Electron Configuration Notes
... This uses a little circle, O, to represent each orbital. We group the orbitals of a subshell together, and label them. An orbital with no electrons in it (an “empty house”) is left as a circle: O. With one electron we put a diagonal line in to show one electron in the orbital. The line can slant eit ...
... This uses a little circle, O, to represent each orbital. We group the orbitals of a subshell together, and label them. An orbital with no electrons in it (an “empty house”) is left as a circle: O. With one electron we put a diagonal line in to show one electron in the orbital. The line can slant eit ...
Set #4 - comsics
... electron typically spends about 10-8 s in an excited state before it drops to a lower state by emitting a photon. How many revolutions does an electron in an n = 2 Bohr orbit make in 10-8 s? ...
... electron typically spends about 10-8 s in an excited state before it drops to a lower state by emitting a photon. How many revolutions does an electron in an n = 2 Bohr orbit make in 10-8 s? ...
AP Notes Chapter 7
... n is the energy level for each energy level the energy is Z is the nuclear charge, which is +1 for hydrogen. E = -2.178 x 10-18 J (Z2 / n2 ) n = 1 is called the ground state when the electron is removed, n = ...
... n is the energy level for each energy level the energy is Z is the nuclear charge, which is +1 for hydrogen. E = -2.178 x 10-18 J (Z2 / n2 ) n = 1 is called the ground state when the electron is removed, n = ...
Lecture9,ch4
... Conservation of energy requires that the electron kinetic energy equal the maximum photon energy where we neglect the work function because it is normally so small compared to the potential energy of the electron. This yields the Duane-Hunt limit which was first found experimentally. The photon wave ...
... Conservation of energy requires that the electron kinetic energy equal the maximum photon energy where we neglect the work function because it is normally so small compared to the potential energy of the electron. This yields the Duane-Hunt limit which was first found experimentally. The photon wave ...
Quantum Mechanics
... There are 3p orbitals, each with a maximum of 2 electrons in each, making a total of 6 electrons. For example Neon, which has a total of 10 electrons has configuration of 1s22s22p6. It has 2 electrons in the s orbital of the first energy level and 8 electrons in the second energy level, 2 in the s o ...
... There are 3p orbitals, each with a maximum of 2 electrons in each, making a total of 6 electrons. For example Neon, which has a total of 10 electrons has configuration of 1s22s22p6. It has 2 electrons in the s orbital of the first energy level and 8 electrons in the second energy level, 2 in the s o ...
Atomic Physics 4
... Wave - Particle Duality of Light • Modern age physics accepts that light sometimes acts as a wave and at other times acts like a particle. • Both matter and electromagnetic energy exhibit some properties of waves and some properties of particles. ...
... Wave - Particle Duality of Light • Modern age physics accepts that light sometimes acts as a wave and at other times acts like a particle. • Both matter and electromagnetic energy exhibit some properties of waves and some properties of particles. ...
Orbits and Orbitals
... More rules • No orbital can have more than 2 e- in it. (one spin up, one spin down) • Orbitals are half filled (with spins in the same direction) before they are doubly filled. • Orbitals are filled from lowest energy to highest energy. ...
... More rules • No orbital can have more than 2 e- in it. (one spin up, one spin down) • Orbitals are half filled (with spins in the same direction) before they are doubly filled. • Orbitals are filled from lowest energy to highest energy. ...
Covalent bonds
... •Although results obtained with current potential energy functions are only approximate they have one great advantage - they are computationally cheap. This allows the introduction of realstic representation of environment - such as having large numbers of explicitly modelled water molecules surron ...
... •Although results obtained with current potential energy functions are only approximate they have one great advantage - they are computationally cheap. This allows the introduction of realstic representation of environment - such as having large numbers of explicitly modelled water molecules surron ...
Revision sheet and answer1
... 8) The quantity of energy required to remove the least bounded electrons from a single atom in the gaseous state. ...
... 8) The quantity of energy required to remove the least bounded electrons from a single atom in the gaseous state. ...
LERE-QSAR Analysis of Binding of γ
... form by hydrolysis. Rheumatism arthritis and Crohn's disease are caused by overproduction of the activated form TNF-alpha. In this study, we examined the atomic and electronic mechanism underlying binding between TACE and hydroxamic acid derivatives, which have a -lactum ring [1] (Figure 1), using ...
... form by hydrolysis. Rheumatism arthritis and Crohn's disease are caused by overproduction of the activated form TNF-alpha. In this study, we examined the atomic and electronic mechanism underlying binding between TACE and hydroxamic acid derivatives, which have a -lactum ring [1] (Figure 1), using ...
Electron Configuration - Warren County Public Schools
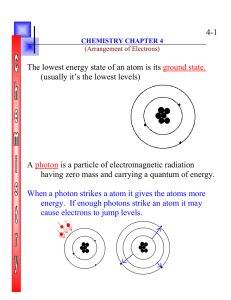
... electromagnetic radiation has a dual wave and particle nature. • Light has wave-like properties but can also be thought of as a stream of particles. • Each particle of light carries a quantum of energy. • He called these particles photons. • A photon is a particle of electromagnetic radiation having ...
... electromagnetic radiation has a dual wave and particle nature. • Light has wave-like properties but can also be thought of as a stream of particles. • Each particle of light carries a quantum of energy. • He called these particles photons. • A photon is a particle of electromagnetic radiation having ...
Electron Configuration and New Atomic Model
... that electromagnetic radiation has a dual wave and particle nature. • Light has wave-like properties but can also be thought of as a stream of particles. • Each particle of light carries a quantum of energy. • He called these particles photons. • A photon is a particle of electromagnetic radiati ...
... that electromagnetic radiation has a dual wave and particle nature. • Light has wave-like properties but can also be thought of as a stream of particles. • Each particle of light carries a quantum of energy. • He called these particles photons. • A photon is a particle of electromagnetic radiati ...
Lecture 9
... = KEMAX = h - h0 (Excess kinetic energy of the electron) (work function to remove the electron from metal) ...
... = KEMAX = h - h0 (Excess kinetic energy of the electron) (work function to remove the electron from metal) ...