Cellular Processes
... semi-permeable cell membrane do so by passive transport Diffusion: the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration ...
... semi-permeable cell membrane do so by passive transport Diffusion: the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration ...
cells-study-guide
... Understand how these relate to each other Organism > Organ System > Organ > Tissue > Cell ...
... Understand how these relate to each other Organism > Organ System > Organ > Tissue > Cell ...
The Magic Universe of Cells Directions
... draw, label, and define the parts of an animal cell and a plant cell. You need to include at least: nucleus, nucleolus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrion, cell membrane, cell wall, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, cytoplasm, vacuoles, centrioles, lysosomes, nuclear envelope, and chromatin. If there is ...
... draw, label, and define the parts of an animal cell and a plant cell. You need to include at least: nucleus, nucleolus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrion, cell membrane, cell wall, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, cytoplasm, vacuoles, centrioles, lysosomes, nuclear envelope, and chromatin. If there is ...
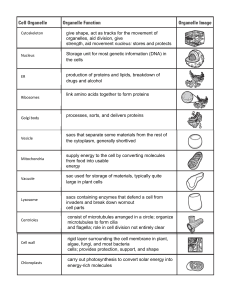
Vacuoles
... Keeps harmful materials away from cell Holds cell waste Stores protein for seeds Lets plants have leaves and flowers because of the high pressure in the cell • Vacuoles are found in plant and fungi cells ...
... Keeps harmful materials away from cell Holds cell waste Stores protein for seeds Lets plants have leaves and flowers because of the high pressure in the cell • Vacuoles are found in plant and fungi cells ...
I`m a real “powerhouse” That`s plain to see. I break down food To
... I transport proteins And other things as well. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM ...
... I transport proteins And other things as well. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM ...
Lecture 11: Cell proliferation, differentiation, and death
... Breaking up nucleus into small pieces. Cell shrinkage Cell fragmentation (apoptotic bodies) Phagocytosis by macrophages and neighboring cells In contrast, cell necrosis results in membrane damage, enlargement of cells, release of intracellular contents, and causing inflammation. ...
... Breaking up nucleus into small pieces. Cell shrinkage Cell fragmentation (apoptotic bodies) Phagocytosis by macrophages and neighboring cells In contrast, cell necrosis results in membrane damage, enlargement of cells, release of intracellular contents, and causing inflammation. ...
Study Guide
... Summary Common Cell Traits All cells have an outer covering called a cell membrane. Cells can be classified as prokaryotic (cells that lack a distinct nucleus) or eukaryotic (cells with a distinct membrane-bound nucleus). Cell Organization Each cell in your body has a specific function. Most ...
... Summary Common Cell Traits All cells have an outer covering called a cell membrane. Cells can be classified as prokaryotic (cells that lack a distinct nucleus) or eukaryotic (cells with a distinct membrane-bound nucleus). Cell Organization Each cell in your body has a specific function. Most ...
carry out photosynthesis to convert solar energy into energy
... link amino acids together to form proteins ...
... link amino acids together to form proteins ...
Biology Notes 3-2
... 2. Cells are the basic unit(s) of life’s function and structure. 3. All cells arise from existing cells. Most Cells cannot be seen with the naked eye: they are 5µm-20 µm (micrometers in diameter) Cells must have a high Surface Area-to-Volume ratio (SA:V) in order to function efficiently. Cell Featur ...
... 2. Cells are the basic unit(s) of life’s function and structure. 3. All cells arise from existing cells. Most Cells cannot be seen with the naked eye: they are 5µm-20 µm (micrometers in diameter) Cells must have a high Surface Area-to-Volume ratio (SA:V) in order to function efficiently. Cell Featur ...
Test 1 Study Guide
... 6. During ______________ the contents inside the cell divide. 7. Why is mitosis important when you are injured? 8. What is a malignant tumor? 9. Why do some cells like skin and stomach lining divide faster than others? 10. What do cells have at the end of the S phase of interphase? 11. What is a sub ...
... 6. During ______________ the contents inside the cell divide. 7. Why is mitosis important when you are injured? 8. What is a malignant tumor? 9. Why do some cells like skin and stomach lining divide faster than others? 10. What do cells have at the end of the S phase of interphase? 11. What is a sub ...
Meiosis And Mitosis - Bloomfield Public Schools
... The process of Meiosis Meiosis is the process by which sex cells divide. Chromosomes make copies of themselves. They line up in the middle of the cell side by side. Then move to opposite ends of the cell. 2 new cells are formed. Again, they line up in the middle. Then they divide and ...
... The process of Meiosis Meiosis is the process by which sex cells divide. Chromosomes make copies of themselves. They line up in the middle of the cell side by side. Then move to opposite ends of the cell. 2 new cells are formed. Again, they line up in the middle. Then they divide and ...
Week 18 - stephen fleenor
... involve timing and coordination of events necessary for normal development in an organism. LO 2.34 describe the role of programmed cell death in development and differentiation, the reuse of molecules, and the maintenance of dynamic homeostasis. LO 3.18 describe the connection between the regulation ...
... involve timing and coordination of events necessary for normal development in an organism. LO 2.34 describe the role of programmed cell death in development and differentiation, the reuse of molecules, and the maintenance of dynamic homeostasis. LO 3.18 describe the connection between the regulation ...
Nanolive AG from Ecublens (VD) – 3D research on living cells
... insemination. This provides for a more specific selection of ovules and sperm cells without causing damaging to the cells. The 3D Cell Explorer offers landmark breakthrough opportunities for completely new fields of research in medicine, pharma and the cosmetic industry. An entry market price of CHF ...
... insemination. This provides for a more specific selection of ovules and sperm cells without causing damaging to the cells. The 3D Cell Explorer offers landmark breakthrough opportunities for completely new fields of research in medicine, pharma and the cosmetic industry. An entry market price of CHF ...
Bozeman Video Guide - Cell Communication
... 1) List the 3 analogies Mr. Anderson gives about communication, then describe the 3 ways cell communicate correspond to these analogies Analogy ...
... 1) List the 3 analogies Mr. Anderson gives about communication, then describe the 3 ways cell communicate correspond to these analogies Analogy ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.