Name Test Review Chapters 4 and 25 Honors Chemistry 1. Fill in
... Discovered the Law of Conservation of Mass. __________________________ Proposed a model of the atom as a hard, indivisible sphere. ________________________ Conducted experiments with cathode rays. ____________________________ Know the 5 points of Dalton’s atomic theory and how two of those points ha ...
... Discovered the Law of Conservation of Mass. __________________________ Proposed a model of the atom as a hard, indivisible sphere. ________________________ Conducted experiments with cathode rays. ____________________________ Know the 5 points of Dalton’s atomic theory and how two of those points ha ...
Study guide for percent abundance chapter 4 spaced out
... 2. The element vanadium has two isotopes, 50V and 51 V, and a relative atomic mass of 50.94. (5pts) a. Define the term isotope. b. State the number of protons, electrons and neutrons in 50V. ...
... 2. The element vanadium has two isotopes, 50V and 51 V, and a relative atomic mass of 50.94. (5pts) a. Define the term isotope. b. State the number of protons, electrons and neutrons in 50V. ...
What is the Biosphere?
... Burning fossil fuels = more CO2 and CH4 in atmosphere More CO2 and CH4 in atmosphere = global warming ...
... Burning fossil fuels = more CO2 and CH4 in atmosphere More CO2 and CH4 in atmosphere = global warming ...
Ch. 14.2 Notes
... 12. Heavier elements like _____________ and ____________ have _____________ _____________. 13. The nucleus __________ particles and becomes __________ ___________. 14. When particles are released, __________ is given off. 15. When the particles ejected from the nucleus include __________, the atomi ...
... 12. Heavier elements like _____________ and ____________ have _____________ _____________. 13. The nucleus __________ particles and becomes __________ ___________. 14. When particles are released, __________ is given off. 15. When the particles ejected from the nucleus include __________, the atomi ...
Atomic Structure - Learn District 196
... To find the weighted average: (% abundance/100)(relative atomic mass of isotope 1) + (% abundance/100)(relative atomic mass of isotope 2) + (% abundance/100)(relative atomic mass of isotope 3)… *Mass # may be substituted for the relative atomic mass when given (99.985%/100)(1.007825 amu) + (.015%/10 ...
... To find the weighted average: (% abundance/100)(relative atomic mass of isotope 1) + (% abundance/100)(relative atomic mass of isotope 2) + (% abundance/100)(relative atomic mass of isotope 3)… *Mass # may be substituted for the relative atomic mass when given (99.985%/100)(1.007825 amu) + (.015%/10 ...
Atomic Structure
... To find the weighted average: (% abundance/100)(relative atomic mass of isotope 1) + (% abundance/100)(relative atomic mass of isotope 2) + (% abundance/100)(relative atomic mass of isotope 3)… *Mass # may be substituted for the relative atomic mass when given (99.985%/100)(1.007825 amu) + (.015%/10 ...
... To find the weighted average: (% abundance/100)(relative atomic mass of isotope 1) + (% abundance/100)(relative atomic mass of isotope 2) + (% abundance/100)(relative atomic mass of isotope 3)… *Mass # may be substituted for the relative atomic mass when given (99.985%/100)(1.007825 amu) + (.015%/10 ...
SS18A - Atoms, Isotopes and Ions
... If you look at a periodic table, you will notice that the atomic number increases by one whole number at a time. This is because you add one proton at a time for each element. The atomic mass (see diagram below) however, increases by amounts greater than one. This difference is due to the neutrons i ...
... If you look at a periodic table, you will notice that the atomic number increases by one whole number at a time. This is because you add one proton at a time for each element. The atomic mass (see diagram below) however, increases by amounts greater than one. This difference is due to the neutrons i ...
1 Subatomic Particles – Lets Review Again! General Information: An
... 1. There are two naturally occurring isotopes of boron. Their atomic masses are 10B (10.0129 amu) and 11B (11.00931 amu). Without using a calculator, choose the best estimate among the following for the percent abundances for the two isotopes. (Hint: Refer to the periodic table for the average atomi ...
... 1. There are two naturally occurring isotopes of boron. Their atomic masses are 10B (10.0129 amu) and 11B (11.00931 amu). Without using a calculator, choose the best estimate among the following for the percent abundances for the two isotopes. (Hint: Refer to the periodic table for the average atomi ...
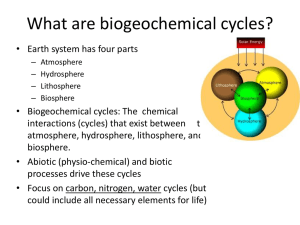
What are biogeochemical cycles?
... • Carbon dioxide is a critical gas: – Taken up by plants in photosynthesis – Released by plants and animals in respiration – Released during decomposition (and fires) – Greenhouse gas (greenhouse effect - your car in the ...
... • Carbon dioxide is a critical gas: – Taken up by plants in photosynthesis – Released by plants and animals in respiration – Released during decomposition (and fires) – Greenhouse gas (greenhouse effect - your car in the ...
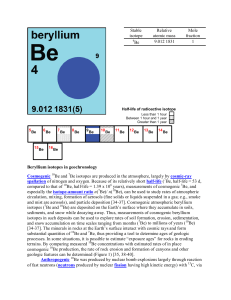
Beryllium isotopes in geochronology Cosmogenic Be and Be
... isotopes (7Be and 10Be) are deposited on the Earth’s surface where they accumulate in soils, sediments, and snow while decaying away. Thus, measurements of cosmogenic beryllium isotopes in such deposits can be used to explore rates of soil formation, erosion, sedimentation, and snow accumulation on ...
... isotopes (7Be and 10Be) are deposited on the Earth’s surface where they accumulate in soils, sediments, and snow while decaying away. Thus, measurements of cosmogenic beryllium isotopes in such deposits can be used to explore rates of soil formation, erosion, sedimentation, and snow accumulation on ...
Chapter 11: The rise of oxygen and ozone – ppt
... oxygenic photosynthesis sunlight + CO2 + H2O organic Ccompounds + O2 anoxygenic photosynthesis sunlight + CO2 + H2N or H2 (instead of H2O) organic C-compounds + no O2! And there is cyanobacteria that can perform both!! and can switch from one to the other depending on whether H2N is there or ...
... oxygenic photosynthesis sunlight + CO2 + H2O organic Ccompounds + O2 anoxygenic photosynthesis sunlight + CO2 + H2N or H2 (instead of H2O) organic C-compounds + no O2! And there is cyanobacteria that can perform both!! and can switch from one to the other depending on whether H2N is there or ...
CHM 123-Chapter 2.7
... What type of radiation occurs when carbon-11 decays to boron -11? How has the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus changed? ...
... What type of radiation occurs when carbon-11 decays to boron -11? How has the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus changed? ...
I. Structure of Matter
... • At a certain temperature, the vapor pressure of benzene is 0.930 atm. A solution prepared by dissolving 10.0 g of a molecular, nonvolatile solute in 78.11 g benzene at that temperature has a vapor pressure of 0.900 atm. Determine the MM of the solute. • A 0.350 g sample of a large biomolecule was ...
... • At a certain temperature, the vapor pressure of benzene is 0.930 atm. A solution prepared by dissolving 10.0 g of a molecular, nonvolatile solute in 78.11 g benzene at that temperature has a vapor pressure of 0.900 atm. Determine the MM of the solute. • A 0.350 g sample of a large biomolecule was ...
File
... Hydrogen usually has a nucleus consisting of only one proton. An isotope of hydrogen called deuterium has a nucleus consisting of one proton and one neutron. When deuterium combines with oxygen, it forms what is called "heavy water" because the deuterium component of the water is twice as heavy as i ...
... Hydrogen usually has a nucleus consisting of only one proton. An isotope of hydrogen called deuterium has a nucleus consisting of one proton and one neutron. When deuterium combines with oxygen, it forms what is called "heavy water" because the deuterium component of the water is twice as heavy as i ...
Chapter 3
... Mass Number and Isotopes • The stable oxygen isotopes provide another example. • 16O is the most abundant stable O isotope. • How many protons and neutrons are in 16O? 8 protons and 8 neutrons 17O is the least abundant stable O isotope. How many protons and neutrons are in 17O? 8 protons and 9 ...
... Mass Number and Isotopes • The stable oxygen isotopes provide another example. • 16O is the most abundant stable O isotope. • How many protons and neutrons are in 16O? 8 protons and 8 neutrons 17O is the least abundant stable O isotope. How many protons and neutrons are in 17O? 8 protons and 9 ...
Chapter 3
... Mass Number and Isotopes • The stable oxygen isotopes provide another example. • 16O is the most abundant stable O isotope. • How many protons and neutrons are in 16O? 8 protons and 8 neutrons 17O is the least abundant stable O isotope. How many protons and neutrons are in 17O? 8 protons and 9 ...
... Mass Number and Isotopes • The stable oxygen isotopes provide another example. • 16O is the most abundant stable O isotope. • How many protons and neutrons are in 16O? 8 protons and 8 neutrons 17O is the least abundant stable O isotope. How many protons and neutrons are in 17O? 8 protons and 9 ...
Isotope Worksheet
... The number of protons in a nucleus determines the identity of the element. For example, any atom having 6 protons will be a "carbon" atom. If we were to add an extra proton to the nucleus, we would have an entirely different element. For example, ! ...
... The number of protons in a nucleus determines the identity of the element. For example, any atom having 6 protons will be a "carbon" atom. If we were to add an extra proton to the nucleus, we would have an entirely different element. For example, ! ...
Isotope Worksheet
... The number of protons in a nucleus determines the identity of the element. For example, any atom having 6 protons will be a "carbon" atom. If we were to add an extra proton to the nucleus, we would have an entirely different element. For example, C (6 protons) + 1 proton ...
... The number of protons in a nucleus determines the identity of the element. For example, any atom having 6 protons will be a "carbon" atom. If we were to add an extra proton to the nucleus, we would have an entirely different element. For example, C (6 protons) + 1 proton ...
Nurse Shark (Ginglymostoma cirratum)
... that are common on earth and there is always some radiation present in every environment – Radiation is the term used to describe the particles and/or energy that are emitted during nuclear decay (Alpha, and beta particles, and ...
... that are common on earth and there is always some radiation present in every environment – Radiation is the term used to describe the particles and/or energy that are emitted during nuclear decay (Alpha, and beta particles, and ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide Physical Science 1. The word atom comes
... 24. If the atomic mass of carbon is 12 amu, 1 mole of pure carbon will have a mass of__________. 25. A mole is an SI base unit that describes the___________. 26. Ionization refers to the process of____________. 27. Group 18 noble gases are inert because___________. 28. Oxygen’s atomic number is 8. T ...
... 24. If the atomic mass of carbon is 12 amu, 1 mole of pure carbon will have a mass of__________. 25. A mole is an SI base unit that describes the___________. 26. Ionization refers to the process of____________. 27. Group 18 noble gases are inert because___________. 28. Oxygen’s atomic number is 8. T ...
Chapter 3
... 2. All atoms of a given element have identical properties that differ from those of other elements. 3. Atoms cannot be created, destroyed, or transformed into atoms of another element. 4. Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine with one another in small wholenumber ratios. 5. T ...
... 2. All atoms of a given element have identical properties that differ from those of other elements. 3. Atoms cannot be created, destroyed, or transformed into atoms of another element. 4. Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine with one another in small wholenumber ratios. 5. T ...
making models of atoms - Mater Academy Charter Middle/ High
... BACKGROUND INFORMATION: An atom is defined as a small particle that makes up most types of matter. Atoms are so mall it would take about 1 million of them lined up in a row to equal the thickness of a human hair. Atoms are made up of even smaller particles. The largest of these particles are protons ...
... BACKGROUND INFORMATION: An atom is defined as a small particle that makes up most types of matter. Atoms are so mall it would take about 1 million of them lined up in a row to equal the thickness of a human hair. Atoms are made up of even smaller particles. The largest of these particles are protons ...
Atomic Structure
... 19. Lead has 4 naturally occurring isotopes. Listed below are symbols for these isotopes along with their percent abundance. Using this information, calculate the “average” atomic mass of Pb. (Note: You may complete this calculation on the back of a one of the sheets in this packet). 122 Pb ...
... 19. Lead has 4 naturally occurring isotopes. Listed below are symbols for these isotopes along with their percent abundance. Using this information, calculate the “average” atomic mass of Pb. (Note: You may complete this calculation on the back of a one of the sheets in this packet). 122 Pb ...
Isotope analysis

Isotope analysis is the identification of isotopic signature, the distribution of certain stable isotopes and chemical elements within chemical compounds. This can be applied to a food web to make it possible to draw direct inferences regarding diet, trophic level, and subsistence. Variations in isotope ratios from isotopic fractionation are measured using mass spectrometry, which separates the different isotopes of an element on the basis of their mass-to-charge ratio.The ratios of isotopic oxygen are also differentially affected by global weather patterns and regional topography as moisture is transported. Areas of lower humidity cause the preferential loss of 18O water in the form of vapor and precipitation. Furthermore, evaporated 16O water returns preferentially to the atmospheric system as it evaporates and 18O remains in liquid form or is incorporated into the body water of plants and animals.