Name: Notes - 4.3 Newton`s Second Law of Motion: Concept of a
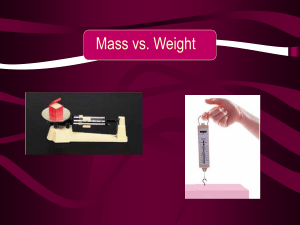
... 10. What is the difference between mass and weight? 11. Bathroom Scales A. What do bathroom scales measure? Mass or Weight? B. Would the bathroom scale reading change if you were on the Moon? How? 12. Suppose that the net external force (push minus friction) exerted on a lawn mower is 51 N (about 11 ...
... 10. What is the difference between mass and weight? 11. Bathroom Scales A. What do bathroom scales measure? Mass or Weight? B. Would the bathroom scale reading change if you were on the Moon? How? 12. Suppose that the net external force (push minus friction) exerted on a lawn mower is 51 N (about 11 ...
Chapter 2 - Forces In Motion
... All forces act in pairs called action-reaction force pairs If a force is exerted, another force occurs that is equal in size and opposite in direction to the first. ...
... All forces act in pairs called action-reaction force pairs If a force is exerted, another force occurs that is equal in size and opposite in direction to the first. ...
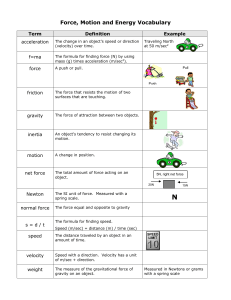
Forces Vocab
... 16. For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This is _____________________________________ ______________________________________. These action-reaction forces are acting on different objects. How does this law apply to a person wearing roller skates pushing off of a wall? 17. ____ ...
... 16. For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This is _____________________________________ ______________________________________. These action-reaction forces are acting on different objects. How does this law apply to a person wearing roller skates pushing off of a wall? 17. ____ ...
Name
... 35. Matt with a mass of 125 kg is running at a velocity of 10 m/s. What is his momentum? a. 1250 kg b. 125 kg/m/s c. 1250 m/s/s d. 1250 kg/m/s 36. The force of an object, with a certain mass is accelerating at a certain rate. The rate can be determined using the equation (Force = Mass X Acceleration ...
... 35. Matt with a mass of 125 kg is running at a velocity of 10 m/s. What is his momentum? a. 1250 kg b. 125 kg/m/s c. 1250 m/s/s d. 1250 kg/m/s 36. The force of an object, with a certain mass is accelerating at a certain rate. The rate can be determined using the equation (Force = Mass X Acceleration ...
Jeopardy - QuestGarden.com
... A body with greater mass has a lesser/greater tendency to continue in uniform straight line motion ...
... A body with greater mass has a lesser/greater tendency to continue in uniform straight line motion ...
Name: Date: ______ Period: ____
... 5. What is air resistance? 6. Why does air resistance affect some objects more than others? 7. What is terminal velocity? 8. What is free fall? 9. When does free fall take place? 10. How are orbiting objects in free fall? 11. What 2 motions combine to cause orbiting? 12. How does gravity play a role ...
... 5. What is air resistance? 6. Why does air resistance affect some objects more than others? 7. What is terminal velocity? 8. What is free fall? 9. When does free fall take place? 10. How are orbiting objects in free fall? 11. What 2 motions combine to cause orbiting? 12. How does gravity play a role ...
Document
... Newton’s Laws of Motion • Law of Inertia: A body continues in state of rest or motion unless acted on by an external force; Mass is a measure of inertia • Law of Acceleration: For a given mass m, the acceleration is proportional to the force applied F=ma • Law of Action equals Reaction: For every a ...
... Newton’s Laws of Motion • Law of Inertia: A body continues in state of rest or motion unless acted on by an external force; Mass is a measure of inertia • Law of Acceleration: For a given mass m, the acceleration is proportional to the force applied F=ma • Law of Action equals Reaction: For every a ...
Newton`s Law of Universal Gravitation Newton`s Law of Universal
... • m1 is the mass of one object, in kg • m2 is the mass of the other object, in kg • Δd is the distance between the centers of the objects, in m • G is the universal gravitational constant, 6.67x 10-11 Nm2/kg2. Question: Two people are sitting on a bench 2m apart. If one has a mass of 60 kg and the o ...
... • m1 is the mass of one object, in kg • m2 is the mass of the other object, in kg • Δd is the distance between the centers of the objects, in m • G is the universal gravitational constant, 6.67x 10-11 Nm2/kg2. Question: Two people are sitting on a bench 2m apart. If one has a mass of 60 kg and the o ...
Monday, January 12
... • Scientist and Mathematician • His accomplishments in mathematics, optics, and physics laid the foundations for modern science and revolutionized the world. • BrainPop about Newton and his laws ...
... • Scientist and Mathematician • His accomplishments in mathematics, optics, and physics laid the foundations for modern science and revolutionized the world. • BrainPop about Newton and his laws ...