The Doppler Effect in Astronomy and Cosmology
... The Doppler Effect for Sound Now the Flash starts running away from the radio. ...
... The Doppler Effect for Sound Now the Flash starts running away from the radio. ...
The Formation of High Mass Stars
... For hyperbolic systems, such as the advection component of fluid dynamics, explicit difference schemes can be used which minimize communication — A serial algorithm can proceed one grid at a time — A parallel algorithm can process many grids at once. Library support for this approach is provided by ...
... For hyperbolic systems, such as the advection component of fluid dynamics, explicit difference schemes can be used which minimize communication — A serial algorithm can proceed one grid at a time — A parallel algorithm can process many grids at once. Library support for this approach is provided by ...
On the Electrodynamics of the Big Bang Universe - SLAC
... of gravitational collapse of an entire pre-galactic/preQuasar plasma cloud, storing it in a Storage Ring, which defines the galactic/quasar central engine. It is this SMF Central Engine (see the Figures) which produces jets and galactic spiral arms, and the phenomena of quasars, galaxies and gamma r ...
... of gravitational collapse of an entire pre-galactic/preQuasar plasma cloud, storing it in a Storage Ring, which defines the galactic/quasar central engine. It is this SMF Central Engine (see the Figures) which produces jets and galactic spiral arms, and the phenomena of quasars, galaxies and gamma r ...
Herschel-ATLAS: SDSS cross-correlation induced by weak lensing
... We report a highly significant spatial correlation between galaxies with S350μm ≥30 mJy detected in the equatorial fields of the Herschel Astrophysical Terahertz Large Area Survey (H-ATLAS) with estimated redshift >1.5 and SDSS galaxies at 0.2 ≤ z ≤ 0.6. The significance of the cross-correlation is ...
... We report a highly significant spatial correlation between galaxies with S350μm ≥30 mJy detected in the equatorial fields of the Herschel Astrophysical Terahertz Large Area Survey (H-ATLAS) with estimated redshift >1.5 and SDSS galaxies at 0.2 ≤ z ≤ 0.6. The significance of the cross-correlation is ...
Studying the Universe Studying the Universe
... required for the Earth to revolve once around the sun. A month is roughly the amount of time required for the moon to revolve once around the Earth. A day is the time required for the Earth to rotate once on its axis. In the early Roman calendar, a year had exactly 365 days. The calendar worked well ...
... required for the Earth to revolve once around the sun. A month is roughly the amount of time required for the moon to revolve once around the Earth. A day is the time required for the Earth to rotate once on its axis. In the early Roman calendar, a year had exactly 365 days. The calendar worked well ...
gravitational wave Universe - UO Physics
... other emit gravitational waves causing them to gradually approach each other over billions of years. Gravitational waves are produced during the final fraction of a second before the merger of the two black holes. During the merger, the black holes collide at nearly one-half the speed of light to fo ...
... other emit gravitational waves causing them to gradually approach each other over billions of years. Gravitational waves are produced during the final fraction of a second before the merger of the two black holes. During the merger, the black holes collide at nearly one-half the speed of light to fo ...
Magnetic Monopoles
... There are theoretical limits on the flux of heavy MM from the galactic MF Monopole, Astrophysics and Cosmic Ray Observatory (MACRO) searched for superheavy MM in the beta < 1 range. ...
... There are theoretical limits on the flux of heavy MM from the galactic MF Monopole, Astrophysics and Cosmic Ray Observatory (MACRO) searched for superheavy MM in the beta < 1 range. ...
First life in primordial-planet oceans: the
... Wickramasinghe, 2010) provides the logical mechanism for distribution of the seeds of life, but how are sufficient numbers of comets and meteors formed? How, when, and where did life begin in the first place, how widely is it distributed, and are life forms likely to be similar everywhere? In earlie ...
... Wickramasinghe, 2010) provides the logical mechanism for distribution of the seeds of life, but how are sufficient numbers of comets and meteors formed? How, when, and where did life begin in the first place, how widely is it distributed, and are life forms likely to be similar everywhere? In earlie ...
Scientific Evidence for A
... the seventh day God completed His work which He had done; and He rested on the seventh day from all His work which He had done. Then God blessed the seventh day and sanctified it, because in it He rested from all His work which God had created and made. This is the account of the heavens and the ear ...
... the seventh day God completed His work which He had done; and He rested on the seventh day from all His work which He had done. Then God blessed the seventh day and sanctified it, because in it He rested from all His work which God had created and made. This is the account of the heavens and the ear ...
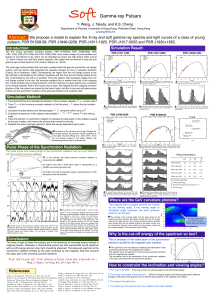
Soft Gamma-ray Pulsars
... light cylinder is dominated by the outflow of particles and that from the null charge surface to the star is dominated by the inflow of particles. Since the electric field decreases rapidly from the null charge surface to the star, the incoming radiation flux is weaker than that of the outgoing flux ...
... light cylinder is dominated by the outflow of particles and that from the null charge surface to the star is dominated by the inflow of particles. Since the electric field decreases rapidly from the null charge surface to the star, the incoming radiation flux is weaker than that of the outgoing flux ...
An Alternative Cosmology to the Big Bang–Dispersive Extinction
... the sky to be blue. Since the space medium absorbs and scatters the blue light more than it does the red component, the Gaussian peak of a spectral line would shift towards the red side, resulting in a spectral redshift. No global galactic movement is needed in this theory to explain the cosmic reds ...
... the sky to be blue. Since the space medium absorbs and scatters the blue light more than it does the red component, the Gaussian peak of a spectral line would shift towards the red side, resulting in a spectral redshift. No global galactic movement is needed in this theory to explain the cosmic reds ...
Results from the High Resolution Fly`s Eye Experiment - CEA-Irfu
... • For isotropic model, get good agreement. • For local LSS model get poor agreement. • Exclude correlation at 95% c.l. for θs < 10°, E ≥ 40 EeV ...
... • For isotropic model, get good agreement. • For local LSS model get poor agreement. • Exclude correlation at 95% c.l. for θs < 10°, E ≥ 40 EeV ...
the effect of an soft X-ray source near the compact object in LS 5039
... In Y&T 2010, e± scattered off stellar photons → each flux modulates by the anisotropy of IC scattering In this study, they scatter off isotropic photons → emerging photons with GeV & keV have isotropic distribution → No modulation in GeV & X-ray band ...
... In Y&T 2010, e± scattered off stellar photons → each flux modulates by the anisotropy of IC scattering In this study, they scatter off isotropic photons → emerging photons with GeV & keV have isotropic distribution → No modulation in GeV & X-ray band ...
Detecting g-ray Sources - Pennsylvania State University
... Search in spatial and time domain Examine >50 time intervals from < 1 msec to 2 hrs to days, weeks, months Shortest time intervals (< 1 sec) use starting times of the single events Longer time intervals are oversampled by factor of two Monte Carlo is used to access trials penalty of oversampling ...
... Search in spatial and time domain Examine >50 time intervals from < 1 msec to 2 hrs to days, weeks, months Shortest time intervals (< 1 sec) use starting times of the single events Longer time intervals are oversampled by factor of two Monte Carlo is used to access trials penalty of oversampling ...
Ch 33) Astrophysics and Cosmology
... galaxies as they appeared then, 13.4 billion years ago, which is when they emitted this light. The most distant galaxies were young and small and grew to become large galaxies by colliding and merging with other small galaxies. We examine the latest theories on how stars and galaxies form and evolve ...
... galaxies as they appeared then, 13.4 billion years ago, which is when they emitted this light. The most distant galaxies were young and small and grew to become large galaxies by colliding and merging with other small galaxies. We examine the latest theories on how stars and galaxies form and evolve ...
What does a spark chamber detect?
... intensity" would change at different times during the day, due to the fact that the Earth is spinning on it's own axis. No such variation is observed. Indeed the cosmic ray intensity on all points on the Earth's surface are roughly the same, at all times during the day. Therefore it is thought cosmi ...
... intensity" would change at different times during the day, due to the fact that the Earth is spinning on it's own axis. No such variation is observed. Indeed the cosmic ray intensity on all points on the Earth's surface are roughly the same, at all times during the day. Therefore it is thought cosmi ...
Ionizing particle fluxes in the near
... Figure 1: Average fluxes of charged particles in the atmosphere: observational and simulated results. P > 950 g/cm2 due to contribution of the ground radioactivity [7]. Lower panel of Fig. 2 presents the results of X-ray measurements. The X-ray fluxes at Murmansk and Moscow regions do not differ at P ...
... Figure 1: Average fluxes of charged particles in the atmosphere: observational and simulated results. P > 950 g/cm2 due to contribution of the ground radioactivity [7]. Lower panel of Fig. 2 presents the results of X-ray measurements. The X-ray fluxes at Murmansk and Moscow regions do not differ at P ...
English Summary
... 000 000 000 kilometers from Earth, which is actually quite near. Most of these galaxies contain the nearest and also lowest luminosity AGN that can be studied. In order to detect even weak signatures of black hole activity, we have used telescopes that detect X-ray and radio waves. At these waveleng ...
... 000 000 000 kilometers from Earth, which is actually quite near. Most of these galaxies contain the nearest and also lowest luminosity AGN that can be studied. In order to detect even weak signatures of black hole activity, we have used telescopes that detect X-ray and radio waves. At these waveleng ...
Lecture01-ASTA01 - University of Toronto
... experience and imagination, seeking to understand the structure of the universe. (that’s coming in ASTA02, next term!) ...
... experience and imagination, seeking to understand the structure of the universe. (that’s coming in ASTA02, next term!) ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... The Expanding Universe • Appears the universe “exploded” from a state in which matter was extremely dense and hot – the Big Bang • Where did the expansion begin? Everywhere! • Every galaxy sees the others receding from it – there is no ...
... The Expanding Universe • Appears the universe “exploded” from a state in which matter was extremely dense and hot – the Big Bang • Where did the expansion begin? Everywhere! • Every galaxy sees the others receding from it – there is no ...
Gravitational Radiation from Rotating White Dwarfs and
... find that J0=3.7⋅1031 erg/s, and h0=10-24 [12]. These calculations show that gravitational waves from rapidly rotating white dwarfs have quite high amplitudes and can be distinguished from the cosmic background by the new generations of detectors. Rapidly rotating white dwarfs are entirely possible, ...
... find that J0=3.7⋅1031 erg/s, and h0=10-24 [12]. These calculations show that gravitational waves from rapidly rotating white dwarfs have quite high amplitudes and can be distinguished from the cosmic background by the new generations of detectors. Rapidly rotating white dwarfs are entirely possible, ...
Cosmic Strings - University of Amsterdam
... transitions can occur, forcing the fields into a particular vacuum state. A cosmic string is a one-dimensional defect, but defects of other dimensions like monopoles and domain walls can also occur. In the context of the Abelian-Higgs model, a simple formulation of a cosmic string will be derived. T ...
... transitions can occur, forcing the fields into a particular vacuum state. A cosmic string is a one-dimensional defect, but defects of other dimensions like monopoles and domain walls can also occur. In the context of the Abelian-Higgs model, a simple formulation of a cosmic string will be derived. T ...
Cosmic Rays 3 - zainab
... These are large mirrors that focus the Cherenkov light generated by the air shower onto an array of photomultiplier tubes PMTs, which form an image of the air shower. Properties of the image are used to distinguish between air showers generated by gamma-ray primaries and nuclear primaries. Though ve ...
... These are large mirrors that focus the Cherenkov light generated by the air shower onto an array of photomultiplier tubes PMTs, which form an image of the air shower. Properties of the image are used to distinguish between air showers generated by gamma-ray primaries and nuclear primaries. Though ve ...
Connecting Stars, Galaxies and the Universe
... and concordance cosmology. In question form we can summarize these goals as: 1) What is the construction history of the Milky Way and other nearly galaxies? 2) what is the age, density and curvature of the Universe? These goals are achievable in the near future by combining micro-arcsecond astrometr ...
... and concordance cosmology. In question form we can summarize these goals as: 1) What is the construction history of the Milky Way and other nearly galaxies? 2) what is the age, density and curvature of the Universe? These goals are achievable in the near future by combining micro-arcsecond astrometr ...
Cosmic microwave background
The cosmic microwave background (CMB) is the thermal radiation left over from the time of recombination in Big Bang cosmology. In older literature, the CMB is also variously known as cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBR) or ""relic radiation."" The CMB is a cosmic background radiation that is fundamental to observational cosmology because it is the oldest light in the universe, dating to the epoch of recombination. With a traditional optical telescope, the space between stars and galaxies (the background) is completely dark. However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope shows a faint background glow, almost exactly the same in all directions, that is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the radio spectrum. The accidental discovery of CMB in 1964 by American radio astronomers Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s, and earned the discoverers the 1978 Nobel Prize.The CMB is a snapshot of the oldest light in our Universe, imprinted on the sky when the Universe was just 380,000 years old. It shows tiny temperature fluctuations that correspond to regions of slightly different densities, representing the seeds of all future structure: the stars and galaxies of today.The CMB is well explained as radiation left over from an early stage in the development of the universe, and its discovery is considered a landmark test of the Big Bang model of the universe. When the universe was young, before the formation of stars and planets, it was denser, much hotter, and filled with a uniform glow from a white-hot fog of hydrogen plasma. As the universe expanded, both the plasma and the radiation filling it grew cooler. When the universe cooled enough, protons and electrons combined to form neutral atoms. These atoms could no longer absorb the thermal radiation, and so the universe became transparent instead of being an opaque fog. Cosmologists refer to the time period when neutral atoms first formed as the recombination epoch, and the event shortly afterwards when photons started to travel freely through space rather than constantly being scattered by electrons and protons in plasma is referred to as photon decoupling. The photons that existed at the time of photon decoupling have been propagating ever since, though growing fainter and less energetic, since the expansion of space causes their wavelength to increase over time (and wavelength is inversely proportional to energy according to Planck's relation). This is the source of the alternative term relic radiation. The surface of last scattering refers to the set of points in space at the right distance from us so that we are now receiving photons originally emitted from those points at the time of photon decoupling.Precise measurements of the CMB are critical to cosmology, since any proposed model of the universe must explain this radiation. The CMB has a thermal black body spectrum at a temperature of 7000272548000000000♠2.72548±0.00057 K. The spectral radiance dEν/dν peaks at 160.2 GHz, in the microwave range of frequencies. (Alternatively if spectral radiance is defined as dEλ/dλ then the peak wavelength is 1.063 mm.) The glow is very nearly uniform in all directions, but the tiny residual variations show a very specific pattern, the same as that expected of a fairly uniformly distributed hot gas that has expanded to the current size of the universe. In particular, the spectral radiance at different angles of observation in the sky contains small anisotropies, or irregularities, which vary with the size of the region examined. They have been measured in detail, and match what would be expected if small thermal variations, generated by quantum fluctuations of matter in a very tiny space, had expanded to the size of the observable universe we see today. This is a very active field of study, with scientists seeking both better data (for example, the Planck spacecraft) and better interpretations of the initial conditions of expansion. Although many different processes might produce the general form of a black body spectrum, no model other than the Big Bang has yet explained the fluctuations. As a result, most cosmologists consider the Big Bang model of the universe to be the best explanation for the CMB.The high degree of uniformity throughout the observable universe and its faint but measured anisotropy lend strong support for the Big Bang model in general and the ΛCDM (""Lambda Cold Dark Matter"") model in particular. Moreover, the fluctuations are coherent on angular scales that are larger than the apparent cosmological horizon at recombination. Either such coherence is acausally fine-tuned, or cosmic inflation occurred.