ADVANCED BIOLOGY Exam III (Chapter 3: Cell Structure and
... cells and their function(s). (Refer to Cell Function Wkshts) 4. What are the functions of all organelles within both the animal and plant cells. 5. Describe one similarity and one difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; cell wall and cell membrane; facilitated diffusion and diffusion. 6 ...
... cells and their function(s). (Refer to Cell Function Wkshts) 4. What are the functions of all organelles within both the animal and plant cells. 5. Describe one similarity and one difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; cell wall and cell membrane; facilitated diffusion and diffusion. 6 ...
CELL PARTS
... TAY-SACHS disease – missing an enzyme of the lysosomes that breaks down a fatty substance. Over time this fat builds up in the brain and nervous tissue, smothering the cells. Results in degeneration and death. ...
... TAY-SACHS disease – missing an enzyme of the lysosomes that breaks down a fatty substance. Over time this fat builds up in the brain and nervous tissue, smothering the cells. Results in degeneration and death. ...
CELL THEORY -And how we got there
... CELL THEORY -And how we got there! The first guy to see cells ...
... CELL THEORY -And how we got there! The first guy to see cells ...
File
... – help cell bear tension (pulling forces) – play a role in cell motility – works with myosin to cause muscle cell contraction in animals & cytoplasmic streaming in plant cells ...
... – help cell bear tension (pulling forces) – play a role in cell motility – works with myosin to cause muscle cell contraction in animals & cytoplasmic streaming in plant cells ...
Eukaryotic cells Section review model answers Ribosomes are
... and through which those materials are delivered to other places in the cell. 4. Plant cells have cell walls, but animal cells do not. Plant cells have chloroplasts, which animal cells do not have. Plant cells do not seem to have small lysosomes (they have large vacuoles instead), which animal cells ...
... and through which those materials are delivered to other places in the cell. 4. Plant cells have cell walls, but animal cells do not. Plant cells have chloroplasts, which animal cells do not have. Plant cells do not seem to have small lysosomes (they have large vacuoles instead), which animal cells ...
Cells key word bingo
... Cells key word bingo! Choose 8 of the key words in BOLD to put into the boxes on your grid. I will read out definitions to the key words and if you have that key word in your grid cross it out. We will see who can get a line first and then a ‘full house’! ...
... Cells key word bingo! Choose 8 of the key words in BOLD to put into the boxes on your grid. I will read out definitions to the key words and if you have that key word in your grid cross it out. We will see who can get a line first and then a ‘full house’! ...
Cell Cycle regulation
... 2. When you cut your skin or break a bone, the cells at the site of the injury will grow until they fill in the empty space. • **These two examples show that there are controls on when cell division occurs. ...
... 2. When you cut your skin or break a bone, the cells at the site of the injury will grow until they fill in the empty space. • **These two examples show that there are controls on when cell division occurs. ...
Robert Hooke (1665) saw cells while looking at a piece of cork
... Cell membrane – protective barrier that controls the passage of material into and out of the cell. Organelles – structures that enable the cell to live, grow, and reproduce. Cytoplasm – cellular fluid Nucleus – membrane covered organelle that holds the DNA Prokaryotic – simple cells (oldest fossils ...
... Cell membrane – protective barrier that controls the passage of material into and out of the cell. Organelles – structures that enable the cell to live, grow, and reproduce. Cytoplasm – cellular fluid Nucleus – membrane covered organelle that holds the DNA Prokaryotic – simple cells (oldest fossils ...
11-14-02
... Robert Hooke , Looked at cork Saw little boxes that reminded him of cells in a monastery; Coined the word cell Anton von Leeuwenhoek observed the first living cell ...
... Robert Hooke , Looked at cork Saw little boxes that reminded him of cells in a monastery; Coined the word cell Anton von Leeuwenhoek observed the first living cell ...
Study Guide
... Study Guide Chapter 2, Section 1 – Cell Structure & Function Summary Common Cell Traits All cells have an outer covering called a cell membrane. Cells can be classified as prokaryotic (cells that lack a distinct nucleus) or eukaryotic (cells with a distinct membrane-bound nucleus). Cell Organiza ...
... Study Guide Chapter 2, Section 1 – Cell Structure & Function Summary Common Cell Traits All cells have an outer covering called a cell membrane. Cells can be classified as prokaryotic (cells that lack a distinct nucleus) or eukaryotic (cells with a distinct membrane-bound nucleus). Cell Organiza ...
Survey of A&P/Chp 3 cells and tissues notes
... Osteocytes- bone cells Chondrocytes- cartilage cells Macrophages- engulf bacteria ...
... Osteocytes- bone cells Chondrocytes- cartilage cells Macrophages- engulf bacteria ...
Cell Review Cell Theory Levels of Organization Organelle
... M - Pre-existing cells make cells. L - All living organisms are made of cells B - Basic structure and function of life. ...
... M - Pre-existing cells make cells. L - All living organisms are made of cells B - Basic structure and function of life. ...
Organelle Notes #2
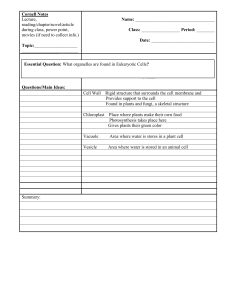
... Cornell Notes Lecture, reading/chapter/novel/article during class, power point, movies (if need to collect info.) ...
... Cornell Notes Lecture, reading/chapter/novel/article during class, power point, movies (if need to collect info.) ...
Unit of life MBBS Prof. Fridoon - King Edward Medical University
... Life is not a random collection of some macromoleulces. Life is a collection of macromoleulces that can perform unique functions because the are enclosed in structural acompartment that provides consistency (homeostasis). All organisms are composed of cells the basic unit of life and all cells come ...
... Life is not a random collection of some macromoleulces. Life is a collection of macromoleulces that can perform unique functions because the are enclosed in structural acompartment that provides consistency (homeostasis). All organisms are composed of cells the basic unit of life and all cells come ...
Meiosis & Mitosis Process
... The process by which the number of chromosomes is reduced by half to form sex cells. Chromosomes make copies of themselves. Then line up in the middle of the cell side by side. Move to upset ends of the cell. Two new cells are formed. Line up in the center of the cell. Then the chromoso ...
... The process by which the number of chromosomes is reduced by half to form sex cells. Chromosomes make copies of themselves. Then line up in the middle of the cell side by side. Move to upset ends of the cell. Two new cells are formed. Line up in the center of the cell. Then the chromoso ...
Cells - Weebly
... AKA the powerhouse. Inner folded membranes= increase in surface area= more energy production during aerobic cellular respiration ...
... AKA the powerhouse. Inner folded membranes= increase in surface area= more energy production during aerobic cellular respiration ...
Subcellular Organelles and Structures
... Liver Cell (TEM x9,400). This image is copyright Dennis Kunkel ...
... Liver Cell (TEM x9,400). This image is copyright Dennis Kunkel ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).