Forces - Wsfcs
... • Force that attracts all objects toward each other • More mass = more gravity • Acceleration because of gravity is 9.8 m/s/s • All objects accelerate at the same rate ...
... • Force that attracts all objects toward each other • More mass = more gravity • Acceleration because of gravity is 9.8 m/s/s • All objects accelerate at the same rate ...
Nuclear Forces
... • Newton's second law of motion can be formally stated as follows: • The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. In terms of an equat ...
... • Newton's second law of motion can be formally stated as follows: • The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. In terms of an equat ...
PHYS1111
... Radius R and moment of inertia I starting from rest. This should look familiar to lab. m, R and acceleration are all measured (knowns). Here the string is wrapped around the outside of the disk at radius R. Write out the equations for i) Net force on the mass m, and for ii) net torque on the disk. ( ...
... Radius R and moment of inertia I starting from rest. This should look familiar to lab. m, R and acceleration are all measured (knowns). Here the string is wrapped around the outside of the disk at radius R. Write out the equations for i) Net force on the mass m, and for ii) net torque on the disk. ( ...
8th PS 9-Weeks 3 Exam
... In the absence of air, a penny and a feather that are dropped from the same height at the same time will ____. a. fall at different rates c. float b. fall at the same rate d. not have momentum The upward force on an object falling through the air is ____. a. air resistance c. momentum b. inertia d. ...
... In the absence of air, a penny and a feather that are dropped from the same height at the same time will ____. a. fall at different rates c. float b. fall at the same rate d. not have momentum The upward force on an object falling through the air is ____. a. air resistance c. momentum b. inertia d. ...
Ch-4-Lecture
... light. Need to use the theory of relativity. • Not valid for atomic sized particles. Need to use quantum mechanics. ...
... light. Need to use the theory of relativity. • Not valid for atomic sized particles. Need to use quantum mechanics. ...
• Introduction
... same speed and in the same direction unless acted on by any kind of force. Newton's second law of motion (fundamental equation of dynamics): the acceleration a of an object is directly dependent upon the net force F acting on the body: F = ma Newton's third law of motion (principle of action and rea ...
... same speed and in the same direction unless acted on by any kind of force. Newton's second law of motion (fundamental equation of dynamics): the acceleration a of an object is directly dependent upon the net force F acting on the body: F = ma Newton's third law of motion (principle of action and rea ...
DYNAMICS
... • He was born on Christmas day, the year Galileo died. • His work influenced today’s world at a monumental level. • He developed three laws that describe the motion of everything. • He very well may have been one of the most influential human beings to ever live. • And you thought he was just some d ...
... • He was born on Christmas day, the year Galileo died. • His work influenced today’s world at a monumental level. • He developed three laws that describe the motion of everything. • He very well may have been one of the most influential human beings to ever live. • And you thought he was just some d ...
Stability and Newton`s Laws
... • This means an object will move at the same rate or continue to not moved unless something else “makes” it What is an example of this? ...
... • This means an object will move at the same rate or continue to not moved unless something else “makes” it What is an example of this? ...
Physical Science: Test Force
... 1. What is the name of the friction that exists between two stationary objects? A. Elastic B. Kinetic C. Sliding D. Inelastic E. Static 2. What is the unbalanced force that slows down a ball rolling across the floor? A. the force of gravity C. the force of inertia B. the force of momentum D. the for ...
... 1. What is the name of the friction that exists between two stationary objects? A. Elastic B. Kinetic C. Sliding D. Inelastic E. Static 2. What is the unbalanced force that slows down a ball rolling across the floor? A. the force of gravity C. the force of inertia B. the force of momentum D. the for ...
Chp+12+Quest REVISED 2012
... 11. Complete the statement; If the mass stays the same, and the force INCREASES then +/acceleration will _____________. So in order to change the motion of a massive object, a ___________ force is needed. 12. Complete the state; If the force stays the same, and the mass INCREASES then acceleration w ...
... 11. Complete the statement; If the mass stays the same, and the force INCREASES then +/acceleration will _____________. So in order to change the motion of a massive object, a ___________ force is needed. 12. Complete the state; If the force stays the same, and the mass INCREASES then acceleration w ...
Section 12.2 Newton’s First and Second Laws of Motion
... 1. Italian scientist who did experiments that helped correct misconceptions about force and motion 2. Scientist who studied in England and introduced several laws describing force and motion 3. An ancient Greek philosopher who made many scientific discoveries through observation and logical reasonin ...
... 1. Italian scientist who did experiments that helped correct misconceptions about force and motion 2. Scientist who studied in England and introduced several laws describing force and motion 3. An ancient Greek philosopher who made many scientific discoveries through observation and logical reasonin ...
Newton`s First Law of Motion
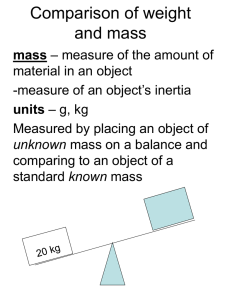
... mass—which is roughly the amount of material present in the object Mass is NOT volume, the measure of space that an object takes up Mass is NOT weight, the force of gravity on an object Mass is a measure of the inertia that an object exhibits in response to any effort made to start it, stop it ...
... mass—which is roughly the amount of material present in the object Mass is NOT volume, the measure of space that an object takes up Mass is NOT weight, the force of gravity on an object Mass is a measure of the inertia that an object exhibits in response to any effort made to start it, stop it ...
24 Slides
... motion will stay in motion and objects at rest will stay at rest…unless a force acts on them. The ball will stay at rest (not move) unless the dog moves it. ...
... motion will stay in motion and objects at rest will stay at rest…unless a force acts on them. The ball will stay at rest (not move) unless the dog moves it. ...
M - Otterbein University
... • Use: distance = velocity x travel time, where the velocity is the speed of light • Remember that the radar signal travels to Venus and back! ...
... • Use: distance = velocity x travel time, where the velocity is the speed of light • Remember that the radar signal travels to Venus and back! ...
I. Newton's Laws of Motion
... I. Newton’s Laws of Motion “If I have seen far, it is because I have stood on the shoulders of giants.” ...
... I. Newton’s Laws of Motion “If I have seen far, it is because I have stood on the shoulders of giants.” ...