Eukaryotic Cells part II - Westerville City Schools
... mitochondria break down sugar from our food to make a special type of cell energy called ATP (that’s short for Adenosintriphosphate). Mitochondria are the entire reason we inhale oxygen. If the mitochondria in our cells didn’t need oxygen, we wouldn’t need to breath. The organelles in the cell use t ...
... mitochondria break down sugar from our food to make a special type of cell energy called ATP (that’s short for Adenosintriphosphate). Mitochondria are the entire reason we inhale oxygen. If the mitochondria in our cells didn’t need oxygen, we wouldn’t need to breath. The organelles in the cell use t ...
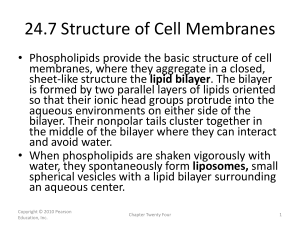
24.7 Structure of Cell Membranes
... in prostate cells) and the leukotrienes (named for their discovery in leukocytes) are two classes of eicosanoids that differ somewhat in their structure. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... in prostate cells) and the leukotrienes (named for their discovery in leukocytes) are two classes of eicosanoids that differ somewhat in their structure. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Note Pages for Monday 12/3 and Tuesday 12/4
... you must collect your energy in another way. All animals, all fungi, some protists, and some prokaryotes are ________________________, or “other makers,” which means they consume calories. We get your energy from _________. Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are reservoirs of energy. A series of chem ...
... you must collect your energy in another way. All animals, all fungi, some protists, and some prokaryotes are ________________________, or “other makers,” which means they consume calories. We get your energy from _________. Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are reservoirs of energy. A series of chem ...
Biology 202 Lecture Notes
... Hypothalamus and Pituitary gland See figure 15.6 The hypothalamus is connected to the pituitary gland by the infundibulum. Hypothalamic neurons go directly to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) and release oxytocin and ADH (antidiuretic hormone or vasopressin) Releasing and inhibiting h ...
... Hypothalamus and Pituitary gland See figure 15.6 The hypothalamus is connected to the pituitary gland by the infundibulum. Hypothalamic neurons go directly to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) and release oxytocin and ADH (antidiuretic hormone or vasopressin) Releasing and inhibiting h ...
Keystone Biology Cram Sheet: MODULE 1 1. Because carbon has 4
... 15. The ER is like a protein assembly line. The workers along it are ribosomes, which actually line up the amino acids in the right order (according to the DNA code) 16. The proteins are finished, tweaked, modified, packaged and shipped by Golgi. 17. Vesicles carry the final protein products through ...
... 15. The ER is like a protein assembly line. The workers along it are ribosomes, which actually line up the amino acids in the right order (according to the DNA code) 16. The proteins are finished, tweaked, modified, packaged and shipped by Golgi. 17. Vesicles carry the final protein products through ...
Essentials of Human Anatomy Special Senses Special Senses
... • group of hearing receptor cells (hair cells) • on upper surface of basilar membrane • different frequencies of vibration move different parts of basilar membrane • particular sound frequencies cause hairs of receptor cells to bend • nerve impulse generated ...
... • group of hearing receptor cells (hair cells) • on upper surface of basilar membrane • different frequencies of vibration move different parts of basilar membrane • particular sound frequencies cause hairs of receptor cells to bend • nerve impulse generated ...
Quiz8ch8.doc
... in the __________, and cellular respiration occurs in the __________. a. mitochondria, cytoplasm b. cytoplasm, mitochondria c. cytoplasm, chloroplasts d. chloroplasts, mitochondria 2. The overall equation for glucose metabolism is C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP and heat. The carbon atoms in the ...
... in the __________, and cellular respiration occurs in the __________. a. mitochondria, cytoplasm b. cytoplasm, mitochondria c. cytoplasm, chloroplasts d. chloroplasts, mitochondria 2. The overall equation for glucose metabolism is C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP and heat. The carbon atoms in the ...
PAPER TITLE: Animal Diversity: Non Chordates
... discusses the fundamental processes that enable cells to grow, move and communicate and will cover topics such as cell architecture, cell chemistry, cell division, functions and cell cycle. Students will also learn current molecular biological techniques that are used to study cell biology. Laborato ...
... discusses the fundamental processes that enable cells to grow, move and communicate and will cover topics such as cell architecture, cell chemistry, cell division, functions and cell cycle. Students will also learn current molecular biological techniques that are used to study cell biology. Laborato ...
AP Bio Summer Work Reading Guide (2013 - 2014).
... 99. Mendel’s model consists of four concepts. Describe each concept in the appropriate space below. ...
... 99. Mendel’s model consists of four concepts. Describe each concept in the appropriate space below. ...
APBioSummerWorkReadingGuide_2014_2015
... 99. Mendel’s model consists of four concepts. Describe each concept in the appropriate space below. ...
... 99. Mendel’s model consists of four concepts. Describe each concept in the appropriate space below. ...
Modification of the K-Ras Signaling Pathway
... • Ras (Rat Sarcoma) - Small GTPase protein • Active only in GTP-bound form • Activation through facilitated nucleotide exchange from GDP GTP via GEF (SOS) • Self-regulates via hydrolysis of GTP GDP – partially dependent on GAP (RASA1) ...
... • Ras (Rat Sarcoma) - Small GTPase protein • Active only in GTP-bound form • Activation through facilitated nucleotide exchange from GDP GTP via GEF (SOS) • Self-regulates via hydrolysis of GTP GDP – partially dependent on GAP (RASA1) ...
Lectures 8 & 9: Powerpoint
... associated with the ER a. Sorts proteins and lipids by destination b. Modifies some molecules c. Packages these materials, then transports them to appropriate location ...
... associated with the ER a. Sorts proteins and lipids by destination b. Modifies some molecules c. Packages these materials, then transports them to appropriate location ...
RAFT, Cell Structure/Organelle Terms, and Formats Cell Cycle
... RAFT, Cell Structure/Organelle Terms, and Formats Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosis RAFT Write about the topics from the desired point of view and to the correct audience.* Be creative with the format. If there is a variation you want to use, please talk to me to see if it fits. ...
... RAFT, Cell Structure/Organelle Terms, and Formats Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosis RAFT Write about the topics from the desired point of view and to the correct audience.* Be creative with the format. If there is a variation you want to use, please talk to me to see if it fits. ...
Naomi`s Nucleants - Molecular Dimensions
... Naomi’s Nucleants have facilitated the crystallization of 14 proteins, the highest number reported for any single nucleant. Many of these proteins have proven difficult to crystallize and some of these, including membrane proteins, have only been crystallized in the presence of Naomi’s Nucleants. Na ...
... Naomi’s Nucleants have facilitated the crystallization of 14 proteins, the highest number reported for any single nucleant. Many of these proteins have proven difficult to crystallize and some of these, including membrane proteins, have only been crystallized in the presence of Naomi’s Nucleants. Na ...
Membrane Structure and Transport
... • Found in animal cells • Pumps out 3 sodium ions for every two potassium ions that enter the cell • Helps to keep the inside of the cell at a net ...
... • Found in animal cells • Pumps out 3 sodium ions for every two potassium ions that enter the cell • Helps to keep the inside of the cell at a net ...
Handou
... 1. Describe 2 similarities and 2 differences between plant cells and animal cells. 2. How are the functions of the endoplasmic reticulum and golgi apparatus related? 3. Six of the organelles (other than the plasma membrane) contain one or more membranes. List these organelles. 4. Different cells con ...
... 1. Describe 2 similarities and 2 differences between plant cells and animal cells. 2. How are the functions of the endoplasmic reticulum and golgi apparatus related? 3. Six of the organelles (other than the plasma membrane) contain one or more membranes. List these organelles. 4. Different cells con ...
Animal cell - Technology in Education with Lara Means
... the Cell Membrane. The Nucleus acts like the brain of the cell. It helps control eating, movement, and reproduction. The Cell Membrane is like a plastic bag around the outside of the cell. It helps to hold all of the cells structures and fluids inside. ...
... the Cell Membrane. The Nucleus acts like the brain of the cell. It helps control eating, movement, and reproduction. The Cell Membrane is like a plastic bag around the outside of the cell. It helps to hold all of the cells structures and fluids inside. ...
Cell Organelles - Shelton School District
... creates energy for cells Uses food to create chemical energy (ATP) ...
... creates energy for cells Uses food to create chemical energy (ATP) ...
Cell Membrane Cellular Transport
... • Endocytosis: Cell surrounds and takes in material from environment – Material does not pass directly through membrane – Is engulfed and enclosed by portion of cell’s plasma membrane – Portion of membrane breaks away, leaving vacuole with contents which moves into cell ...
... • Endocytosis: Cell surrounds and takes in material from environment – Material does not pass directly through membrane – Is engulfed and enclosed by portion of cell’s plasma membrane – Portion of membrane breaks away, leaving vacuole with contents which moves into cell ...
Document
... dominant allele of a gene and can be inherited from only one parent • Cystic fibrosis is caused by a recessive allele of a gene and so must be inherited from both parents ...
... dominant allele of a gene and can be inherited from only one parent • Cystic fibrosis is caused by a recessive allele of a gene and so must be inherited from both parents ...
Chapter Objectives
... 33. Define osmosis and predict the direction of water movement based upon differences in solute concentration 34. Explain how bound water affects the osmotic behavior of dilute biological fluids 35. Describe how living cells with and without walls regulate water balance 36. Explain how transport pro ...
... 33. Define osmosis and predict the direction of water movement based upon differences in solute concentration 34. Explain how bound water affects the osmotic behavior of dilute biological fluids 35. Describe how living cells with and without walls regulate water balance 36. Explain how transport pro ...
APOPTOSIS AND NECROSIS APOPTOSIS All the cells in our body
... Pathological atrophy in parenchymal organs after duct obstruction Cell death in tumors In some situations where cell death is mainly due to necrosis, the pathway of apoptosis may also contribute ...
... Pathological atrophy in parenchymal organs after duct obstruction Cell death in tumors In some situations where cell death is mainly due to necrosis, the pathway of apoptosis may also contribute ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.