Cells Glossary
... Nucleus - large organelle, controls all cell activities (growth, repair & reproduction) ...
... Nucleus - large organelle, controls all cell activities (growth, repair & reproduction) ...
Biology Chapter 7 Notes I. Cell Theory A. Discovered since 1600 by
... Biology Chapter 7 Notes I. ...
... Biology Chapter 7 Notes I. ...
STANDARDS ADDRESSED: Cellular function is maintained through
... Topic: Mitosis and cell division Activity: Cell cycle and Mitosis review Ameoba sisters Online root tip HMWK: Complete root tip ---------------Topic: Assessment and Stem cells in the News Activity: Quiz on cell cycle and mitosis After quiz- Article on human-animal hybrids HMWK: Complete article ...
... Topic: Mitosis and cell division Activity: Cell cycle and Mitosis review Ameoba sisters Online root tip HMWK: Complete root tip ---------------Topic: Assessment and Stem cells in the News Activity: Quiz on cell cycle and mitosis After quiz- Article on human-animal hybrids HMWK: Complete article ...
Cell Structure Cloze - Science
... Fill in the blanks with words from the box. cells mitochondria plant ...
... Fill in the blanks with words from the box. cells mitochondria plant ...
Cell Transport PP
... Active transport: ____________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... Active transport: ____________________________________________________________________________________ ...
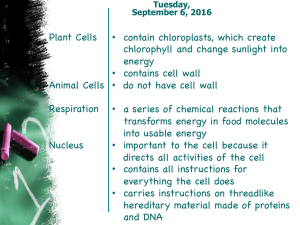
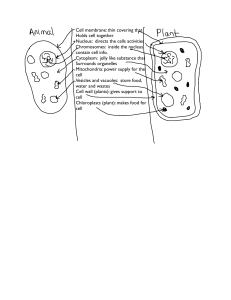
Differences between the animal and plant cell: The plant cell has a
... Differences between the animal and plant cell: ...
... Differences between the animal and plant cell: ...
Chapter 1 Eukaryotic Cells Section 1
... Chapter 1 Eukaryotic Cells Section 1.2 Cell Wall – rigid (stiff) structure that gives support to plant cells Cell membrane – protective barrier that encloses a cell Cytoskeleton – web of proteins in the cytoplasm that keep the membrane from collapsing Nucleus – largest organelle in a eukaryotic cell ...
... Chapter 1 Eukaryotic Cells Section 1.2 Cell Wall – rigid (stiff) structure that gives support to plant cells Cell membrane – protective barrier that encloses a cell Cytoskeleton – web of proteins in the cytoplasm that keep the membrane from collapsing Nucleus – largest organelle in a eukaryotic cell ...
Study Guide for Chapter 5 – Lesson 1, “What are Cells?” Be a
... Study Guide for Chapter 5 – Lesson 1, “What are Cells?” Be a biology detective and search the lesson for answers…… Who discovered cells? __________________________________________________________________ Why did he name them cells? ____________________________________________________________________ ...
... Study Guide for Chapter 5 – Lesson 1, “What are Cells?” Be a biology detective and search the lesson for answers…… Who discovered cells? __________________________________________________________________ Why did he name them cells? ____________________________________________________________________ ...
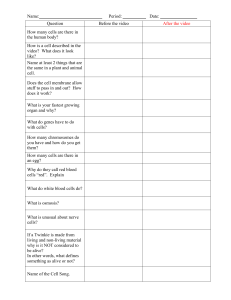
Question Before the video After the video How many cells are there
... How many cells are there in the human body? How is a cell described in the video? What does it look like? Name at least 2 things that are the same in a plant and animal cell. Does the cell membrane allow stuff to pass in and out? How does it work? What is your fastest growing organ and why? What do ...
... How many cells are there in the human body? How is a cell described in the video? What does it look like? Name at least 2 things that are the same in a plant and animal cell. Does the cell membrane allow stuff to pass in and out? How does it work? What is your fastest growing organ and why? What do ...
Unit 5 SCA Review Sheet
... 4. I am a group of cells who work together to perform a particular function. __________________________________________________ 5. I am one of the four different types of tissue. I add support and structure to the body, I fill spaces and I also store fat. ___________________________________________ ...
... 4. I am a group of cells who work together to perform a particular function. __________________________________________________ 5. I am one of the four different types of tissue. I add support and structure to the body, I fill spaces and I also store fat. ___________________________________________ ...
CELLS AND TISSUES WORKSHEET ANATOMY AND
... 1. Forms the lining of the small intestine______________________________ 2. A single layer of flattened cells___________________________________3. Lines the esophagus__________________________ 4. A single layer of hexagonal cells_________________________ 5. A single layer of square-like cells_______ ...
... 1. Forms the lining of the small intestine______________________________ 2. A single layer of flattened cells___________________________________3. Lines the esophagus__________________________ 4. A single layer of hexagonal cells_________________________ 5. A single layer of square-like cells_______ ...
Cell Study Guide
... to do. These are called life processes: 1. They all grow. 2. They all get food. 3. They all respond to the environment. 4. They all reproduce. 2. You need to know where cells come from. ...
... to do. These are called life processes: 1. They all grow. 2. They all get food. 3. They all respond to the environment. 4. They all reproduce. 2. You need to know where cells come from. ...
Tissue Repair - Johns Hopkins Medicine
... • Types I, II, III, V form fibrills • Type IV forms sheets and basement membrane • Inherited disorder = Ehlers Danlos • Acquired defect = Scurvy ...
... • Types I, II, III, V form fibrills • Type IV forms sheets and basement membrane • Inherited disorder = Ehlers Danlos • Acquired defect = Scurvy ...
8 CELL THEORY Handouts - Hewlett
... living things (cells carry out the life processes). - All cells come from _________ ________________________ ...
... living things (cells carry out the life processes). - All cells come from _________ ________________________ ...
Nanolive AG from Ecublens (VD) – 3D research on living cells
... Nanolive SA is a start-up operating from the EPFL Innovation Park at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (ETHL). The biotech company was founded in 2013 and developed a tomographic microscope which, for the first time ever, allows for the research of living cells in a 3D environment – witho ...
... Nanolive SA is a start-up operating from the EPFL Innovation Park at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (ETHL). The biotech company was founded in 2013 and developed a tomographic microscope which, for the first time ever, allows for the research of living cells in a 3D environment – witho ...
Chapter 6 Learning Targets 2016
... Each of your cells is a miniature marvel. Consider taking a complex machine with millions of parte – say a jumbo jet – and shrinking it to microscopic size while keeping everything in working order. It would still seem simple compared to a living cell. Everything you do, every action and every thoug ...
... Each of your cells is a miniature marvel. Consider taking a complex machine with millions of parte – say a jumbo jet – and shrinking it to microscopic size while keeping everything in working order. It would still seem simple compared to a living cell. Everything you do, every action and every thoug ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).