be known is the probability for an electron to occupy a certain ...
Spectroscopy - Birmingham City Schools
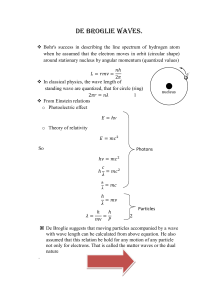
... 1924 deBroglie says: perhaps electrons are both wave and particle 1925 Erwin Schrödinger worked out equations that took wave nature of electrons into account. ...
... 1924 deBroglie says: perhaps electrons are both wave and particle 1925 Erwin Schrödinger worked out equations that took wave nature of electrons into account. ...
Atom 2 - UF Physics
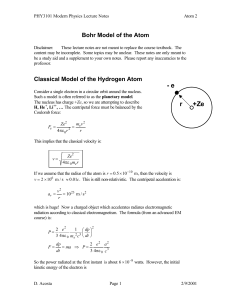
... In other words, quantization of angular momentum implies that only particular circular orbits are allowed in the atom. The Ground State is the state when n = 1, the lowest level and smallest radius. This derived size of the atom is about what was expected at the ...
... In other words, quantization of angular momentum implies that only particular circular orbits are allowed in the atom. The Ground State is the state when n = 1, the lowest level and smallest radius. This derived size of the atom is about what was expected at the ...
3.7 The Pauli principle
... Only symmetric or antisymmetric wave functions are allowed when exchanging two indices. Within quantum field theory one can show that particles with an integer number as spin have symmetric state functions while particles with a half number of the spin have always antisymmetric state functions. Thus ...
... Only symmetric or antisymmetric wave functions are allowed when exchanging two indices. Within quantum field theory one can show that particles with an integer number as spin have symmetric state functions while particles with a half number of the spin have always antisymmetric state functions. Thus ...
Quantum Numbers Primer The quantum numbers
... ml is the magnetic quantum number (ml = -ℓ, …, –2, -1, 0, +1, +2, …, +ℓ) (note: ℓ is lowercase L... it was used here so it is not confused with the number one). ml determines the number and orientation of the orbital. When n = 1, l must be 0. When l = 0, ml = 0. Because ml has only one value (the va ...
... ml is the magnetic quantum number (ml = -ℓ, …, –2, -1, 0, +1, +2, …, +ℓ) (note: ℓ is lowercase L... it was used here so it is not confused with the number one). ml determines the number and orientation of the orbital. When n = 1, l must be 0. When l = 0, ml = 0. Because ml has only one value (the va ...
Unit 1: Kinematics - Pre University Courses
... (b) Answers may vary. Students should add the following information to their concept maps: Louis de Broglie believed that all entities have wave-like properties but these properties are only significant and measureable for tiny, fast-moving particles like the electron. Erwin Schrödinger imagined el ...
... (b) Answers may vary. Students should add the following information to their concept maps: Louis de Broglie believed that all entities have wave-like properties but these properties are only significant and measureable for tiny, fast-moving particles like the electron. Erwin Schrödinger imagined el ...
Abstract
... the ensuing century his heuristic hypotheses were con rmed as facts. They de ne what might be called the \atomic world view." Today we stand on the threshold of a new era: the information age. Far from replacing the atomic view of the world, the concept of information can be enlisted to build upon o ...
... the ensuing century his heuristic hypotheses were con rmed as facts. They de ne what might be called the \atomic world view." Today we stand on the threshold of a new era: the information age. Far from replacing the atomic view of the world, the concept of information can be enlisted to build upon o ...
e- are outside nucleus nucleus
... - quantized energy levels) • Difference: e- do not travel in fixed paths; they exist in an e- cloud e- cloud: region around the nucleus where the probability of finding an e- is about 90% ...
... - quantized energy levels) • Difference: e- do not travel in fixed paths; they exist in an e- cloud e- cloud: region around the nucleus where the probability of finding an e- is about 90% ...
Chapter 7: The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom I. The
... D. The Bohr Model of the Atom: 1. Bohr s major idea was that the energy states of the atom were _________, and that the amount of energy in the atom was related to the electron s position in the atom. 2. The electrons travel in orbits that are at a fixed distance from the nucleus. ...
... D. The Bohr Model of the Atom: 1. Bohr s major idea was that the energy states of the atom were _________, and that the amount of energy in the atom was related to the electron s position in the atom. 2. The electrons travel in orbits that are at a fixed distance from the nucleus. ...
Electrons in Atoms
... A. Based on mathematical equation (previous models were basically physical) B. Concerned with predicting the probable location of electrons 1. when all the possible mathematical solutions are graphed, a 3-D shape results (a "cloud" of probability) (orbital) 2. although drawn spherical, atom is not n ...
... A. Based on mathematical equation (previous models were basically physical) B. Concerned with predicting the probable location of electrons 1. when all the possible mathematical solutions are graphed, a 3-D shape results (a "cloud" of probability) (orbital) 2. although drawn spherical, atom is not n ...
Electrons in Atoms
... A. Based on mathematical equation (previous models were basically physical) B. Concerned with predicting the probable location of electrons 1. when all the possible mathematical solutions are graphed, a 3-D shape results (a "cloud" of probability) (orbital) 2. although drawn spherical, atom is not n ...
... A. Based on mathematical equation (previous models were basically physical) B. Concerned with predicting the probable location of electrons 1. when all the possible mathematical solutions are graphed, a 3-D shape results (a "cloud" of probability) (orbital) 2. although drawn spherical, atom is not n ...
Atomic and Molecular Physics for Physicists Ben-Gurion University of the Negev
... Every microscope has the limit (the so-called diffraction limit) of observing a point like particle with a width of ∆x = λ / sinθ . This is then the accuracy With which we know the particles position ...
... Every microscope has the limit (the so-called diffraction limit) of observing a point like particle with a width of ∆x = λ / sinθ . This is then the accuracy With which we know the particles position ...
Term Symbols
... Note: Molecular orbitals have symbols corresponding to the quantum number as follows: Symbol: for 0 Symbol: for 1 Symbol: for 2 etc… Further discussions of these topics can be found in Mortimer pages 651 and 663. Term symbols can be used to determine the allowed electronic tran ...
... Note: Molecular orbitals have symbols corresponding to the quantum number as follows: Symbol: for 0 Symbol: for 1 Symbol: for 2 etc… Further discussions of these topics can be found in Mortimer pages 651 and 663. Term symbols can be used to determine the allowed electronic tran ...
PHY215: Study Guide for Introductory Quantum Mechanics Explain 1. Cathode Ray tubes, Cathode rays, and the generation of X‐rays.
... hand to alert the course staff members present at the exam. You have 25 minutes to work out the quiz problems. The relevant formulae are provided in on the last sheet, which you can detach when you solve the problems. Do not separate the remaining sheets. Calculator Policy: all memories and register ...
... hand to alert the course staff members present at the exam. You have 25 minutes to work out the quiz problems. The relevant formulae are provided in on the last sheet, which you can detach when you solve the problems. Do not separate the remaining sheets. Calculator Policy: all memories and register ...