Chap. 12 P.P - Moline High School
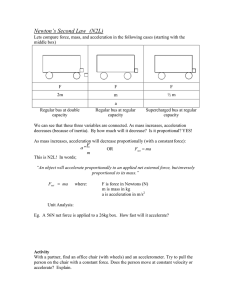
... Newton’s second law could also be written as: - When a force is applied to an object, the object accelerates in the direction of the greater force. ...
... Newton’s second law could also be written as: - When a force is applied to an object, the object accelerates in the direction of the greater force. ...
Chapter Eight
... • Previously, we developed the first principles of linear dynamics; now we adapt the principles of linear dynamics to rotating bodies. • Newton's laws, momentum, energy, and power all have equations equivalent to their linear counterparts. ...
... • Previously, we developed the first principles of linear dynamics; now we adapt the principles of linear dynamics to rotating bodies. • Newton's laws, momentum, energy, and power all have equations equivalent to their linear counterparts. ...
Bell Work 2/23/10
... Newton’s First Law of Motion An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion remains in motion at a constant speed and in a straight line unless acted on by an unbalanced force. ...
... Newton’s First Law of Motion An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion remains in motion at a constant speed and in a straight line unless acted on by an unbalanced force. ...
1st law lab
... Sir Isaac Newton is a British scientist who was able to describe the effects of forces on the motion of objects. The rules are known as Newton’s laws of motion. These rules apply to all objects that you encounter every day. His first law states that an object moving at a constant velocity keeps movi ...
... Sir Isaac Newton is a British scientist who was able to describe the effects of forces on the motion of objects. The rules are known as Newton’s laws of motion. These rules apply to all objects that you encounter every day. His first law states that an object moving at a constant velocity keeps movi ...
FORCES AND MOTIONS TEST REVIEW FORCE BALANCED
... WHAT IS THE BOATS AVERAGE SPEED IN Km/h? 10 K/H 12. AN OBJECT AT REST RECEIVES A 65N FORCE TO THE LEFT AND A 75N FORCE TO THE RIGHT, WHAT IS THE NET FORCE? And, WHAT IS THE DIRECTION OF THE MOTION? 10 Newtons to the RIGHT 13. WHAT IS THE SPEED OF A TRAIN THAT TRAVELS 125 MILES IN 2 HOURS? USE THE FO ...
... WHAT IS THE BOATS AVERAGE SPEED IN Km/h? 10 K/H 12. AN OBJECT AT REST RECEIVES A 65N FORCE TO THE LEFT AND A 75N FORCE TO THE RIGHT, WHAT IS THE NET FORCE? And, WHAT IS THE DIRECTION OF THE MOTION? 10 Newtons to the RIGHT 13. WHAT IS THE SPEED OF A TRAIN THAT TRAVELS 125 MILES IN 2 HOURS? USE THE FO ...
I. Newton's Laws of Motion - x10Hosting
... I. Newton’s Laws of Motion “If I have seen far, it is because I have stood on the shoulders of giants.” - Sir Isaac Newton (referring to Galileo) ...
... I. Newton’s Laws of Motion “If I have seen far, it is because I have stood on the shoulders of giants.” - Sir Isaac Newton (referring to Galileo) ...
Newton`s Law of Motion.
... What is inertia? Inertia is the idea that an object keeps moving unless acted upon by an outside force. Much of the initial work written about inertia was done by Isaac Newton in the 17th century and became known as his first law of motion. It is one of the basic principles of physics and has a numb ...
... What is inertia? Inertia is the idea that an object keeps moving unless acted upon by an outside force. Much of the initial work written about inertia was done by Isaac Newton in the 17th century and became known as his first law of motion. It is one of the basic principles of physics and has a numb ...
Chapter 4 Motion
... look in the chapter if you need help. speed p. 146 velocity p. 146 acceleration p. 148 inertia p. 155 1. The speed and direction of a moving object is its ____. 2. The distance an object travels in a certain amount of time is its ____. 3. The rate of change of velocity over time is ____. 4. The tend ...
... look in the chapter if you need help. speed p. 146 velocity p. 146 acceleration p. 148 inertia p. 155 1. The speed and direction of a moving object is its ____. 2. The distance an object travels in a certain amount of time is its ____. 3. The rate of change of velocity over time is ____. 4. The tend ...
Newton's Laws
... • Inertia property of matter that resists changes in its motion. • Basically, because of inertia, objects want to maintain whatever motion they have. This was described initially by Galileo, later Sir Isaac Newton formulated it into one of his basic laws of motion. • Inertia is proportional to mas ...
... • Inertia property of matter that resists changes in its motion. • Basically, because of inertia, objects want to maintain whatever motion they have. This was described initially by Galileo, later Sir Isaac Newton formulated it into one of his basic laws of motion. • Inertia is proportional to mas ...
gravity and motion - carswellsciencetms
... Gravity is a force that attracts all objects toward each other(law of universal gravitation) The strength of the force of gravity between two objects depends on: The masses of the objects The distance between the objects ...
... Gravity is a force that attracts all objects toward each other(law of universal gravitation) The strength of the force of gravity between two objects depends on: The masses of the objects The distance between the objects ...
Forces and the Laws of Motion Section 3
... •Objects at rest stay at rest and objects in motion stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. (also called the law of inertia). ...
... •Objects at rest stay at rest and objects in motion stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. (also called the law of inertia). ...