Chapter 5
... Orbitals can hold only 2 electrons Each electron in the orbital has an opposite spin ...
... Orbitals can hold only 2 electrons Each electron in the orbital has an opposite spin ...
operators
... f x sin kx •An operator is something that turns functions into functions ...
... f x sin kx •An operator is something that turns functions into functions ...
Electron Configuration
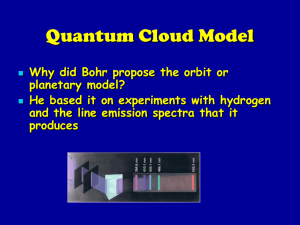
... Max Planck’s Quantum Energy Theory Energy is always absorbed or emitted in “packets” which he called quanta. Bohr’s Model (Planetary) Bohr used the quantum energy theory and proposed that electrons move in particular paths with fixed energy in “orbits” around the ...
... Max Planck’s Quantum Energy Theory Energy is always absorbed or emitted in “packets” which he called quanta. Bohr’s Model (Planetary) Bohr used the quantum energy theory and proposed that electrons move in particular paths with fixed energy in “orbits” around the ...
Unit 4 review sheet
... 40. What is the maximum number of electrons that may occupy one p orbital? 41. Who stated that no two electrons in the same atom could have the same set of four quantum numbers? 42. The Lewis electron dot diagram is used to represent only which electrons in an atom? 43. What is the periodic table us ...
... 40. What is the maximum number of electrons that may occupy one p orbital? 41. Who stated that no two electrons in the same atom could have the same set of four quantum numbers? 42. The Lewis electron dot diagram is used to represent only which electrons in an atom? 43. What is the periodic table us ...
Many-electron wave functions
... It is then possible to “orthonormalize” them. i.e define two linear combinations which are orthonormal. Define: ...
... It is then possible to “orthonormalize” them. i.e define two linear combinations which are orthonormal. Define: ...
Lecture 14 1 Entanglement and Spin
... where C > 0. This is our electron interaction Hamiltonian. You might wonder what C is. C should be a strong function of the relative position, but we don’t want to worry about that now. You can just imagine that C is determined through experiment, but is equal to some value that is yet to be determi ...
... where C > 0. This is our electron interaction Hamiltonian. You might wonder what C is. C should be a strong function of the relative position, but we don’t want to worry about that now. You can just imagine that C is determined through experiment, but is equal to some value that is yet to be determi ...
PhET Tips for Teachers Models of the Hydrogen Atom Written by
... model as a cloud of negative charged filled with little specks of positive charge, rather than the other way around. The word “cloud” suggests that they are mixing up the Plum Pudding model with the Schrodinger model, in which the electrons are often described as a cloud of negative charge. These st ...
... model as a cloud of negative charged filled with little specks of positive charge, rather than the other way around. The word “cloud” suggests that they are mixing up the Plum Pudding model with the Schrodinger model, in which the electrons are often described as a cloud of negative charge. These st ...
4.8-Quantum Mechanics
... Schroedinger’s wave equation, and Born’s interpretation, can equally be applied to “free” particles, or those which are trapped Classically, a particle trapped in a potential well cannot escape…. ….but a trapped quantum particle (eg a particle in an atomic nucleus) can tunnel out of the well, even w ...
... Schroedinger’s wave equation, and Born’s interpretation, can equally be applied to “free” particles, or those which are trapped Classically, a particle trapped in a potential well cannot escape…. ….but a trapped quantum particle (eg a particle in an atomic nucleus) can tunnel out of the well, even w ...
Atomic Structure and Periodic Trends
... Use quantum numbers to describe orbitals. A given orbital can be described by a set of 3 quantum numbers: 1. Principal quantum number (n) 2. Angular momentum quantum number (l) 3. Magnetic quantum number (ml) ...
... Use quantum numbers to describe orbitals. A given orbital can be described by a set of 3 quantum numbers: 1. Principal quantum number (n) 2. Angular momentum quantum number (l) 3. Magnetic quantum number (ml) ...
Final Review
... how to “build-up” the order of occupation of hydrogenic orbitals, that is the atomic electronic configuration for the ground state of a many-electron or ion. Remember the special exceptions and that the s electrons are lost before the d electrons for a metal cation. Why do the s, p, and d orbitals w ...
... how to “build-up” the order of occupation of hydrogenic orbitals, that is the atomic electronic configuration for the ground state of a many-electron or ion. Remember the special exceptions and that the s electrons are lost before the d electrons for a metal cation. Why do the s, p, and d orbitals w ...
chapter 7: atomic structure and periodicity
... Wavelength (λ) - ____________________ between 2 successive crests or troughs Frequency (ν) - the number of _____________ (cycles) per second that pass a certain point. (unit: Speed (c) – speed of light = _______________________________ ...
... Wavelength (λ) - ____________________ between 2 successive crests or troughs Frequency (ν) - the number of _____________ (cycles) per second that pass a certain point. (unit: Speed (c) – speed of light = _______________________________ ...
Kinds of Chemistry - Louisiana State University
... frequency…and one wave pattern gives way to another by a “jump”. ...
... frequency…and one wave pattern gives way to another by a “jump”. ...
Atomic Structure
... To predict how many electrons will be in each energy level and sublevel we need to know the energies of electron orbitals. We will use as a general rule the idea that electrons will fill the lowest energy orbitals available. This is called the Aufbau principle. Due to the increasing closeness of the ...
... To predict how many electrons will be in each energy level and sublevel we need to know the energies of electron orbitals. We will use as a general rule the idea that electrons will fill the lowest energy orbitals available. This is called the Aufbau principle. Due to the increasing closeness of the ...
E k
... also Live in another Space: kx-ky-kz Space or Wavevector Space or Momentum Space Remember: Our EE’s Terminologies like V and I want us to see Semiconductors in this additional space as well. ...
... also Live in another Space: kx-ky-kz Space or Wavevector Space or Momentum Space Remember: Our EE’s Terminologies like V and I want us to see Semiconductors in this additional space as well. ...