Structure of the Atom
... 4. What structural characteristics do all hydrogen atoms have in common? ...
... 4. What structural characteristics do all hydrogen atoms have in common? ...
Basic Background Review: Acid-Base , Redox, and Stable Isotopes
... thus Stable Isotopes represent an imbedded tag in every molecule for 1) Source and 2) process history ...
... thus Stable Isotopes represent an imbedded tag in every molecule for 1) Source and 2) process history ...
The Band of Stability
... Radioactive decay changes the nature of an atom’s nucleus, and it happens for a reason. Each element from hydrogen (atomic number 1) to lead (atomic number 82) has stable isotopes in which the tendency of protons to repel one another is overcome by attractive nuclear forces. These attractive nuclear ...
... Radioactive decay changes the nature of an atom’s nucleus, and it happens for a reason. Each element from hydrogen (atomic number 1) to lead (atomic number 82) has stable isotopes in which the tendency of protons to repel one another is overcome by attractive nuclear forces. These attractive nuclear ...
atoms - Groupfusion.net
... Normally, this is the same for every atom of an element, therefore number of protons identifies the element. In a “normal”, neutral atom, number of protons = number of electrons Mass Number = the number of protons + number of neutrons = A Number of neutrons in an atom of an element can vary. These a ...
... Normally, this is the same for every atom of an element, therefore number of protons identifies the element. In a “normal”, neutral atom, number of protons = number of electrons Mass Number = the number of protons + number of neutrons = A Number of neutrons in an atom of an element can vary. These a ...
Isotopes and Ions - Wando High School
... Isotope Example Naturally occurring carbon consists of three isotopes, 14N, 15N, and 16N. State the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in each of these carbon atoms. 14N ...
... Isotope Example Naturally occurring carbon consists of three isotopes, 14N, 15N, and 16N. State the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in each of these carbon atoms. 14N ...
Isotopes
... left of the chemical symbol, For iron (Fe) we have, for example: 54Fe, 56Fe, 57Fe, and 58Fe. Since the iron has the atomic number zFe = 26, we have 54 - 26 = 28 neutrons in 54Fe, and 30, 31, and 32 neutrons, respectively, in the other three isotopes given. Isotopes come in two basic variants: 1. Rad ...
... left of the chemical symbol, For iron (Fe) we have, for example: 54Fe, 56Fe, 57Fe, and 58Fe. Since the iron has the atomic number zFe = 26, we have 54 - 26 = 28 neutrons in 54Fe, and 30, 31, and 32 neutrons, respectively, in the other three isotopes given. Isotopes come in two basic variants: 1. Rad ...
Practice questions
... a) neutrons. b) atomic number. c) nuclear charge. d) electron configuration. e) number of protons. ...
... a) neutrons. b) atomic number. c) nuclear charge. d) electron configuration. e) number of protons. ...
Isotopes
... 1. Use Video #5 – to take notes over isotopes on the back of your paper from today. Then write the paragraph at the bottom of the page. 2. Study for quiz tomorrow! (over scientists and subatomic particles) REMINDERS ...
... 1. Use Video #5 – to take notes over isotopes on the back of your paper from today. Then write the paragraph at the bottom of the page. 2. Study for quiz tomorrow! (over scientists and subatomic particles) REMINDERS ...
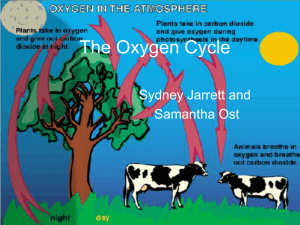
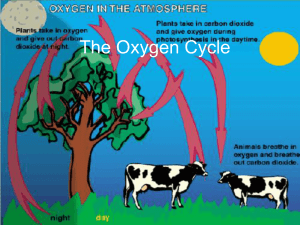
The Oxygen Cycle - EDHSGreenSea.net
... off in plants. • Plants use photosynthesis to produce carbohydrates and oxygen • Plants “breathe” in carbon dioxide and “breathe” out oxygen ...
... off in plants. • Plants use photosynthesis to produce carbohydrates and oxygen • Plants “breathe” in carbon dioxide and “breathe” out oxygen ...
The Oxygen Cycle
... • When the water in a steam enters a pond, microorganisms in the pond begin to break down organic matter, consuming oxygen in the process. ...
... • When the water in a steam enters a pond, microorganisms in the pond begin to break down organic matter, consuming oxygen in the process. ...
MASS-INDEPENDENT ISOTOPE FRACTIONATION OF CHROMIUM
... Cr anomalies observed in primitive meteorites and planetary bodies [9,10] are now accepted as widespread nebula wide phenomena. There are some unresolved issues in Cr isotope cosmochemistry, however. For example 54Cr anomalies were observed by one laboratory [9] but not by the other [7] in the same ...
... Cr anomalies observed in primitive meteorites and planetary bodies [9,10] are now accepted as widespread nebula wide phenomena. There are some unresolved issues in Cr isotope cosmochemistry, however. For example 54Cr anomalies were observed by one laboratory [9] but not by the other [7] in the same ...
Rhenium isotopes in geochronology Stable isotope Relative atomic
... neutron – an elementary particle with no net charge and a rest mass of about 1.675 × 10–27 kg, slightly more than that of the proton. All atoms contain neutrons in their nucleus except for protium (1H). normal material – a reasonably possible source for an element or its compounds in commerce, for ...
... neutron – an elementary particle with no net charge and a rest mass of about 1.675 × 10–27 kg, slightly more than that of the proton. All atoms contain neutrons in their nucleus except for protium (1H). normal material – a reasonably possible source for an element or its compounds in commerce, for ...
2.1 The Nature of Matter - Sonoma Valley High School
... 24+ elements are found in living things (of 100+ elements) Some elements have isotopes, with different #s of neutrons and different mass. All isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties b/c their electrons are the same. ...
... 24+ elements are found in living things (of 100+ elements) Some elements have isotopes, with different #s of neutrons and different mass. All isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties b/c their electrons are the same. ...
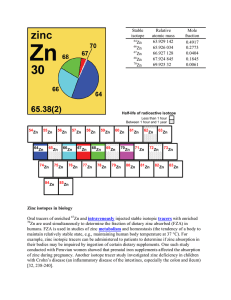
Zinc isotopes in biology Oral tracers of enriched Zn and
... they are now used rarely because of radiation hazards [32, 241-243]. ZnO nanoparticles enriched with 67Zn are being studied for use as biological/environmental nanotoxicity tracers [32, 244]. Zinc isotopes in Earth/planetary science Molecules, atoms, and ions of the stable isotopes of zinc possess s ...
... they are now used rarely because of radiation hazards [32, 241-243]. ZnO nanoparticles enriched with 67Zn are being studied for use as biological/environmental nanotoxicity tracers [32, 244]. Zinc isotopes in Earth/planetary science Molecules, atoms, and ions of the stable isotopes of zinc possess s ...
Isotope Notes
... a. NUCLEAR DECAY is a nuclear reaction (not chemical) in which energy or particles are ____________________ (given off) from the nucleus. i. Result is a more stable nucleus. b. ______________________ is the particles and/or energy that are emitted during nuclear decay. i. It can include: ...
... a. NUCLEAR DECAY is a nuclear reaction (not chemical) in which energy or particles are ____________________ (given off) from the nucleus. i. Result is a more stable nucleus. b. ______________________ is the particles and/or energy that are emitted during nuclear decay. i. It can include: ...
The discovery of the natural radioactive decay of uranium in 1896 by
... process in which an isotope (the parent) loses particles from its nucleus to form an isotope of a new element (the daughter). The rate of decay is conveniently expressed in terms of an isotope's half-life, or the time it takes for one-half of a particular radioactive isotope in a sample to decay. Mo ...
... process in which an isotope (the parent) loses particles from its nucleus to form an isotope of a new element (the daughter). The rate of decay is conveniently expressed in terms of an isotope's half-life, or the time it takes for one-half of a particular radioactive isotope in a sample to decay. Mo ...
Worksheet
... 15. __________ He used the term “atomos” to describe an indivisible part at the base of all matter. 16. __________ He is the Father of the Atomic Theory. 17. __________ He designed a mathematical equation for the model of the atom. 18. __________ He determined the charge of the electron. 19. _______ ...
... 15. __________ He used the term “atomos” to describe an indivisible part at the base of all matter. 16. __________ He is the Father of the Atomic Theory. 17. __________ He designed a mathematical equation for the model of the atom. 18. __________ He determined the charge of the electron. 19. _______ ...
Global temperature vs. years as extracted from an Antarctic ice core
... two forms, called isotopes.The two isotopes are oxygen-16 (written 16O) and oxygen-18 (written 18O).They are the same chemically, but they have slightly different weights. 18O is slightly heavier than 16O.The proportion of these two isotopes in snow depends on average global temperatures. Snow that ...
... two forms, called isotopes.The two isotopes are oxygen-16 (written 16O) and oxygen-18 (written 18O).They are the same chemically, but they have slightly different weights. 18O is slightly heavier than 16O.The proportion of these two isotopes in snow depends on average global temperatures. Snow that ...
Nuclear Power Plant Notes
... travel many meters in air and many centimeters in human tissue. It readily penetrates most materials and is sometimes called "penetrating radiation." ...
... travel many meters in air and many centimeters in human tissue. It readily penetrates most materials and is sometimes called "penetrating radiation." ...
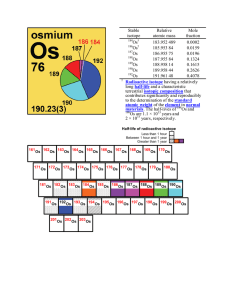
Stable isotope Relative atomic mass Mole fraction Os 183.952 489
... number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is the atomic number. radioactive decay – the process by which unstable (or radioactive) isotopes lose energy by emitting alpha particles (helium nuclei), beta particles (positive or negative electrons), gamma radiation, neutrons or protons to reach a fina ...
... number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is the atomic number. radioactive decay – the process by which unstable (or radioactive) isotopes lose energy by emitting alpha particles (helium nuclei), beta particles (positive or negative electrons), gamma radiation, neutrons or protons to reach a fina ...
Chemical Basis of Life
... 3- Atoms – the word comes from the Latin word atomos, which means indivisible. An atom is the simplest part of an element that contains all of the properties of the element. It would take 3 million carbon atoms lined next to each other to be the size of the period at the end of this sentence. 4- Al ...
... 3- Atoms – the word comes from the Latin word atomos, which means indivisible. An atom is the simplest part of an element that contains all of the properties of the element. It would take 3 million carbon atoms lined next to each other to be the size of the period at the end of this sentence. 4- Al ...
Intro Biochemistry/Ecology
... Acidic solutions contain higher concentrations of H+ ions than pure water and have pH values below 7. Basic, or alkaline, solutions contain lower concentrations of H+ ions than pure water and have pH values above 7. Chapter 3 Essential Learning Keys Section 3-2: Energy Flow Sunlight is the main ener ...
... Acidic solutions contain higher concentrations of H+ ions than pure water and have pH values below 7. Basic, or alkaline, solutions contain lower concentrations of H+ ions than pure water and have pH values above 7. Chapter 3 Essential Learning Keys Section 3-2: Energy Flow Sunlight is the main ener ...
Isotope analysis

Isotope analysis is the identification of isotopic signature, the distribution of certain stable isotopes and chemical elements within chemical compounds. This can be applied to a food web to make it possible to draw direct inferences regarding diet, trophic level, and subsistence. Variations in isotope ratios from isotopic fractionation are measured using mass spectrometry, which separates the different isotopes of an element on the basis of their mass-to-charge ratio.The ratios of isotopic oxygen are also differentially affected by global weather patterns and regional topography as moisture is transported. Areas of lower humidity cause the preferential loss of 18O water in the form of vapor and precipitation. Furthermore, evaporated 16O water returns preferentially to the atmospheric system as it evaporates and 18O remains in liquid form or is incorporated into the body water of plants and animals.