Traffic between the plant endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi
... essential residues (i.e. Y717 or K719; [22]) can affect the integrity of the plant TGN or its subdomains, as has been demonstrated in mammalian cells [34,35]. Recent studies have shown that the Golgi apparatus plays a role in transporting some proteins to the chloroplast [36,37], although import rou ...
... essential residues (i.e. Y717 or K719; [22]) can affect the integrity of the plant TGN or its subdomains, as has been demonstrated in mammalian cells [34,35]. Recent studies have shown that the Golgi apparatus plays a role in transporting some proteins to the chloroplast [36,37], although import rou ...
Regulation of the initiation of chromosomal replication in bacteria
... Free-living bacteria A global network relevant to regulating replication is likely to be more intricate in organisms that undergo a complex life cycle or in those that have to adapt to highly fluctuating environmental conditions. Under unfavourable conditions, the growth rate should be reduced and/o ...
... Free-living bacteria A global network relevant to regulating replication is likely to be more intricate in organisms that undergo a complex life cycle or in those that have to adapt to highly fluctuating environmental conditions. Under unfavourable conditions, the growth rate should be reduced and/o ...
Structural Basis for Bivalent Smac-Mimetics Recognition in the IAP
... Monomeric compound 2 and dimeric compound 3 were tested for their in vitro binding to XIAP-BIR3 and -lkBIR2BIR3, using two reported assay formats.34,35 The Ki values (Table 1) show that compound 3 is a better inhibitor for both XIAP-BIR3 and -lkBIR2BIR3 relative to compound 2. The higher affinity of ...
... Monomeric compound 2 and dimeric compound 3 were tested for their in vitro binding to XIAP-BIR3 and -lkBIR2BIR3, using two reported assay formats.34,35 The Ki values (Table 1) show that compound 3 is a better inhibitor for both XIAP-BIR3 and -lkBIR2BIR3 relative to compound 2. The higher affinity of ...
INTEINS: Structure, Function, and Evolution
... Among other data it lists the inteins’ sequences, conserved motifs, host organisms, and host proteins. More than 130 inteins are known in 34 different types of proteins (68, 76, 77). The inteins are between 134 and 608 amino acids long, and they are found in members of all three domains of life: Euk ...
... Among other data it lists the inteins’ sequences, conserved motifs, host organisms, and host proteins. More than 130 inteins are known in 34 different types of proteins (68, 76, 77). The inteins are between 134 and 608 amino acids long, and they are found in members of all three domains of life: Euk ...
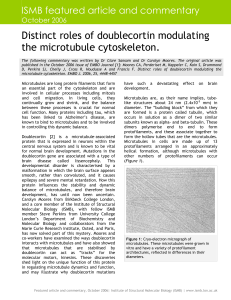
Distinct roles of doublecortin modulating the microtubule cytoskeleton.
... that the doublecortin might protrude from the grooves between protofilaments and that it might therefore impede kinesin movement along the microtubules. Moores and co-workers therefore examined kinesin motion along doublecortinstabilised tracks and found, surprisingly, that doublecortin binding did ...
... that the doublecortin might protrude from the grooves between protofilaments and that it might therefore impede kinesin movement along the microtubules. Moores and co-workers therefore examined kinesin motion along doublecortinstabilised tracks and found, surprisingly, that doublecortin binding did ...
Signal Peptidases
... process nonlipoprotein substrates that are exported by the SecYEG pathway or the twin arginine translocation (Tat) pathway. Lipoproteins that are exported by the Sec pathway are cleaved by SPase II. SPase IV cleaves type IV prepilins and prepilin-like proteins that are components of the type II secr ...
... process nonlipoprotein substrates that are exported by the SecYEG pathway or the twin arginine translocation (Tat) pathway. Lipoproteins that are exported by the Sec pathway are cleaved by SPase II. SPase IV cleaves type IV prepilins and prepilin-like proteins that are components of the type II secr ...
6.3. La supervivencia de las motoneuronas espinales de pollo mantenidas
... The members of the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) family of neurotrophic factors (GDNF, neurturin, persephin, and artemin) are able to promote in vivo and in vitro survival of different neuronal populations, including spinal cord motoneurons. These factors signal via multicompone ...
... The members of the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) family of neurotrophic factors (GDNF, neurturin, persephin, and artemin) are able to promote in vivo and in vitro survival of different neuronal populations, including spinal cord motoneurons. These factors signal via multicompone ...
Type III secretion: The bacteria-eukaryotic cell
... L.J. Mota et al. / FEMS Microbiology Letters 252 (2005) 1–10 ...
... L.J. Mota et al. / FEMS Microbiology Letters 252 (2005) 1–10 ...
Serine/Threonine Kinase 3-Phosphoinositide
... protein kinase and protein kinase C), and control a plethora of cellular processes, downstream either to PI3K or to other pathways, such as RAS GTPase-MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase). Interestingly, PDK1 has been demonstrated to be crucial for the regulation of each step of cell migration, b ...
... protein kinase and protein kinase C), and control a plethora of cellular processes, downstream either to PI3K or to other pathways, such as RAS GTPase-MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase). Interestingly, PDK1 has been demonstrated to be crucial for the regulation of each step of cell migration, b ...
Ornithodoros savignyi CHAPTER 2 SIGNALING PATHWAYS REGULATING PROTEIN SECRETION FROM
... SDS-PAGE analysis of the secreted proteins showed variable results in response to different agonists. The highest number of proteins was detected from ticks in the earliest stages of feeding. In some ticks, proteins were identified at one collection time but not at another time in secretions from th ...
... SDS-PAGE analysis of the secreted proteins showed variable results in response to different agonists. The highest number of proteins was detected from ticks in the earliest stages of feeding. In some ticks, proteins were identified at one collection time but not at another time in secretions from th ...
With No Lysine (WNK) Family Proteins and Their
... in β strand 3 conserved in all other functional kinase domains, the WNKs contain a cysteine. An alternate lysine in β strand 2 functions in its place. The four mammalian genes of the WNK family code for long proteins, 1200 to 2400 amino acids in length. However, outside of the kinase domain, there a ...
... in β strand 3 conserved in all other functional kinase domains, the WNKs contain a cysteine. An alternate lysine in β strand 2 functions in its place. The four mammalian genes of the WNK family code for long proteins, 1200 to 2400 amino acids in length. However, outside of the kinase domain, there a ...
Ammonium utilization in Bacillus subtilis: transport and regulatory
... Bacillus subtilis uses glutamine as the best source of nitrogen. In the absence of glutamine, alternative nitrogen sources such as ammonium can be used. Ammonium utilization involves the uptake of the gas or the ammonium ion, the synthesis of glutamine by the glutamine synthetase and the recycling o ...
... Bacillus subtilis uses glutamine as the best source of nitrogen. In the absence of glutamine, alternative nitrogen sources such as ammonium can be used. Ammonium utilization involves the uptake of the gas or the ammonium ion, the synthesis of glutamine by the glutamine synthetase and the recycling o ...
Functional analysis of a novel baculovirus envelope fusion protein
... To improve the exploitation of baculoviruses as bioinsecticides, eukaryotic expression vector or as gene delivery system for gene therapy, in-depth studies of their infection cycle and in virus-host cell interaction are required. Baculoviruses are excellent models to study the biology of large envel ...
... To improve the exploitation of baculoviruses as bioinsecticides, eukaryotic expression vector or as gene delivery system for gene therapy, in-depth studies of their infection cycle and in virus-host cell interaction are required. Baculoviruses are excellent models to study the biology of large envel ...
Cell-to-cell communication and virulence in Vibrio anguillarum
... Vibrios in the environment Vibrios belong to the Gammaproteobacteria and are gram-negative rod shaped bacteria found in marine environments such as marine coastal waters, estuaries, sediments, and aquaculture facilities. The Vibrio genus consists of more than 50 species that may be associated with m ...
... Vibrios in the environment Vibrios belong to the Gammaproteobacteria and are gram-negative rod shaped bacteria found in marine environments such as marine coastal waters, estuaries, sediments, and aquaculture facilities. The Vibrio genus consists of more than 50 species that may be associated with m ...
Evidence That Ternary Complex (eIF2-GTP-tRNAi
... cells, the untranslated mRNAs that accumulate in heatstressed cells are concentrated at discrete cytoplasmic foci known as heat-shock granules (Nover et al., 1989). In mammalian cells, poly(A)⫹ RNA accumulates at similar cytoplasmic foci in response to environmental stress (Kedersha et al., 1999). I ...
... cells, the untranslated mRNAs that accumulate in heatstressed cells are concentrated at discrete cytoplasmic foci known as heat-shock granules (Nover et al., 1989). In mammalian cells, poly(A)⫹ RNA accumulates at similar cytoplasmic foci in response to environmental stress (Kedersha et al., 1999). I ...
Interaction of the endothelial nitric oxide synthase with the CAT
... relaxation and release of NO [12–15]. This circumstance, in which exogenous arginine drives endothelial NO production even though intracellular levels of arginine are in excess, has been termed the arginine paradox. McDonald et al. [5] have suggested that this paradox may be explained by the existen ...
... relaxation and release of NO [12–15]. This circumstance, in which exogenous arginine drives endothelial NO production even though intracellular levels of arginine are in excess, has been termed the arginine paradox. McDonald et al. [5] have suggested that this paradox may be explained by the existen ...
Antibiotic use and abuse: A threat to mitochondria and chloroplasts
... Recently, several studies have demonstrated that tetracyclines, the antibiotics most intensively used in livestock and that are also widely applied in biomedical research, interrupt mitochondrial proteostasis and physiology in animals ranging from round worms, fruit flies, and mice to human cell lin ...
... Recently, several studies have demonstrated that tetracyclines, the antibiotics most intensively used in livestock and that are also widely applied in biomedical research, interrupt mitochondrial proteostasis and physiology in animals ranging from round worms, fruit flies, and mice to human cell lin ...
Cell-Free Synthesis for Analyzing the Membrane
... Expressing a protein in a cell-free system appears attractive since protein biosynthesis can be studied independently of the complex mechanisms occurring in a complete cell. In addition, the system is readily accessible to scientific manipulations. Other advantages of this method include speed, rela ...
... Expressing a protein in a cell-free system appears attractive since protein biosynthesis can be studied independently of the complex mechanisms occurring in a complete cell. In addition, the system is readily accessible to scientific manipulations. Other advantages of this method include speed, rela ...
Dynamics of the Cell Cycle: Checkpoints, Sizers, and Timers
... A (CycA), cyclin B (CycB), and cyclin E (CycE), and the major cyclindependent kinases (CDKs) are CDK1 and CDK2. Increased CycE:CDK2 activity marks the G1/S transition, whereas increased CycB:CDK1 activity marks the G2/M transition. Although their functions are different, the signaling networks regul ...
... A (CycA), cyclin B (CycB), and cyclin E (CycE), and the major cyclindependent kinases (CDKs) are CDK1 and CDK2. Increased CycE:CDK2 activity marks the G1/S transition, whereas increased CycB:CDK1 activity marks the G2/M transition. Although their functions are different, the signaling networks regul ...
Biogenesis of proteins of the mitochondrial intermembrane space
... 1.1. Origin, structure and function of mitochondria Mitochondria are ubiquitous organelles of eukaryotic cells that are involved in many cellular processes from energy production to apoptosis. This is quite astonishing, considering that mitochondria are believed to have evolved from a bacterial endo ...
... 1.1. Origin, structure and function of mitochondria Mitochondria are ubiquitous organelles of eukaryotic cells that are involved in many cellular processes from energy production to apoptosis. This is quite astonishing, considering that mitochondria are believed to have evolved from a bacterial endo ...
Study of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide (NO) as
... Nitric oxide (NO) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) are constitutively synthesized in skeletal muscle, and they are produced in large quantities during active inflammatory processes such as in sepsis. These molecules modulate skeletal muscle contractility in both normal and septic muscles. Modificat ...
... Nitric oxide (NO) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) are constitutively synthesized in skeletal muscle, and they are produced in large quantities during active inflammatory processes such as in sepsis. These molecules modulate skeletal muscle contractility in both normal and septic muscles. Modificat ...
Site-selective incorporation and ligation of
... when using this method however as other amino acids can be oxidised under certain conditions (cysteine and methionine residues in particular).23 Therefore, the reaction is usually performed with or quenched by another component such as excess methionine or ethylene glycol, followed by purification o ...
... when using this method however as other amino acids can be oxidised under certain conditions (cysteine and methionine residues in particular).23 Therefore, the reaction is usually performed with or quenched by another component such as excess methionine or ethylene glycol, followed by purification o ...
Isolation and Characterization of a Novel Ribosome
... pokeweed containing PAP-H and other defenserelated proteins showed strong antifungal activity against fungi causing root rot. We have previously reported that in vitro root secretions of secondary metabolites and proteins compare with root secretions under natural settings (Flores et al., 1999), sug ...
... pokeweed containing PAP-H and other defenserelated proteins showed strong antifungal activity against fungi causing root rot. We have previously reported that in vitro root secretions of secondary metabolites and proteins compare with root secretions under natural settings (Flores et al., 1999), sug ...
iii. acidic and basic properties of amino acids
... • However, when histidine is incorporated into a protein, its R group can be either positively charged (protonated) or neutral, depending on the ionic environment provided by the protein. • This is an important property of histidine that contributes to the buffering role it plays in the functioning ...
... • However, when histidine is incorporated into a protein, its R group can be either positively charged (protonated) or neutral, depending on the ionic environment provided by the protein. • This is an important property of histidine that contributes to the buffering role it plays in the functioning ...
Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson`s disease
... The direct linkage of mitochondrial dysfunction with PD came from the discovery of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,5, 6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP), a neurotoxin that induces PD symptoms in drug-abused patients in 1983 [18]. Soon, the neurotoxicity of MPTP was confirmed in primate and rodent models [19–21]. Lat ...
... The direct linkage of mitochondrial dysfunction with PD came from the discovery of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,5, 6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP), a neurotoxin that induces PD symptoms in drug-abused patients in 1983 [18]. Soon, the neurotoxicity of MPTP was confirmed in primate and rodent models [19–21]. Lat ...
Protein phosphorylation

Protein phosphorylation is a post-translational modification of proteins in which an amino acid residue is phosphorylated by a protein kinase by the addition of a covalently bound phosphate group. Phosphorylation alters the structural conformation of a protein, causing it to become activated, deactivated, or modifying its function. The reverse reaction of phosphorylation is called dephosphorylation, and is catalyzed by protein phosphatases. Protein kinases and phosphatases work independently and in a balance to regulate the function of proteins. The amino acids most commonly phosphorylated are serine, threonine, and tyrosine in eukaryotes, and histidine in prokaryotes, which play important and well-characterized roles in signaling pathways and metabolism. However, many other amino acids can also be phosphorylated, including arginine, lysine, and cysteine. Protein phosphorylation was first reported in 1906 by Phoebus Levene at the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research with the discovery of phosphorylated vitellin. However, it was nearly 50 years until the enzymatic phosphorylation of proteins by protein kinases was discovered.