11.2 Questions Force and Mass Determine Acceleration 1. What 3
... 1. What 3 concepts are involved in Newton’s second law? 8. A mass is 2kg. What other information do you need to calculate acceleration? 2. Look at the picture on page 354. What do the arrows in the diagrams show? 9. If an object moves at a constant speed, but it accelerates, what changes? 3. What ha ...
... 1. What 3 concepts are involved in Newton’s second law? 8. A mass is 2kg. What other information do you need to calculate acceleration? 2. Look at the picture on page 354. What do the arrows in the diagrams show? 9. If an object moves at a constant speed, but it accelerates, what changes? 3. What ha ...
Force = mass x acceleration
... 1. Any push or pull -can cause change in motion: a. friction b. inertia c. burn d. force 2. A force that always works against motion a. friction b. gravity c. inertia d. momentum ...
... 1. Any push or pull -can cause change in motion: a. friction b. inertia c. burn d. force 2. A force that always works against motion a. friction b. gravity c. inertia d. momentum ...
Newton`s 1st Law Lab Activities
... describe your test and its results. Is the hypothesis confirmed or disconfirmed? ...
... describe your test and its results. Is the hypothesis confirmed or disconfirmed? ...
Ch_3 Presentation
... A ball rolls down and endless/frictionless surface. It rolls until the end of time. An object that is not affected by any outside forces will keep on keeping on, this is based on an innate property of matter called inertia. By your book: Inertia is the property of a body to resist change to its stat ...
... A ball rolls down and endless/frictionless surface. It rolls until the end of time. An object that is not affected by any outside forces will keep on keeping on, this is based on an innate property of matter called inertia. By your book: Inertia is the property of a body to resist change to its stat ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 19. Explain Legendre transformation. Discuss how the transformation equations can be obtained from the generating functions of type F 1 and F2. 20. What are action angle variables? Explain how they can be used to obtain the frequencies of periodic motion. 21. Discuss the double pendulum and obtain i ...
... 19. Explain Legendre transformation. Discuss how the transformation equations can be obtained from the generating functions of type F 1 and F2. 20. What are action angle variables? Explain how they can be used to obtain the frequencies of periodic motion. 21. Discuss the double pendulum and obtain i ...
Study Guide for Force, Motion, and Energy
... □ define and identify the definitions of these words: speed, mass, force, velocity, friction, net force, inertia, acceleration, unbalance forces, balanced forces, braking distance, kinetic energy, potential energy, Newton’s 1st Law of Motion, Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion, and Newton’s 3rd Law of Motio ...
... □ define and identify the definitions of these words: speed, mass, force, velocity, friction, net force, inertia, acceleration, unbalance forces, balanced forces, braking distance, kinetic energy, potential energy, Newton’s 1st Law of Motion, Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion, and Newton’s 3rd Law of Motio ...
Chapter 2 Newton`s First Law of Motion
... Knocked down Aristotle's push or pull ideas. Rest was not a natural state. The concept of inertia was introduced. ...
... Knocked down Aristotle's push or pull ideas. Rest was not a natural state. The concept of inertia was introduced. ...
Motion and Forces
... Calculate force, mass, and acceleration with Newton’s second law. Recognize that the free-fall acceleration near Earth’s surface is independent of the mass of the falling object. Explain the difference between mass and weight. Identify paired forces on interacting objects. ...
... Calculate force, mass, and acceleration with Newton’s second law. Recognize that the free-fall acceleration near Earth’s surface is independent of the mass of the falling object. Explain the difference between mass and weight. Identify paired forces on interacting objects. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion - SchHavenFoundationsofScience
... Italian scientist Studied interaction between gravity and object acceleration. Predicted that without friction or other forces, objects would move indefinitely. Galileo Clip ...
... Italian scientist Studied interaction between gravity and object acceleration. Predicted that without friction or other forces, objects would move indefinitely. Galileo Clip ...
Newton`s First Law - Inertia
... A moving body keeps moving Galileo – Concerned with how it worked – not why – Experiments (not logic) leads to knowledge ...
... A moving body keeps moving Galileo – Concerned with how it worked – not why – Experiments (not logic) leads to knowledge ...
Newton’s Laws of Motion
... the Law of Inertia Inertia: the tendency of an object to resist changes in its state of motion The First Law states that all objects have inertia. The more mass an object has, the more inertia it has (and the harder it is to change its motion). So, which has more inertia? A bowling ball or a basebal ...
... the Law of Inertia Inertia: the tendency of an object to resist changes in its state of motion The First Law states that all objects have inertia. The more mass an object has, the more inertia it has (and the harder it is to change its motion). So, which has more inertia? A bowling ball or a basebal ...
9-4,5,6,7
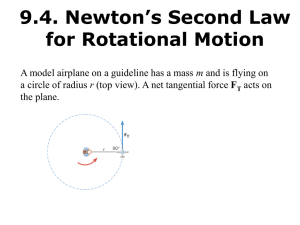
... 9.4. Newton’s Second Law for Rotational Motion A model airplane on a guideline has a mass m and is flying on a circle of radius r (top view). A net tangential force FT acts on the plane. ...
... 9.4. Newton’s Second Law for Rotational Motion A model airplane on a guideline has a mass m and is flying on a circle of radius r (top view). A net tangential force FT acts on the plane. ...
1 Newton`s Laws
... Two blocks, one 8 times as massive as the other, are connected by a compressed spring (sitting on a frictionless surface). When the spring is released the blocks fly apart. a) Draw the free body diagram showing the forces acting on each object. b) What is the acceleration of the lighter block relati ...
... Two blocks, one 8 times as massive as the other, are connected by a compressed spring (sitting on a frictionless surface). When the spring is released the blocks fly apart. a) Draw the free body diagram showing the forces acting on each object. b) What is the acceleration of the lighter block relati ...