Science 9, Unit 1: Reproduction
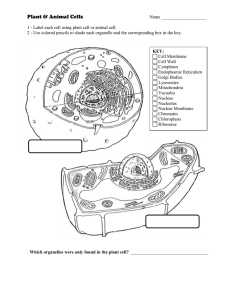
... 6. Contains the cell's information 7. Outer layer of plant cells 8. Where proteins are made 10. Powerhouse of the cell 11. Basic unit of structure and function ...
... 6. Contains the cell's information 7. Outer layer of plant cells 8. Where proteins are made 10. Powerhouse of the cell 11. Basic unit of structure and function ...
Cells and Organelles Test Review C) recognize levels of
... Cells and Organelles Test Review C) recognize levels of organization in plants and animals, including cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms; (D) differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mi ...
... Cells and Organelles Test Review C) recognize levels of organization in plants and animals, including cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms; (D) differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mi ...
sgCh1Cell
... Name _______________________________Date______________ Block ______________ Science Chapter 1 (Study Guide) Introduction to Cells Complete the following Questions. 1.______________basic units of structure and __________in living things. 2. Hooke observed _________________ 3. What did Leeuwenhoek obs ...
... Name _______________________________Date______________ Block ______________ Science Chapter 1 (Study Guide) Introduction to Cells Complete the following Questions. 1.______________basic units of structure and __________in living things. 2. Hooke observed _________________ 3. What did Leeuwenhoek obs ...
Layout
... In order to meet the Given Signal to interference ratio, We need to try N( Reuse factor) with different combination of Sectoring(60 120 180 360) and through this calculating Number of First level interfering channels n. The aim here is to minimize the Reuse factor N. ...
... In order to meet the Given Signal to interference ratio, We need to try N( Reuse factor) with different combination of Sectoring(60 120 180 360) and through this calculating Number of First level interfering channels n. The aim here is to minimize the Reuse factor N. ...
Cell Structure and Function Study Guide
... What are the contributions of Robert Hooke, Anton van Leuwenhoek, Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolph Virchow to our understanding of cells? What are the three parts of the cell theory? How are molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms related? Be ...
... What are the contributions of Robert Hooke, Anton van Leuwenhoek, Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolph Virchow to our understanding of cells? What are the three parts of the cell theory? How are molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms related? Be ...
Cell-to-cell junctions
... • Structure: Tightly bound, leakproof, fibrous claudin protein seal that surrounds the cell • Function: Holds cells together such that materials pass through not between the cells • Example: Junctions between epithelial cells in the gut ...
... • Structure: Tightly bound, leakproof, fibrous claudin protein seal that surrounds the cell • Function: Holds cells together such that materials pass through not between the cells • Example: Junctions between epithelial cells in the gut ...
cells_can_you
... Describe the structure of each of these organelles and relate this to their function in the cell. Recognise the organelles in electron micrographs. List the main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Describe the ultrastructure of a typical bacterial cell, showing its cell wall, cell ...
... Describe the structure of each of these organelles and relate this to their function in the cell. Recognise the organelles in electron micrographs. List the main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Describe the ultrastructure of a typical bacterial cell, showing its cell wall, cell ...
Cell Specialization
... Cell Specialization • Not all cells are alike (structure or function) • Many different, types, sizes, shapes – Our body has over 200 different cell types ...
... Cell Specialization • Not all cells are alike (structure or function) • Many different, types, sizes, shapes – Our body has over 200 different cell types ...
12-1 pm Location: Room HSW1057 UCSF
... Presented By: Antonia Livolsi, Ph.D, Research Application Scientist Traditional methods for examining gene expression involve lysed or fixed cell populations. The ability to do so in live cells would allow for more physiologically relevant information based on a cell’s response to given stimuli. Det ...
... Presented By: Antonia Livolsi, Ph.D, Research Application Scientist Traditional methods for examining gene expression involve lysed or fixed cell populations. The ability to do so in live cells would allow for more physiologically relevant information based on a cell’s response to given stimuli. Det ...
Cell Biology Jeopardy
... • Which organelle in plant cells captures the radiant energy from sunlight to create glucose in a process called photosynthesis? ...
... • Which organelle in plant cells captures the radiant energy from sunlight to create glucose in a process called photosynthesis? ...
Biology Notes 3-2
... 1. All living things are made of 1 or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit(s) of life’s function and structure. 3. All cells arise from existing cells. Most Cells cannot be seen with the naked eye: they are 5µm-20 µm (micrometers in diameter) Cells must have a high Surface Area-to-Volume ratio (S ...
... 1. All living things are made of 1 or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit(s) of life’s function and structure. 3. All cells arise from existing cells. Most Cells cannot be seen with the naked eye: they are 5µm-20 µm (micrometers in diameter) Cells must have a high Surface Area-to-Volume ratio (S ...
“brains” of the cell, the nucleus directs cell activities and contains
... Rigid outermost layer in plant cells ...
... Rigid outermost layer in plant cells ...
Structures and Organelles
... Contains most of cell’s DNA Stores info used to make proteins for cell growth, function, and reproduction Surrounded by the Nuclear Envelope similar to plasma membrane ...
... Contains most of cell’s DNA Stores info used to make proteins for cell growth, function, and reproduction Surrounded by the Nuclear Envelope similar to plasma membrane ...
Cell-matrix mechanical crosstalk as key factor for improving
... worldwide. The myocardial tissue that is damaged by MI lacks the ability to significantly self-regenerate, which leads to adverse left ventricular remodeling and eventual heart failure. While total heart transplantation remains the only successful treatment for end-stage post-MI heart failure, this ...
... worldwide. The myocardial tissue that is damaged by MI lacks the ability to significantly self-regenerate, which leads to adverse left ventricular remodeling and eventual heart failure. While total heart transplantation remains the only successful treatment for end-stage post-MI heart failure, this ...
Name: Date: Class Period: Video questions: Video 1: Gene
... What is a regulatory gene? What is an example of a regulatory sequence? What is lactose? What does it mean when a gene is expressed? What is the function of the TATA box? What is the function of an operator sequence? Why would bacteria want to make enzymes (proteins) that break down lactose only whe ...
... What is a regulatory gene? What is an example of a regulatory sequence? What is lactose? What does it mean when a gene is expressed? What is the function of the TATA box? What is the function of an operator sequence? Why would bacteria want to make enzymes (proteins) that break down lactose only whe ...
Chapter 7 Review Questions
... 2. Which of the following is NOT a principle of the cell theory? a. Cells are the basic units of life. b. All living things are made of cells. c. Very few cells are able to reproduce. d. All cells are produced from existing cells. 6. Looking at a cell under a microscope, you note that it is a prokar ...
... 2. Which of the following is NOT a principle of the cell theory? a. Cells are the basic units of life. b. All living things are made of cells. c. Very few cells are able to reproduce. d. All cells are produced from existing cells. 6. Looking at a cell under a microscope, you note that it is a prokar ...
instruction2.mtsac.edu
... Made up of proteins: Microtubules, Microfilaments, Intermediate Filaments Present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells ...
... Made up of proteins: Microtubules, Microfilaments, Intermediate Filaments Present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells ...
ch08_Cell-Cell Communication
... •In young cells, enzymes called expansins allow microfibrils to slide past each other, and turgor pressure then forces the cell wall to elongate, allowing cell growth. ...
... •In young cells, enzymes called expansins allow microfibrils to slide past each other, and turgor pressure then forces the cell wall to elongate, allowing cell growth. ...
Cell Structure and Function: Review
... ***Directions: Circle the correct multiple choice answer. Use your workbook if needed. 4. Which cell part is found in both plant cells and animal cells? (Lesson 1 pg. 200-203) A. cell membrane B. cell wall C. chloroplast D. large vacuole 5. Which of these organisms lacks (does not have) tissues, org ...
... ***Directions: Circle the correct multiple choice answer. Use your workbook if needed. 4. Which cell part is found in both plant cells and animal cells? (Lesson 1 pg. 200-203) A. cell membrane B. cell wall C. chloroplast D. large vacuole 5. Which of these organisms lacks (does not have) tissues, org ...
Ch6 Cell homework
... e. Composed of 9 cylinders of microtubules ______________________ f. Sends secretory vesicles to the plasma membrane for exocytosis _____________ g. Site of chromosomes ______________________ h. Engages in autophagy ______________________ i. Site of cellular respiration/ATP production_______________ ...
... e. Composed of 9 cylinders of microtubules ______________________ f. Sends secretory vesicles to the plasma membrane for exocytosis _____________ g. Site of chromosomes ______________________ h. Engages in autophagy ______________________ i. Site of cellular respiration/ATP production_______________ ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).