Cell Analogies Worksheet
... Cell Structure Extra Credit Instructions: Fill in the spaces below for each cell part in order to create a one-sentence analogy that shows the similarity between the cell part and another object. Be sure to explain the reasoning behind your analogies (see the underlined section of the example). Exem ...
... Cell Structure Extra Credit Instructions: Fill in the spaces below for each cell part in order to create a one-sentence analogy that shows the similarity between the cell part and another object. Be sure to explain the reasoning behind your analogies (see the underlined section of the example). Exem ...
Bill Nye Reviews Cells
... Part 1 What are cells? What does Bill say? Click on the link to find out! ...
... Part 1 What are cells? What does Bill say? Click on the link to find out! ...
Tissue engineering of intervertebral disc (Prof. Sarit Sivan and Dr
... developed by Sivan et al., to function as BM-MSC carriers and to promote the production of NP-like ECM via cues delivered to the cells by their unique structural characteristics. To this aim, BM-MSCs will be cultured in GAG analogue hydrogels of different stiffness; constructs will be incubated unde ...
... developed by Sivan et al., to function as BM-MSC carriers and to promote the production of NP-like ECM via cues delivered to the cells by their unique structural characteristics. To this aim, BM-MSCs will be cultured in GAG analogue hydrogels of different stiffness; constructs will be incubated unde ...
Name: Date: Concept Check Questions Chapter 6 – A Tour of the
... 1. Describe at least two common characteristics of chloroplasts and mitochondria. 2. Explain the characteristics of mitochondria and chloroplasts that place them in a separate category from organelles in the endomembrane system. 6.6 The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes the structur ...
... 1. Describe at least two common characteristics of chloroplasts and mitochondria. 2. Explain the characteristics of mitochondria and chloroplasts that place them in a separate category from organelles in the endomembrane system. 6.6 The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes the structur ...
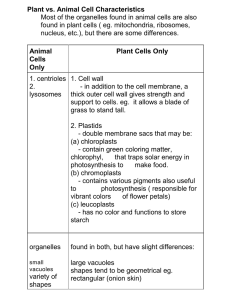
Plant vs. Animal Cell Characteristics Most of the organelles found in
... Most of the organelles found in animal cells are also found in plant cells ( eg. mitochondria, ribosomes, nucleus, etc.), but there are some differences. Animal Cells Only ...
... Most of the organelles found in animal cells are also found in plant cells ( eg. mitochondria, ribosomes, nucleus, etc.), but there are some differences. Animal Cells Only ...
I`m a real “powerhouse.” That`s plain to see. I break down food to
... That’s plain to see. I break down food to release energy (ATP) ...
... That’s plain to see. I break down food to release energy (ATP) ...
Quiz D - exam Q`s
... B. Found only in eukaryotic cells C. Found exclusively in the nucleus D. Formed during transcription of DNA 3. Lipids are A. Used as an energy source B. Involved in active transport C. Part of glycoproteins D. Transported by rough ER ...
... B. Found only in eukaryotic cells C. Found exclusively in the nucleus D. Formed during transcription of DNA 3. Lipids are A. Used as an energy source B. Involved in active transport C. Part of glycoproteins D. Transported by rough ER ...
013368718X_CH02_015
... A. Convert energy from sunlight into chemical energy that is stored in food B. Stack of membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials for storage or release C. Convert chemical energy stored in food into a form that can be easily used by the cell ...
... A. Convert energy from sunlight into chemical energy that is stored in food B. Stack of membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials for storage or release C. Convert chemical energy stored in food into a form that can be easily used by the cell ...
Cell Review
... 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of function in all living things 3. All cells come from preexisting cells Exceptions 1. Virus- can not reproduce on their own 2. Mitochondria and Chloroplasts contain their own DNA Organelles ...
... 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of function in all living things 3. All cells come from preexisting cells Exceptions 1. Virus- can not reproduce on their own 2. Mitochondria and Chloroplasts contain their own DNA Organelles ...
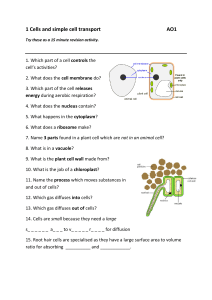
1 Cells and simple cell transport AO1
... 1. Which part of a cell controls the cell’s activities? 2. What does the cell membrane do? 3. Which part of the cell releases energy during aerobic respiration? 4. What does the nucleus contain? 5. What happens in the cytoplasm? 6. What does a ribosome make? 7. Name 3 parts found in a plant cell whi ...
... 1. Which part of a cell controls the cell’s activities? 2. What does the cell membrane do? 3. Which part of the cell releases energy during aerobic respiration? 4. What does the nucleus contain? 5. What happens in the cytoplasm? 6. What does a ribosome make? 7. Name 3 parts found in a plant cell whi ...
Chapter 2 Cells to Systems
... saucers. How does this shape help them perform their function? In what body part would you find cells with hair like structures? What is their purpose? What is the order of organization in an animal from simplest to most complex? ...
... saucers. How does this shape help them perform their function? In what body part would you find cells with hair like structures? What is their purpose? What is the order of organization in an animal from simplest to most complex? ...
Cell Structure PPT Part 2
... Cell walls are found in prokaryotes, plants, fungi and some protists. Cell walls of plants are made of cellulose; in fungi they are made of chitin; in prokaryotes they are murein (or muramic acid) and in protists they vary. ...
... Cell walls are found in prokaryotes, plants, fungi and some protists. Cell walls of plants are made of cellulose; in fungi they are made of chitin; in prokaryotes they are murein (or muramic acid) and in protists they vary. ...
Chapter 3 Lesson 3.2
... Eukaryotic Cells have many parts to help the cell stay alive. They are called ORGANELLES ...
... Eukaryotic Cells have many parts to help the cell stay alive. They are called ORGANELLES ...
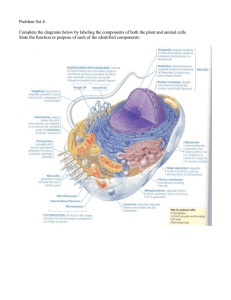
Problem Set 4:
... 8.6 What osmotic problems do fresh water protists face? Hypertonic protests will gain water from their hypotonic environment. What adaptations may help them osmoregulate? Some have membranes that are less permeable to water and contractile vacuoles that expel excess water. 8.7 The ideal osmotic env ...
... 8.6 What osmotic problems do fresh water protists face? Hypertonic protests will gain water from their hypotonic environment. What adaptations may help them osmoregulate? Some have membranes that are less permeable to water and contractile vacuoles that expel excess water. 8.7 The ideal osmotic env ...
http://en
... CELLS Visit this web page: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_%28biology%29 and answer the questions. ...
... CELLS Visit this web page: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_%28biology%29 and answer the questions. ...
投影片 1
... smooth muscle cells and epithelial cells • More than 20 distinct types of collagen have been identified • All share at least two structural features: trimers of α chains and wound around each other to form a rod-like triple helix ...
... smooth muscle cells and epithelial cells • More than 20 distinct types of collagen have been identified • All share at least two structural features: trimers of α chains and wound around each other to form a rod-like triple helix ...
The Cell Theory
... __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 2. Why didn’t anyone know about cells before the late 17th century? __________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
... __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 2. Why didn’t anyone know about cells before the late 17th century? __________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
cell theory
... Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of structure All living things are composed of cells Unicellular and multi cellular all cells come from pre-existing cell Important organs in a cell Nuclease: contains the cells DNA brain of the cell Mitochondria: site of respiring provides the energy for the c ...
... Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of structure All living things are composed of cells Unicellular and multi cellular all cells come from pre-existing cell Important organs in a cell Nuclease: contains the cells DNA brain of the cell Mitochondria: site of respiring provides the energy for the c ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).