Chapter : 6: A Tour of the Cell
... 21. Your intestine is lined with individual cells. No fluids leak between these cells from the gut into your body. Why? (Concept 6.7 ) a) The intestinal cells are fused together into one giant cell. b) The intestinal cells are bound together by plasmodesmata. c) The intestinal cells are bound togeth ...
... 21. Your intestine is lined with individual cells. No fluids leak between these cells from the gut into your body. Why? (Concept 6.7 ) a) The intestinal cells are fused together into one giant cell. b) The intestinal cells are bound together by plasmodesmata. c) The intestinal cells are bound togeth ...
Cell Fate Specification
... • Remove a cell and the cell types normally derived from that cell will not form. • Isolate a cell and it will form the cell types it normally would have. B. Conditional Specification • Remove a cell and the cell types normally formed by that cell will be contributed by other cells (compensation) C. ...
... • Remove a cell and the cell types normally derived from that cell will not form. • Isolate a cell and it will form the cell types it normally would have. B. Conditional Specification • Remove a cell and the cell types normally formed by that cell will be contributed by other cells (compensation) C. ...
lecture13_06
... coloring of the corresponding region of the dendrogram. The sequence-verified named genes in these clusters contain multiple genes involved in (A) cholesterol biosynthesis, (B) the cell cycle, (C) the immediate-early response, (D) signaling and angiogenesis, and (E) wound healing and tissue remodeli ...
... coloring of the corresponding region of the dendrogram. The sequence-verified named genes in these clusters contain multiple genes involved in (A) cholesterol biosynthesis, (B) the cell cycle, (C) the immediate-early response, (D) signaling and angiogenesis, and (E) wound healing and tissue remodeli ...
Two important chemical molecules made by plant cells. What are
... Organelles that turn sugars into an energy molecule. Also known as “cell’s “powerhouse”. ...
... Organelles that turn sugars into an energy molecule. Also known as “cell’s “powerhouse”. ...
Cell Boundaries
... hypertonic (“above strength”): the more concentrated solution hypotonic (“below strength”): the more dilute solution isotonic (”same strength”): When concentrations of solutions are the same on both sides of a membrane ...
... hypertonic (“above strength”): the more concentrated solution hypotonic (“below strength”): the more dilute solution isotonic (”same strength”): When concentrations of solutions are the same on both sides of a membrane ...
Title: Development of a novel class of hyper-multi
... convert inhibitors with low affinity to ones with high avidity and/or biological "activity" gauged by some relevant parameter: (for example, values of IC50 the concentration of free ligand, often approximated as the total ligand, that reduces the experimental signal to 50% of its initial value). In ...
... convert inhibitors with low affinity to ones with high avidity and/or biological "activity" gauged by some relevant parameter: (for example, values of IC50 the concentration of free ligand, often approximated as the total ligand, that reduces the experimental signal to 50% of its initial value). In ...
Passive Transport
... Result: Water moves equally in both directions and the cell remains same size! (Dynamic Equilibrium) ...
... Result: Water moves equally in both directions and the cell remains same size! (Dynamic Equilibrium) ...
Study Guide, Section 2
... 6. Chromosomes attach to spindle fibers and line up along the equator of the cell during metaphase. 7. The nucleus reappears during prophase. 8. Centrioles migrate to the poles of the cell during telophase. 9. Chromatids are pulled apart during anaphase. 10. The first stage of mitosis is telophase. ...
... 6. Chromosomes attach to spindle fibers and line up along the equator of the cell during metaphase. 7. The nucleus reappears during prophase. 8. Centrioles migrate to the poles of the cell during telophase. 9. Chromatids are pulled apart during anaphase. 10. The first stage of mitosis is telophase. ...
name date ______ period
... MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle all that are TRUE. There may be MORE THAN ONE correct answer. Example: Which of the following is TRUE of a cell membrane? A. Cell membranes allow ALL substances to pass through easily B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts mor ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle all that are TRUE. There may be MORE THAN ONE correct answer. Example: Which of the following is TRUE of a cell membrane? A. Cell membranes allow ALL substances to pass through easily B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts mor ...
Cell Cycle part 2 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... • Question: All organisms must be able to reproduce to keep the species existent. Prokaryotes undergo Binary Fission and Eukaryotic cells undergo Mitosis. In no more than four sentences, explain one similarity and one difference between the two processes. In addition, explain the evolution link bet ...
... • Question: All organisms must be able to reproduce to keep the species existent. Prokaryotes undergo Binary Fission and Eukaryotic cells undergo Mitosis. In no more than four sentences, explain one similarity and one difference between the two processes. In addition, explain the evolution link bet ...
Please
... Stages of Mitosis Telophase - in this final stage, spindle fibers disappear and a nuclear membrane forms around each separated set of chromosomes -cell is ready to divide Cytokinesis -is the separation of the nuclei into two daughter cells -animal cells- cell pinches together and divides -plant cel ...
... Stages of Mitosis Telophase - in this final stage, spindle fibers disappear and a nuclear membrane forms around each separated set of chromosomes -cell is ready to divide Cytokinesis -is the separation of the nuclei into two daughter cells -animal cells- cell pinches together and divides -plant cel ...
The Cell - Mr regh`s science site
... Centriole: small structure in animal cells that help to organize microtubules Used during cell division Flagella- long and few in #, propel unicellular organisms Cilia- shorter and more numerous, locomotion, move fluids over surface of tissue (lining of trachea) ECM (Extracellular Matrix)- just ex ...
... Centriole: small structure in animal cells that help to organize microtubules Used during cell division Flagella- long and few in #, propel unicellular organisms Cilia- shorter and more numerous, locomotion, move fluids over surface of tissue (lining of trachea) ECM (Extracellular Matrix)- just ex ...
Biology 12 - The Cell – REVIEW WORKSHEET
... Which of the cell organelle could be seen with a. the naked eye? _________________________________________________________________ b. the compound light microscope?____________________________________________________ c. the electron microscope? _______________________________________________________ ...
... Which of the cell organelle could be seen with a. the naked eye? _________________________________________________________________ b. the compound light microscope?____________________________________________________ c. the electron microscope? _______________________________________________________ ...
NEUROSCIENCE FACTS
... nections is more easily seen in the hippocampal formation , where the homogeneous population of principal cell bodies anc;J equivalent parts of their dendrites are aligned. In the dentate gyrus, granule cells receive inputs from at least five distinct types of GABAergic neuron, four of which termina ...
... nections is more easily seen in the hippocampal formation , where the homogeneous population of principal cell bodies anc;J equivalent parts of their dendrites are aligned. In the dentate gyrus, granule cells receive inputs from at least five distinct types of GABAergic neuron, four of which termina ...
Cell - Review
... Which of the cell organelle could be seen with a. the naked eye? _________________________________________________________________ b. the compound light microscope?____________________________________________________ c. the electron microscope? _______________________________________________________ ...
... Which of the cell organelle could be seen with a. the naked eye? _________________________________________________________________ b. the compound light microscope?____________________________________________________ c. the electron microscope? _______________________________________________________ ...
Cell Factory Analogy
... o Using most of the poster to draw your cell factory analogy. o Using colored pencils, draw in the organelles that represent your cell parts o Label them with both their factory analogy name and in parenthesis-their cell part name. Example: -Office of Manager (nucleus) ...
... o Using most of the poster to draw your cell factory analogy. o Using colored pencils, draw in the organelles that represent your cell parts o Label them with both their factory analogy name and in parenthesis-their cell part name. Example: -Office of Manager (nucleus) ...
Cell Review Worksheet - ANSWERS Cell Theory
... a. Lipids and Carbohydrates protection for plant cell and both are energy storage for the cells b. Lipids and Proteins both in the cell membrane and function to protected the cell, transport proteins in the membrane c. Lipids and Nucleic Acids nuclear envelope – made of lipids and protects the nucle ...
... a. Lipids and Carbohydrates protection for plant cell and both are energy storage for the cells b. Lipids and Proteins both in the cell membrane and function to protected the cell, transport proteins in the membrane c. Lipids and Nucleic Acids nuclear envelope – made of lipids and protects the nucle ...
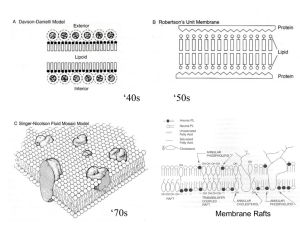
lecture 11
... 4 reviews on domain formation in model membranes and physical properties that underlie raft formation 2 reviews to describe techniques used for studying rafts (FRET) – and uncertainty for detecting rafts in cell membranes Raft Function in Cells: 4 on signal transduction(IgE receptor signaling, Growt ...
... 4 reviews on domain formation in model membranes and physical properties that underlie raft formation 2 reviews to describe techniques used for studying rafts (FRET) – and uncertainty for detecting rafts in cell membranes Raft Function in Cells: 4 on signal transduction(IgE receptor signaling, Growt ...
BCL-2 Family Proteins: Critical Checkpoints of Apoptotic
... 2) apoptotic protease : APAF-1, caspase-9, cythchrome c, mitochondrial electron transport chain 3) release during apoptosis ...
... 2) apoptotic protease : APAF-1, caspase-9, cythchrome c, mitochondrial electron transport chain 3) release during apoptosis ...
Study Guide
... The _______________________ is made of closely stacked, flattened sacs that resemble ...
... The _______________________ is made of closely stacked, flattened sacs that resemble ...
BIOLOGY
... 7. In most stable desert environments, a particular species of lizard found are all female. However, when there are extremely long periods of drought, or extremely high temperatures, male versions of the lizards can be found. A scientist predicts that females are able to morph into male versions of ...
... 7. In most stable desert environments, a particular species of lizard found are all female. However, when there are extremely long periods of drought, or extremely high temperatures, male versions of the lizards can be found. A scientist predicts that females are able to morph into male versions of ...
Proteins: Primary Structure
... the term quaternary structure Describe the properties and functions of fibrous proteins ...
... the term quaternary structure Describe the properties and functions of fibrous proteins ...
PRODUCT SPECIFICATION SHEET
... BD BioCoat Cellware provides researchers with the ability to control in vitro cellular environments for cell growth and differentiation under physiologically relevant conditions. Extracellular Matrix (ECM) is secreted by cells to form interstitial matrix and basement membrane which constitutes the f ...
... BD BioCoat Cellware provides researchers with the ability to control in vitro cellular environments for cell growth and differentiation under physiologically relevant conditions. Extracellular Matrix (ECM) is secreted by cells to form interstitial matrix and basement membrane which constitutes the f ...
4NucleicAcidsProteins - San Elijo Elementary School
... Transport proteins move substances Hormonal proteins coordinate multicellular organisms • Receptor proteins respond to environmental stimuli • Contractile and motor proteins allow for movement • Defensive proteins protect against disease (antibodies) ...
... Transport proteins move substances Hormonal proteins coordinate multicellular organisms • Receptor proteins respond to environmental stimuli • Contractile and motor proteins allow for movement • Defensive proteins protect against disease (antibodies) ...
Ribosomes
... components of a house, you would be left with a basic skeletal structure and a foundation. Similarly, a cell's foundation starts with the Cytoplasm and the Cytoskeleton ...
... components of a house, you would be left with a basic skeletal structure and a foundation. Similarly, a cell's foundation starts with the Cytoplasm and the Cytoskeleton ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.