Physics 1b - The Thomas Cowley High School
... galaxies in the Universe a.Red shift – Light from distant galaxies is red-shifted to longer wavelengths, the further the galaxy the greater the red shift. b.The Big Bang Red shift shows us that distant galaxies are moving away from us. An Expanding Universe Universe started with a massive explos ...
... galaxies in the Universe a.Red shift – Light from distant galaxies is red-shifted to longer wavelengths, the further the galaxy the greater the red shift. b.The Big Bang Red shift shows us that distant galaxies are moving away from us. An Expanding Universe Universe started with a massive explos ...
Where are we? Matter is made of atoms and molecules Atoms
... The electroweak theory introduces particles that act as mediators of weak interactions in the same way that photons mediate EM interactions. In the electroweak theory, these four particles (photons, W¯, W+, and Z°) are closely related. The strength of the interaction of the W and Z bosons is compara ...
... The electroweak theory introduces particles that act as mediators of weak interactions in the same way that photons mediate EM interactions. In the electroweak theory, these four particles (photons, W¯, W+, and Z°) are closely related. The strength of the interaction of the W and Z bosons is compara ...
Chapter 1 Notes
... • understand how you fit into the history of the universe; • understand how science works to help us understand our world, solar system and the entire universe; and • learn about the wonders of our solar system and the continuing series of discoveries being made right now! ...
... • understand how you fit into the history of the universe; • understand how science works to help us understand our world, solar system and the entire universe; and • learn about the wonders of our solar system and the continuing series of discoveries being made right now! ...
10.1
... the spectrum. If the star is moving away from you, there is a red shift, which means its wavelengths get longer. They are stretched out and shifted toward the red end of the spectrum. This red-shifting of wavelengths has been observed with many individual stars, as well as with collections of stars. ...
... the spectrum. If the star is moving away from you, there is a red shift, which means its wavelengths get longer. They are stretched out and shifted toward the red end of the spectrum. This red-shifting of wavelengths has been observed with many individual stars, as well as with collections of stars. ...
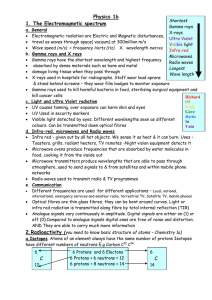
Electromagnetic Spectrum
... and turn into your favorite Mozart, Madonna, or The Fray tunes. • But radio waves are also emitted by other things ... such as stars and gases in space. ...
... and turn into your favorite Mozart, Madonna, or The Fray tunes. • But radio waves are also emitted by other things ... such as stars and gases in space. ...
Bellringer - Madison County Schools
... In 1965, another piece of evidence to support the Big Bang Theory was discovered. Two American Physicists noticed that no matter where they pointed there radio telescope, there was always some faint radiation detected. ...
... In 1965, another piece of evidence to support the Big Bang Theory was discovered. Two American Physicists noticed that no matter where they pointed there radio telescope, there was always some faint radiation detected. ...
Early Universe : 2015 Open Note Test
... 45 g∗ T . Consider the case of (spin 2) gravitons, which decouple at T ≈ 10 GeV. Assume a hot bing bang model without inflation, so that at T > 1019 GeV the gravitons and other particles were in thermal equilibrium. (a) Describe in your own words what it means for a particle to decouple, and qualita ...
... 45 g∗ T . Consider the case of (spin 2) gravitons, which decouple at T ≈ 10 GeV. Assume a hot bing bang model without inflation, so that at T > 1019 GeV the gravitons and other particles were in thermal equilibrium. (a) Describe in your own words what it means for a particle to decouple, and qualita ...
Looking back in time to the big bang theory activity
... ICT, English skills, and presentation skills. You can also link this work to how science works. The redshift analysis task gives learners an opportunity to relate what they have learned to a real life scenario. The evidence for the Big Bang task gives learners an opportunity to voice their opinions ...
... ICT, English skills, and presentation skills. You can also link this work to how science works. The redshift analysis task gives learners an opportunity to relate what they have learned to a real life scenario. The evidence for the Big Bang task gives learners an opportunity to voice their opinions ...
Discovery Of A Major Contradiction In Big Bang Cosmology Points
... wavelength, λs , and having a common origin at time te . Its unusual implications begin to be evident when it is applied to objects with z > 6. But its most extraordinary implications are even more evident when applying it to redshifts in the early stages of the CBR. For example, if we apply Equatio ...
... wavelength, λs , and having a common origin at time te . Its unusual implications begin to be evident when it is applied to objects with z > 6. But its most extraordinary implications are even more evident when applying it to redshifts in the early stages of the CBR. For example, if we apply Equatio ...
ASTRONOMY WEBQUEST…… EXPLORE THE UNIVERSE
... 12. There are 3 main pieces of evidence that support The Big Bang Theory: a) Evidence of the _______________________________of the universe. In the year ________, Edwin Hubble observed that galaxies were generally receding from us provided the first clue that the Big Bang theory might be right b) Th ...
... 12. There are 3 main pieces of evidence that support The Big Bang Theory: a) Evidence of the _______________________________of the universe. In the year ________, Edwin Hubble observed that galaxies were generally receding from us provided the first clue that the Big Bang theory might be right b) Th ...
Chap 18 Cosmology v2
... from forming clumps. Then it was matter-dominated, during which time superclusters and smaller clumps of matter formed. Today it is dark-energy-dominated. Dark energy of some sort supplies a repulsive gravitational force that causes superclusters to accelerate away from each other. Astronomers think ...
... from forming clumps. Then it was matter-dominated, during which time superclusters and smaller clumps of matter formed. Today it is dark-energy-dominated. Dark energy of some sort supplies a repulsive gravitational force that causes superclusters to accelerate away from each other. Astronomers think ...
Introducing Higher Physics
... All that remains to do in physics is to fill in the sixth decimal place (Albert Michelson, 1894) ...
... All that remains to do in physics is to fill in the sixth decimal place (Albert Michelson, 1894) ...
Take Home #1 Complete the following on your own paper. Do not
... A. Scientists usually work in direct competition with each other. B. Scientists often build upon the evidence gathered by other scientists. C. Scientists work individually and do not usually interact with each other. D. Scientists each have jobs where they study completely different areas of science ...
... A. Scientists usually work in direct competition with each other. B. Scientists often build upon the evidence gathered by other scientists. C. Scientists work individually and do not usually interact with each other. D. Scientists each have jobs where they study completely different areas of science ...
Take Home #1 Complete the following on your own paper. Do not
... A. Scientists usually work in direct competition with each other. B. Scientists often build upon the evidence gathered by other scientists. C. Scientists work individually and do not usually interact with each other. D. Scientists each have jobs where they study completely different areas of science ...
... A. Scientists usually work in direct competition with each other. B. Scientists often build upon the evidence gathered by other scientists. C. Scientists work individually and do not usually interact with each other. D. Scientists each have jobs where they study completely different areas of science ...
1_Introduction
... The earliest stars contain 75% hydrogen, 25% helium, as predicted from Big Bang Nucleosynthesis. ...
... The earliest stars contain 75% hydrogen, 25% helium, as predicted from Big Bang Nucleosynthesis. ...
Name
... 11. Explain the big bang theory in as much detail as possible. Make sure you answer the following questions: 1. Is the universe expanding or getting smaller? 2. What evidence did the WMAP provide scientists about the big bang theory? 3. Is the universe cooling or getting hotter? 4. How has the amou ...
... 11. Explain the big bang theory in as much detail as possible. Make sure you answer the following questions: 1. Is the universe expanding or getting smaller? 2. What evidence did the WMAP provide scientists about the big bang theory? 3. Is the universe cooling or getting hotter? 4. How has the amou ...
Cosmology – The Origin and Evolution of the Universe
... • But ionized gas is opaque: So, we should see through closer and cooler transparent gas until our line-of-sight hits gas so young and so hot that it’s ionized and opaque. • Thus: Prediction - We should see 3,000 K gas in all directions = The Cosmic Background Radiation • Universe was hot & opaque u ...
... • But ionized gas is opaque: So, we should see through closer and cooler transparent gas until our line-of-sight hits gas so young and so hot that it’s ionized and opaque. • Thus: Prediction - We should see 3,000 K gas in all directions = The Cosmic Background Radiation • Universe was hot & opaque u ...
The Nature of Space and Time
... Since pre-history people have gazed into the sky and pondered the nature of the universe All early civilizations studied the stars and the motions of the five naked-eye planets known to them as the “wanderers” They used their observations to tell time, for navigation, to predict the coming of season ...
... Since pre-history people have gazed into the sky and pondered the nature of the universe All early civilizations studied the stars and the motions of the five naked-eye planets known to them as the “wanderers” They used their observations to tell time, for navigation, to predict the coming of season ...
Wien`s law - Uplift Education
... • Perhaps the Universe is not infinite. But current model of the Universe is that it is infinite. • Perhaps the light is absorbed before it gets to us. But then Universe would warm up and eventually reradiate energy. Real help: the Big Bang model leads to the idea that the observable universe is not ...
... • Perhaps the Universe is not infinite. But current model of the Universe is that it is infinite. • Perhaps the light is absorbed before it gets to us. But then Universe would warm up and eventually reradiate energy. Real help: the Big Bang model leads to the idea that the observable universe is not ...
The Universe - staff.harrisonburg.k12.va
... What do Quasars indicate…. • If the Big Bang really happened, the oldest objects should be at the edge of the universe. • Quasars are very old objects that give off large amounts of energy located at the edge of the Universe. ...
... What do Quasars indicate…. • If the Big Bang really happened, the oldest objects should be at the edge of the universe. • Quasars are very old objects that give off large amounts of energy located at the edge of the Universe. ...
The Universe
... What do Quasars indicate…. • If the Big Bang really happened, the oldest objects should be at the edge of the universe. • Quasars are very old objects that give off large amounts of energy located at the edge of the Universe. ...
... What do Quasars indicate…. • If the Big Bang really happened, the oldest objects should be at the edge of the universe. • Quasars are very old objects that give off large amounts of energy located at the edge of the Universe. ...
Stefan-Boltzmann`s law Wien`s law
... ► light from distant galaxies/stars is red-shifted (which means they move away from us – as the red-shifting occurs in all direction, the universe must be expanding) ► existence of CMB ► the helium abundance in the universe which is about 25 % and is consistent with a hot beginning of the universe; ...
... ► light from distant galaxies/stars is red-shifted (which means they move away from us – as the red-shifting occurs in all direction, the universe must be expanding) ► existence of CMB ► the helium abundance in the universe which is about 25 % and is consistent with a hot beginning of the universe; ...
Cosmic microwave background
The cosmic microwave background (CMB) is the thermal radiation left over from the time of recombination in Big Bang cosmology. In older literature, the CMB is also variously known as cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBR) or ""relic radiation."" The CMB is a cosmic background radiation that is fundamental to observational cosmology because it is the oldest light in the universe, dating to the epoch of recombination. With a traditional optical telescope, the space between stars and galaxies (the background) is completely dark. However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope shows a faint background glow, almost exactly the same in all directions, that is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the radio spectrum. The accidental discovery of CMB in 1964 by American radio astronomers Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s, and earned the discoverers the 1978 Nobel Prize.The CMB is a snapshot of the oldest light in our Universe, imprinted on the sky when the Universe was just 380,000 years old. It shows tiny temperature fluctuations that correspond to regions of slightly different densities, representing the seeds of all future structure: the stars and galaxies of today.The CMB is well explained as radiation left over from an early stage in the development of the universe, and its discovery is considered a landmark test of the Big Bang model of the universe. When the universe was young, before the formation of stars and planets, it was denser, much hotter, and filled with a uniform glow from a white-hot fog of hydrogen plasma. As the universe expanded, both the plasma and the radiation filling it grew cooler. When the universe cooled enough, protons and electrons combined to form neutral atoms. These atoms could no longer absorb the thermal radiation, and so the universe became transparent instead of being an opaque fog. Cosmologists refer to the time period when neutral atoms first formed as the recombination epoch, and the event shortly afterwards when photons started to travel freely through space rather than constantly being scattered by electrons and protons in plasma is referred to as photon decoupling. The photons that existed at the time of photon decoupling have been propagating ever since, though growing fainter and less energetic, since the expansion of space causes their wavelength to increase over time (and wavelength is inversely proportional to energy according to Planck's relation). This is the source of the alternative term relic radiation. The surface of last scattering refers to the set of points in space at the right distance from us so that we are now receiving photons originally emitted from those points at the time of photon decoupling.Precise measurements of the CMB are critical to cosmology, since any proposed model of the universe must explain this radiation. The CMB has a thermal black body spectrum at a temperature of 7000272548000000000♠2.72548±0.00057 K. The spectral radiance dEν/dν peaks at 160.2 GHz, in the microwave range of frequencies. (Alternatively if spectral radiance is defined as dEλ/dλ then the peak wavelength is 1.063 mm.) The glow is very nearly uniform in all directions, but the tiny residual variations show a very specific pattern, the same as that expected of a fairly uniformly distributed hot gas that has expanded to the current size of the universe. In particular, the spectral radiance at different angles of observation in the sky contains small anisotropies, or irregularities, which vary with the size of the region examined. They have been measured in detail, and match what would be expected if small thermal variations, generated by quantum fluctuations of matter in a very tiny space, had expanded to the size of the observable universe we see today. This is a very active field of study, with scientists seeking both better data (for example, the Planck spacecraft) and better interpretations of the initial conditions of expansion. Although many different processes might produce the general form of a black body spectrum, no model other than the Big Bang has yet explained the fluctuations. As a result, most cosmologists consider the Big Bang model of the universe to be the best explanation for the CMB.The high degree of uniformity throughout the observable universe and its faint but measured anisotropy lend strong support for the Big Bang model in general and the ΛCDM (""Lambda Cold Dark Matter"") model in particular. Moreover, the fluctuations are coherent on angular scales that are larger than the apparent cosmological horizon at recombination. Either such coherence is acausally fine-tuned, or cosmic inflation occurred.