Beyond Element 83 are very unstable (radioactive)
... • All Elements 83 and above on PT are radioactive • Other elements may have radioactive isotopes applet ...
... • All Elements 83 and above on PT are radioactive • Other elements may have radioactive isotopes applet ...
Candidate 2 - Elgin Academy
... The alpha particles are constantly released and knock electrons off the atoms in air. This makes these atoms into ions which are attracted to the negatively charged plate and the electrons are attracted to the positively charged plate generating a small current. When smoke enters the chamber the smo ...
... The alpha particles are constantly released and knock electrons off the atoms in air. This makes these atoms into ions which are attracted to the negatively charged plate and the electrons are attracted to the positively charged plate generating a small current. When smoke enters the chamber the smo ...
How Atoms Differ Elements, Isotopes, and Ions
... Atoms are arranged in order by their atomic #. ...
... Atoms are arranged in order by their atomic #. ...
Isotopes Models
... sometimes called Protium. A hydrogen atom that has one proton and one neutron in its nucleus is called Deuterium. Deuterium is not radioactive. Water made from deuterium is called heavy water because the extra neutron makes it heavier. It is used in nuclear reactors. The third isotope of hydrogen is ...
... sometimes called Protium. A hydrogen atom that has one proton and one neutron in its nucleus is called Deuterium. Deuterium is not radioactive. Water made from deuterium is called heavy water because the extra neutron makes it heavier. It is used in nuclear reactors. The third isotope of hydrogen is ...
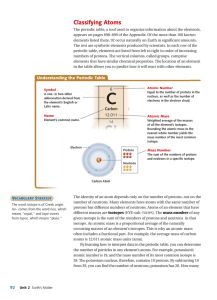
Classifying Atoms
... The periodic table, a tool used to organize information about the elements, appears on pages 698–699 of the Appendix. Of the more than 100 known elements listed there, 92 occur naturally on Earth in significant amounts. The rest are synthetic elements produced by scientists. In each row of the perio ...
... The periodic table, a tool used to organize information about the elements, appears on pages 698–699 of the Appendix. Of the more than 100 known elements listed there, 92 occur naturally on Earth in significant amounts. The rest are synthetic elements produced by scientists. In each row of the perio ...
Lesson Outline - WordPress.com
... up 80.22%. What is the average atomic mass of Boron? 2. Silver has two isotopes, the first has a mass of 106.9 u and an abundance of 51.8%, the second has a mass of 108.9 u and an abundance of 48.2. What is the average atomic mass of ...
... up 80.22%. What is the average atomic mass of Boron? 2. Silver has two isotopes, the first has a mass of 106.9 u and an abundance of 51.8%, the second has a mass of 108.9 u and an abundance of 48.2. What is the average atomic mass of ...
Lecture 2: Atoms - U of L Class Index
... Atmospheric 14C levels increased sharply during testing of nuclear bombs (1955-1963). Since banning the tests, 14C levels decreased. The amount of 14C incorporated in tooth enamel can be used to determine the year in which the enamel was formed and, therefore, the year of birth (to within 1.6 years) ...
... Atmospheric 14C levels increased sharply during testing of nuclear bombs (1955-1963). Since banning the tests, 14C levels decreased. The amount of 14C incorporated in tooth enamel can be used to determine the year in which the enamel was formed and, therefore, the year of birth (to within 1.6 years) ...
Chemistry Notes (pg. # 1)
... The Atomic Mass Unit: 1 a.m.u. is defined to be _____ the mass of a ________ isotope. - In other words, a ________ isotope has a mass of exactly ______ a.m.u. Average Atomic Mass and Relative Abundances of Isotopes: - All isotopes of an element do not have the same _______. - The Average Atomic Mas ...
... The Atomic Mass Unit: 1 a.m.u. is defined to be _____ the mass of a ________ isotope. - In other words, a ________ isotope has a mass of exactly ______ a.m.u. Average Atomic Mass and Relative Abundances of Isotopes: - All isotopes of an element do not have the same _______. - The Average Atomic Mas ...
Unit Test: Atomic Structure
... A. Methane is a compound of carbon and hydrogen. A sample contains 1.2 g of carbon and 0.40 g of hydrogen. What is the mass % of hydrogen in methane? B. Benzene is another compound of carbon and hydrogen. A 78 g sample of bnzene contains 72 g of hydrogen. What is the mass % of hydrogen in benzene? 6 ...
... A. Methane is a compound of carbon and hydrogen. A sample contains 1.2 g of carbon and 0.40 g of hydrogen. What is the mass % of hydrogen in methane? B. Benzene is another compound of carbon and hydrogen. A 78 g sample of bnzene contains 72 g of hydrogen. What is the mass % of hydrogen in benzene? 6 ...
Isotope PPT - MrsPage.com
... • You will be able to determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in different isotopes of the same element. • You will understand that atomic mass • You will understand what radioactivity is the average of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element. • You will be able to give examp ...
... • You will be able to determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in different isotopes of the same element. • You will understand that atomic mass • You will understand what radioactivity is the average of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element. • You will be able to give examp ...
Atomic Structure - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... In nature elements are not made up of atoms that are all exactly the same! Some will be heavier than others, even though they are still the same type of atom. C-12 and C-14 are both Carbon, with all the usual Carbon properties, but the C-14 has two more neutrons, and is heavier. Both Carbons exist i ...
... In nature elements are not made up of atoms that are all exactly the same! Some will be heavier than others, even though they are still the same type of atom. C-12 and C-14 are both Carbon, with all the usual Carbon properties, but the C-14 has two more neutrons, and is heavier. Both Carbons exist i ...
Production of stable isotopes by membrane method
... enrichment methods showed the competitiveness of membrane process. The process was experimentally tested with different multistage systems. The method can be applied for a separation of isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen in natural water. It can be used separately or in combination with other separatio ...
... enrichment methods showed the competitiveness of membrane process. The process was experimentally tested with different multistage systems. The method can be applied for a separation of isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen in natural water. It can be used separately or in combination with other separatio ...
sub
... The gas hydrogen has three isotopes. The most common isotope of hydrogen has a nucleus that is made up of one proton and no neutrons. More than 99% of hydrogen is this isotope. It is sometimes called Protium. A hydrogen atom that has one proton and one neutron in its nucleus is called Deuterium. Deu ...
... The gas hydrogen has three isotopes. The most common isotope of hydrogen has a nucleus that is made up of one proton and no neutrons. More than 99% of hydrogen is this isotope. It is sometimes called Protium. A hydrogen atom that has one proton and one neutron in its nucleus is called Deuterium. Deu ...
File
... Some atomic masses may be written as a decimal (e.g. Carbon is actually 12.01, not ‘12’) This is because some elements have atoms with varying numbers of neutrons in the nucleus. ...
... Some atomic masses may be written as a decimal (e.g. Carbon is actually 12.01, not ‘12’) This is because some elements have atoms with varying numbers of neutrons in the nucleus. ...
Lecture 2
... Who thought of the atom? •Ancient Greek philosophers proposed that all matter consisted of some combination of four elements: air, earth, fire, water. Democritus (~460370 B.C.) disagreed, proposing that all matter could be repeatedly subdivided until an indivisible particle was reached. He called th ...
... Who thought of the atom? •Ancient Greek philosophers proposed that all matter consisted of some combination of four elements: air, earth, fire, water. Democritus (~460370 B.C.) disagreed, proposing that all matter could be repeatedly subdivided until an indivisible particle was reached. He called th ...
14_1_atoms and isotopes FPS3
... You have learned that atoms contain three smaller particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons, and that the number of protons determines the type of atom. How can you figure out how many neutrons an atom contains, and whether it is neutral or has a charge? Once you know how many protons and ne ...
... You have learned that atoms contain three smaller particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons, and that the number of protons determines the type of atom. How can you figure out how many neutrons an atom contains, and whether it is neutral or has a charge? Once you know how many protons and ne ...
Atoms and Isotopes Worksheet
... 4. One isotope of lead has 82 protons and 124 neutrons in its nucleus. What is the number of protons in the nucleus of any other isotope of lead? ...
... 4. One isotope of lead has 82 protons and 124 neutrons in its nucleus. What is the number of protons in the nucleus of any other isotope of lead? ...
12.1 Atoms and Isotopes
... You have learned that atoms contain three smaller particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons, and that the number of protons determines the type of atom. How can you figure out how many neutrons an atom contains, and whether it is neutral or has a charge? Once you know how many protons and ne ...
... You have learned that atoms contain three smaller particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons, and that the number of protons determines the type of atom. How can you figure out how many neutrons an atom contains, and whether it is neutral or has a charge? Once you know how many protons and ne ...
Lecture 2 - U of L Class Index
... An element is defined by its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have mo ...
... An element is defined by its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have mo ...
Subatomic Heavyweights
... Atoms of the same element will ALWAYS have the same number of protons • Atomic weight: the weighted average atomic mass of the naturally occurring isotopes (the # on the periodic table) ...
... Atoms of the same element will ALWAYS have the same number of protons • Atomic weight: the weighted average atomic mass of the naturally occurring isotopes (the # on the periodic table) ...
ISOTOPES 3 SUBATOMIC PARTICLES Proton Located inside the
... Located outside of the nucleus in an “electron cloud” Involved in chemical bonding Negative charge Equal to the # of protons in a neutral atom How many electrons does Potassium have? How many electrons does Nitrogen have? o Neutron Located inside the nucleus of an atom No charge # ...
... Located outside of the nucleus in an “electron cloud” Involved in chemical bonding Negative charge Equal to the # of protons in a neutral atom How many electrons does Potassium have? How many electrons does Nitrogen have? o Neutron Located inside the nucleus of an atom No charge # ...
Chemistry: The Nature of Matter
... o 2nd shell has a little more energy and holds 8 electrons o 3rd shell has even more energy, etc. ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Electron config ...
... o 2nd shell has a little more energy and holds 8 electrons o 3rd shell has even more energy, etc. ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Electron config ...
Lecture 2 - U of L Class Index
... An element is defined by its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have mo ...
... An element is defined by its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have mo ...
Lecture 2
... Atmospheric 14C levels increased sharply during testing of nuclear bombs (1955-1963). Since banning the tests, 14C levels decreased. The amount of 14C incorporated in tooth enamel can be used to determine the year in which the enamel was formed and, therefore, the year of birth (to within 1.6 years) ...
... Atmospheric 14C levels increased sharply during testing of nuclear bombs (1955-1963). Since banning the tests, 14C levels decreased. The amount of 14C incorporated in tooth enamel can be used to determine the year in which the enamel was formed and, therefore, the year of birth (to within 1.6 years) ...
Isotope analysis

Isotope analysis is the identification of isotopic signature, the distribution of certain stable isotopes and chemical elements within chemical compounds. This can be applied to a food web to make it possible to draw direct inferences regarding diet, trophic level, and subsistence. Variations in isotope ratios from isotopic fractionation are measured using mass spectrometry, which separates the different isotopes of an element on the basis of their mass-to-charge ratio.The ratios of isotopic oxygen are also differentially affected by global weather patterns and regional topography as moisture is transported. Areas of lower humidity cause the preferential loss of 18O water in the form of vapor and precipitation. Furthermore, evaporated 16O water returns preferentially to the atmospheric system as it evaporates and 18O remains in liquid form or is incorporated into the body water of plants and animals.