Formation of the Most Distant & Luminous Quasars
... reproduces the observed properties of SDSSJ1148+5251 in the LCDM cosmology. – Both BHs and host galaxies build up through hierarchical mergers. – BHs accrete gas under Eddington limit in a selfregulated manner owing to feedback. • Our model should provide a viable mechanism for other luminous quasar ...
... reproduces the observed properties of SDSSJ1148+5251 in the LCDM cosmology. – Both BHs and host galaxies build up through hierarchical mergers. – BHs accrete gas under Eddington limit in a selfregulated manner owing to feedback. • Our model should provide a viable mechanism for other luminous quasar ...
Large-scale, Optical/Near-IR Galaxy Surveys with a 4
... distribution of an L* galaxy (Re~2-4 kpc) can be mapped in detail. The spectrograph will consists of ~10 multi-object spectrographs each having a digital micro-mirror device (DMD) to isolate galaxies for spectroscopy, and each DMD consisting of a 2Kx1K array of 0.25x0.25 micromirrors. The spectr ...
... distribution of an L* galaxy (Re~2-4 kpc) can be mapped in detail. The spectrograph will consists of ~10 multi-object spectrographs each having a digital micro-mirror device (DMD) to isolate galaxies for spectroscopy, and each DMD consisting of a 2Kx1K array of 0.25x0.25 micromirrors. The spectr ...
10) Physics and Chemistry of the Diffuse Interstellar Medium
... • One of the first interstellar molecules that were discovered (McKellar PASP 1940) (actually Interstellar molecule no 2, after CH in 1937) ...
... • One of the first interstellar molecules that were discovered (McKellar PASP 1940) (actually Interstellar molecule no 2, after CH in 1937) ...
the first three thresholds - McGraw
... Then they explain how something appeared out of nothing. Many of them insist that a creator made the world, but always there is the nagging problem: How was the creator created? Or, to put it more generally, how did something come out of nothing We will see that the account of origin contained withi ...
... Then they explain how something appeared out of nothing. Many of them insist that a creator made the world, but always there is the nagging problem: How was the creator created? Or, to put it more generally, how did something come out of nothing We will see that the account of origin contained withi ...
The Case for a Kilometer-Scale High Energy Neutrino Detector
... stronger if the source luminosity were increasing with z, i.e. cosmic ray sources were more active at large redshifts – ‘bright phase’ models. Early speculations on bright phase models led to the suggestion of kilometer-scale neutrino detectors over a decade ago[2]. The other guaranteed extraterrest ...
... stronger if the source luminosity were increasing with z, i.e. cosmic ray sources were more active at large redshifts – ‘bright phase’ models. Early speculations on bright phase models led to the suggestion of kilometer-scale neutrino detectors over a decade ago[2]. The other guaranteed extraterrest ...
Image filtering
... Optimizing SExtractor performance • Execution speed Current rule of thumb: ~1Mpix/s per GHz at high galactic latitude • Turns out to be I/O-limited in some cases: might be useful to use different devices for reading and writing data • In crowded fields, limited by source-density: 500+ extractions ...
... Optimizing SExtractor performance • Execution speed Current rule of thumb: ~1Mpix/s per GHz at high galactic latitude • Turns out to be I/O-limited in some cases: might be useful to use different devices for reading and writing data • In crowded fields, limited by source-density: 500+ extractions ...
URL - StealthSkater
... a. String-like objects -- with string tension of same order of magnitude as possessed by the cosmic strings of GUTs -- have a crucial role in TGD-inspired model for the galaxy formation and in the TGD-based cosmology. b. The so-called massless extremals describe nonlinear plane waves propagating wit ...
... a. String-like objects -- with string tension of same order of magnitude as possessed by the cosmic strings of GUTs -- have a crucial role in TGD-inspired model for the galaxy formation and in the TGD-based cosmology. b. The so-called massless extremals describe nonlinear plane waves propagating wit ...
PILE22_1.20040629144..
... A gas is ionized when one or more electrons are removed from some of its atoms. Ionization produces ion pairs which consist of positive ions and free electrons. ...
... A gas is ionized when one or more electrons are removed from some of its atoms. Ionization produces ion pairs which consist of positive ions and free electrons. ...
Chapter 2 Observing the Electromagnetic Spectrum
... This nuisance radiation is also minimized by cooling and reducing the surface area along the optical path of instruments. The Near-IR background sky is also very bright and highly variable on short time scales. Observations from the excellent ground-based IR sites of the Antarctic, Chile and Mauna K ...
... This nuisance radiation is also minimized by cooling and reducing the surface area along the optical path of instruments. The Near-IR background sky is also very bright and highly variable on short time scales. Observations from the excellent ground-based IR sites of the Antarctic, Chile and Mauna K ...
The formation and evolution of galaxies
... • Overcooling leads to the formation of hundreds more small galaxies than are observed. ...
... • Overcooling leads to the formation of hundreds more small galaxies than are observed. ...
cosmo_01_overview - Mullard Space Science Laboratory
... What is to be covered in the course: • Galaxies: – what they are, the different types, clustering – high redshift quasars, giant starbursts and evolution ...
... What is to be covered in the course: • Galaxies: – what they are, the different types, clustering – high redshift quasars, giant starbursts and evolution ...
The PAMELA Space Experiment
... ZZ: in this scenario not only such a signal would be visible by PAMELA but also be consistent with the increase of positrons measured by HEAT [Barwick 1999]. In conclusion a detailed measurement of the positron spectrum, its spectral features and its dependence from solar modulation will either prov ...
... ZZ: in this scenario not only such a signal would be visible by PAMELA but also be consistent with the increase of positrons measured by HEAT [Barwick 1999]. In conclusion a detailed measurement of the positron spectrum, its spectral features and its dependence from solar modulation will either prov ...
Interpretation of the evolution of universe through the consciousness
... die, and probably will die," Dr. Linde [16] said, "but the universe as a whole is immortal." Some theorists suggest that the Big Bang was not so much a birth as a transition, a "quantum leap" from some formless era of imaginary time, or from nothing at all. According to Heisenberg’s uncertainty prin ...
... die, and probably will die," Dr. Linde [16] said, "but the universe as a whole is immortal." Some theorists suggest that the Big Bang was not so much a birth as a transition, a "quantum leap" from some formless era of imaginary time, or from nothing at all. According to Heisenberg’s uncertainty prin ...
The Hubble Law
... would produce the observed red-shift if velocity were really the cause of the red-shifts. The formula states that galaxy speed increases linearly with distance outward into space. The Hubble relation is much used to measure galaxy distances on the scale of billions of light years. First, in this tec ...
... would produce the observed red-shift if velocity were really the cause of the red-shifts. The formula states that galaxy speed increases linearly with distance outward into space. The Hubble relation is much used to measure galaxy distances on the scale of billions of light years. First, in this tec ...
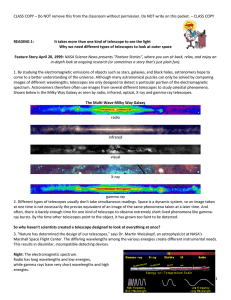
unit a activity 4d - telescopes - student readings-klh.ss
... somehow interpret the energy emitted from astronomical objects. This energy is in the form of electromagnetic waves. Although the first telescope was created 400 years ago, we didn't have a complete picture of the electromagnetic spectrum until the early part of this century. As our knowledge of phy ...
... somehow interpret the energy emitted from astronomical objects. This energy is in the form of electromagnetic waves. Although the first telescope was created 400 years ago, we didn't have a complete picture of the electromagnetic spectrum until the early part of this century. As our knowledge of phy ...
Masers (Microwave Amplification by Stimulated Electromagnetic
... What this means is that a molecule is in a certain environment where its outer electrons are in a high energy state and is bombarded by a photon (in this case a microwave) which causes the electrons to ‘jump down’ in energy level and release another photon so that both photons have the same phase, f ...
... What this means is that a molecule is in a certain environment where its outer electrons are in a high energy state and is bombarded by a photon (in this case a microwave) which causes the electrons to ‘jump down’ in energy level and release another photon so that both photons have the same phase, f ...
Astro-2: History of the Universe
... • Redshifts can be measured very precisely, much more precisely than you know your height!!! For this reason astronomers generally say a galaxy is at a redshift z=0.4231, rather than quoting its distance • Distances can be known only to about 5% • In cosmology, as in all of physics, measurements ...
... • Redshifts can be measured very precisely, much more precisely than you know your height!!! For this reason astronomers generally say a galaxy is at a redshift z=0.4231, rather than quoting its distance • Distances can be known only to about 5% • In cosmology, as in all of physics, measurements ...
CANGAROO and VHE γ-ray Astronomy: Past, present and future
... difficulty to obtain signal in spite of long-continued efforts : • PKS2155-304 (necessary to be blessed by outburst) ...
... difficulty to obtain signal in spite of long-continued efforts : • PKS2155-304 (necessary to be blessed by outburst) ...
Calculations of Gamma Ray Dose from Gamma Ray Bursters and
... Gamma ray bursters (GRB) were first identified over 30 years ago but their origin was unknown until very recently. There is a growing consensus that they are the result of extremely high-energy supernovae events that have been dubbed “GRB” and they can be detected at cosmological distances, but many ...
... Gamma ray bursters (GRB) were first identified over 30 years ago but their origin was unknown until very recently. There is a growing consensus that they are the result of extremely high-energy supernovae events that have been dubbed “GRB” and they can be detected at cosmological distances, but many ...
non-locality, consciousness and the emerging new
... used to measure the Hubble flow and overall structure of the universe cannot be unequivocally determined independently of the cosmology framework itself (Kafatos ...
... used to measure the Hubble flow and overall structure of the universe cannot be unequivocally determined independently of the cosmology framework itself (Kafatos ...
P1 09 Red Shift - Animated Science
... Some people think that Penzias and Wilson’s discovery of cosmic microwave background radiation was just lucky. Others disagree. What do you think? Give reasons for your answer. ...
... Some people think that Penzias and Wilson’s discovery of cosmic microwave background radiation was just lucky. Others disagree. What do you think? Give reasons for your answer. ...
© Taganov I
... studies [1-5] termed Hydro-Gravitational-Dynamics (HGD). Standard cold-dark-matter hierarchicalclustering (CDMHC) cosmological models neglect critically important HGD concepts such as viscosity1, diffusion2, turbulence3, fossil turbulence4 and fossil turbulence waves5, and should be abandoned [6-10] ...
... studies [1-5] termed Hydro-Gravitational-Dynamics (HGD). Standard cold-dark-matter hierarchicalclustering (CDMHC) cosmological models neglect critically important HGD concepts such as viscosity1, diffusion2, turbulence3, fossil turbulence4 and fossil turbulence waves5, and should be abandoned [6-10] ...
(PDF, Unknown) - Natural Philosophy Alliance
... might expect. Note that the cosmic background radiation is nonisotropic and shows variations reflecting the matter distribution in space as shown in additional COBE satellite data in Fig. 5. In summary the derived radial term of the electrodynamic force of gravity is not only able to predict the obs ...
... might expect. Note that the cosmic background radiation is nonisotropic and shows variations reflecting the matter distribution in space as shown in additional COBE satellite data in Fig. 5. In summary the derived radial term of the electrodynamic force of gravity is not only able to predict the obs ...
A Map of the Universe
... picture, at a scale of 1/108 , shows the entire Earth. The 14th picture, at a scale of 1/1014 , shows the entire Solar system. The 18th picture, at a scale of 1/1018 , includes α Centauri, The 22nd picture, at a scale of 1/1022 shows all of the Milky Way Galaxy. The 26th and last picture in the sequ ...
... picture, at a scale of 1/108 , shows the entire Earth. The 14th picture, at a scale of 1/1014 , shows the entire Solar system. The 18th picture, at a scale of 1/1018 , includes α Centauri, The 22nd picture, at a scale of 1/1022 shows all of the Milky Way Galaxy. The 26th and last picture in the sequ ...
LIGO Listens for Gravitational Waves
... Finding an optical/radio/X-ray/neutrino transient will put the GW event candidate in an astronomical context Much more science! May be able to confidently detect a somewhat weaker GW event (spectral) Localize in a host galaxy (or outside!) Compare GW and electromagnetic emissions: strength, time, et ...
... Finding an optical/radio/X-ray/neutrino transient will put the GW event candidate in an astronomical context Much more science! May be able to confidently detect a somewhat weaker GW event (spectral) Localize in a host galaxy (or outside!) Compare GW and electromagnetic emissions: strength, time, et ...
Cosmic microwave background
The cosmic microwave background (CMB) is the thermal radiation left over from the time of recombination in Big Bang cosmology. In older literature, the CMB is also variously known as cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBR) or ""relic radiation."" The CMB is a cosmic background radiation that is fundamental to observational cosmology because it is the oldest light in the universe, dating to the epoch of recombination. With a traditional optical telescope, the space between stars and galaxies (the background) is completely dark. However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope shows a faint background glow, almost exactly the same in all directions, that is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the radio spectrum. The accidental discovery of CMB in 1964 by American radio astronomers Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s, and earned the discoverers the 1978 Nobel Prize.The CMB is a snapshot of the oldest light in our Universe, imprinted on the sky when the Universe was just 380,000 years old. It shows tiny temperature fluctuations that correspond to regions of slightly different densities, representing the seeds of all future structure: the stars and galaxies of today.The CMB is well explained as radiation left over from an early stage in the development of the universe, and its discovery is considered a landmark test of the Big Bang model of the universe. When the universe was young, before the formation of stars and planets, it was denser, much hotter, and filled with a uniform glow from a white-hot fog of hydrogen plasma. As the universe expanded, both the plasma and the radiation filling it grew cooler. When the universe cooled enough, protons and electrons combined to form neutral atoms. These atoms could no longer absorb the thermal radiation, and so the universe became transparent instead of being an opaque fog. Cosmologists refer to the time period when neutral atoms first formed as the recombination epoch, and the event shortly afterwards when photons started to travel freely through space rather than constantly being scattered by electrons and protons in plasma is referred to as photon decoupling. The photons that existed at the time of photon decoupling have been propagating ever since, though growing fainter and less energetic, since the expansion of space causes their wavelength to increase over time (and wavelength is inversely proportional to energy according to Planck's relation). This is the source of the alternative term relic radiation. The surface of last scattering refers to the set of points in space at the right distance from us so that we are now receiving photons originally emitted from those points at the time of photon decoupling.Precise measurements of the CMB are critical to cosmology, since any proposed model of the universe must explain this radiation. The CMB has a thermal black body spectrum at a temperature of 7000272548000000000♠2.72548±0.00057 K. The spectral radiance dEν/dν peaks at 160.2 GHz, in the microwave range of frequencies. (Alternatively if spectral radiance is defined as dEλ/dλ then the peak wavelength is 1.063 mm.) The glow is very nearly uniform in all directions, but the tiny residual variations show a very specific pattern, the same as that expected of a fairly uniformly distributed hot gas that has expanded to the current size of the universe. In particular, the spectral radiance at different angles of observation in the sky contains small anisotropies, or irregularities, which vary with the size of the region examined. They have been measured in detail, and match what would be expected if small thermal variations, generated by quantum fluctuations of matter in a very tiny space, had expanded to the size of the observable universe we see today. This is a very active field of study, with scientists seeking both better data (for example, the Planck spacecraft) and better interpretations of the initial conditions of expansion. Although many different processes might produce the general form of a black body spectrum, no model other than the Big Bang has yet explained the fluctuations. As a result, most cosmologists consider the Big Bang model of the universe to be the best explanation for the CMB.The high degree of uniformity throughout the observable universe and its faint but measured anisotropy lend strong support for the Big Bang model in general and the ΛCDM (""Lambda Cold Dark Matter"") model in particular. Moreover, the fluctuations are coherent on angular scales that are larger than the apparent cosmological horizon at recombination. Either such coherence is acausally fine-tuned, or cosmic inflation occurred.