19.2 Gravity and the Moon
... r is the distance between the (centers) of the bodies G is a proportionality constant that depends on units ...
... r is the distance between the (centers) of the bodies G is a proportionality constant that depends on units ...
Forces and Motion Commotion 2012
... Part C: Newton’s 3 Laws of Motion 11. Define, give, recognize, and understand examples of both balanced and unbalanced forces. 12. Define, give, recognize, and understand examples of Newton’s First Law of Motion. 13. Define, give, recognize, and understand examples of Newton’s Second Law of Motion. ...
... Part C: Newton’s 3 Laws of Motion 11. Define, give, recognize, and understand examples of both balanced and unbalanced forces. 12. Define, give, recognize, and understand examples of Newton’s First Law of Motion. 13. Define, give, recognize, and understand examples of Newton’s Second Law of Motion. ...
Free Response and calculations
... Think about the relationship between the amount of gas you have in your car and how far you can travel. Make a graph showing this relationship. Which is the dependent variable and which is the independent variable? ...
... Think about the relationship between the amount of gas you have in your car and how far you can travel. Make a graph showing this relationship. Which is the dependent variable and which is the independent variable? ...
Newton`s Laws - Uplands blogs
... Newton’s 2nd Law proves that different masses accelerate to the earth at the same rate, but with ...
... Newton’s 2nd Law proves that different masses accelerate to the earth at the same rate, but with ...
Magic Square Vocabulary Game Combinations
... 1. Forces always act in equal but opposite pairs 2. A push or a pull 3. Distance traveled divided by the time needed to travel the distance. 4. An object will remain at rest or move in a straight line with constant speed Unless acted upon by a force. 5. The change in velocity divided by the time nee ...
... 1. Forces always act in equal but opposite pairs 2. A push or a pull 3. Distance traveled divided by the time needed to travel the distance. 4. An object will remain at rest or move in a straight line with constant speed Unless acted upon by a force. 5. The change in velocity divided by the time nee ...
Study Guide - Motion Name Key Date Pd 1. An object is in ___
... 20. If you are in a spacecraft that has been launched into space, your weight would (increase, decrease) because gravitational force is (increasing, decreasing). 21. Newton’s third law states that the forces two objects exert on each other are always ___equal ______________ but in ___opposite_______ ...
... 20. If you are in a spacecraft that has been launched into space, your weight would (increase, decrease) because gravitational force is (increasing, decreasing). 21. Newton’s third law states that the forces two objects exert on each other are always ___equal ______________ but in ___opposite_______ ...
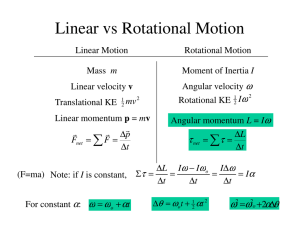
Linear vs Rotational Motion ∑ ω
... In a light wind, a windmill experiences a constant torque of 255 N m. If the windmill is initially at rest, what is its angular momentum after 2.00 s? ...
... In a light wind, a windmill experiences a constant torque of 255 N m. If the windmill is initially at rest, what is its angular momentum after 2.00 s? ...
Forces and Motion Learning Outcomes
... 6. Balanced forces are equal forces that act in opposite directions on an object and cancel one another out 7. Unbalanced forces are forces that don’t cancel one another out Newton’s Laws of Motion 8. 1st Inertia This law states that … An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an unba ...
... 6. Balanced forces are equal forces that act in opposite directions on an object and cancel one another out 7. Unbalanced forces are forces that don’t cancel one another out Newton’s Laws of Motion 8. 1st Inertia This law states that … An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an unba ...
Document
... What is the relationship between time, g, and the distance fallen by a freelyfalling object? ...
... What is the relationship between time, g, and the distance fallen by a freelyfalling object? ...
Newton`s 2nd Law
... Second Law of Motion: “The Law of Acceleration” The acceleration produced by a net force on an object is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, is in the same direction as the net force, and is inversely proportional to the mass of the object ...
... Second Law of Motion: “The Law of Acceleration” The acceleration produced by a net force on an object is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, is in the same direction as the net force, and is inversely proportional to the mass of the object ...
Air Pressure, Forces, and Motion
... of uniform motion in a straight line, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces impressed upon it. acceleration = 0.0 unless the objected is acted on by an unbalanced force ...
... of uniform motion in a straight line, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces impressed upon it. acceleration = 0.0 unless the objected is acted on by an unbalanced force ...