Newton`s Second Law I
... The condition of zero acceleration is called equilibrium. In equilibrium, all forces cancel out leaving zero net force. Objects that are standing still are in equilibrium because their acceleration is zero. Objects that are moving at constant speed and direction are also in equilibrium. A static pro ...
... The condition of zero acceleration is called equilibrium. In equilibrium, all forces cancel out leaving zero net force. Objects that are standing still are in equilibrium because their acceleration is zero. Objects that are moving at constant speed and direction are also in equilibrium. A static pro ...
Newton`s second law of motion
... Newton’s first law of motion: Q: State Newton’s first law of motion. Newton’ first law states that every body continuous to be in a state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line unless an external force acts upon it. Q : Define Inertia. Inertia is the tendency of undisturbed objects to stay ...
... Newton’s first law of motion: Q: State Newton’s first law of motion. Newton’ first law states that every body continuous to be in a state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line unless an external force acts upon it. Q : Define Inertia. Inertia is the tendency of undisturbed objects to stay ...
Effective Force & Newton`s Laws
... Momentum = mass (kg) x velocity (m/s) An object can only have momentum if it is ...
... Momentum = mass (kg) x velocity (m/s) An object can only have momentum if it is ...
Newton`s 3 Laws
... Universal Law of Gravitation explains how the planets stay in orbit around the sun. Demo—Penny on Card What forces keep the coin at rest on the note card? o Friction? o Gravity? o Both? Why didn’t the coin fly away with the card? o Did the coin’s own “stubbornness” prevent it from doing so? o ...
... Universal Law of Gravitation explains how the planets stay in orbit around the sun. Demo—Penny on Card What forces keep the coin at rest on the note card? o Friction? o Gravity? o Both? Why didn’t the coin fly away with the card? o Did the coin’s own “stubbornness” prevent it from doing so? o ...
Jeopardy - Fair Lawn Schools
... The total momentum in a system cannot change as long as all the forces act only between the objects in the system. ...
... The total momentum in a system cannot change as long as all the forces act only between the objects in the system. ...
laws of motion
... Dropped big and small rock Fell at same rate If no interference – motion will go on forever ...
... Dropped big and small rock Fell at same rate If no interference – motion will go on forever ...
The Aristotelian approach
... if any of these were out of its hierarchical position, it’s natural motion would be to return. speed determined by: weight/resistance if in hierarchical position: tendency not to move! ...
... if any of these were out of its hierarchical position, it’s natural motion would be to return. speed determined by: weight/resistance if in hierarchical position: tendency not to move! ...
Chapter 3 Review
... ____________________ 1. Newton’s Second Law shows the relationship between force, mass, and __________________. _____________________ 2. _______________ is the force that opposes motion. _____________________ 3. _____________ friction is experienced when a box is pushed across a floor. _____________ ...
... ____________________ 1. Newton’s Second Law shows the relationship between force, mass, and __________________. _____________________ 2. _______________ is the force that opposes motion. _____________________ 3. _____________ friction is experienced when a box is pushed across a floor. _____________ ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... • The orbit will increase its altitude, becoming elliptical. • When a speed of around 18 mps is reached, the cannonball escapes. Newton’s Cannon Animation ...
... • The orbit will increase its altitude, becoming elliptical. • When a speed of around 18 mps is reached, the cannonball escapes. Newton’s Cannon Animation ...
Newton Review
... Use Chapters 1 & 2 in your book to help you find the answers to the questions below. 1. Write Newton’s first law. Law of Inertia: objects remain in motion, or at rest, until a force acts upon them. 2. Give an example of Newton’s first law using a rocket in your example. A rocket lifts off until grav ...
... Use Chapters 1 & 2 in your book to help you find the answers to the questions below. 1. Write Newton’s first law. Law of Inertia: objects remain in motion, or at rest, until a force acts upon them. 2. Give an example of Newton’s first law using a rocket in your example. A rocket lifts off until grav ...
File newtons 1st and 2nd law 2015
... – Tendency of an object to resist a change in motion – Inertia means that the object’s motion will stay constant in terms of speed and direction – Depends on the mass of an object – Does NOT depend of the presence of gravity • An object’s inertia is the same on Earth and in space ...
... – Tendency of an object to resist a change in motion – Inertia means that the object’s motion will stay constant in terms of speed and direction – Depends on the mass of an object – Does NOT depend of the presence of gravity • An object’s inertia is the same on Earth and in space ...
Physics 117
... At the University of Pisa, Galileo learned the physics of the Ancient Greek scientist, Aristotle. However, Galileo questioned the Aristotelian approach to physics. Galileo eventually disproved this idea by asserting that all objects, regardless of their density, fall at the same rate in a vacuum ...
... At the University of Pisa, Galileo learned the physics of the Ancient Greek scientist, Aristotle. However, Galileo questioned the Aristotelian approach to physics. Galileo eventually disproved this idea by asserting that all objects, regardless of their density, fall at the same rate in a vacuum ...
Newton`s Three Laws of Motion
... • A force is what we call a push or a pull, or any action that has the ability to change motion of an object. • The metric unit used to describe force is called the Newton (N). One Newton is equal to: 1 Kg x 1 m/s/s Thus, one Newton of force causes a one kilogram object to accelerate at a rate of on ...
... • A force is what we call a push or a pull, or any action that has the ability to change motion of an object. • The metric unit used to describe force is called the Newton (N). One Newton is equal to: 1 Kg x 1 m/s/s Thus, one Newton of force causes a one kilogram object to accelerate at a rate of on ...
Newtons 1st Law notes
... Balanced Forces Net Force—when 2 or more forces act on an object at the same time The object does not move if the forces cancel each other out. Balanced Forces—forces on an object that are equal in size and opposite in direction. ...
... Balanced Forces Net Force—when 2 or more forces act on an object at the same time The object does not move if the forces cancel each other out. Balanced Forces—forces on an object that are equal in size and opposite in direction. ...
SCIENCE NOTES – FORCE AND MOTION
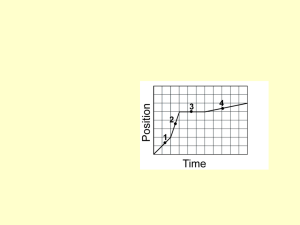
... - Newton’s First Law of Motion – Objects at rest remain at rest and objects traveling at a steady rate in a straight line continue that way until a force acts on them. Where is it? - You are moving if you are changing position. Position is the location of an object. ...
... - Newton’s First Law of Motion – Objects at rest remain at rest and objects traveling at a steady rate in a straight line continue that way until a force acts on them. Where is it? - You are moving if you are changing position. Position is the location of an object. ...
HOMEWORK – DUE FRIDAY, NOVEMBER 22ND NEWTON`S
... __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ ...
... __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ ...