Levels of Organization/Cells/Cell Organelle Notes
... Levels of Organization/Cells/Cell Organelle Notes ...
... Levels of Organization/Cells/Cell Organelle Notes ...
Cell Surfaces and Junctions
... together into strong sheets, much like rivets. • Intermediate filaments of keratin reinforce desmosomes. ...
... together into strong sheets, much like rivets. • Intermediate filaments of keratin reinforce desmosomes. ...
Biology Study guide
... Microscope use and calculations Diagram with parts and function Total magnification Field of view ...
... Microscope use and calculations Diagram with parts and function Total magnification Field of view ...
Cells Alive Internet Activity
... Answer the following questions in the following categories. Cell Biology: Pumping myocytes 1. What enzyme is used to dissolve heart tissue into individual cells? 2. How do cell physiologists measure how ion channels work? Apoptosis 3. How do cells “commit suicide”? Microbiology: HIV infection 4. Wha ...
... Answer the following questions in the following categories. Cell Biology: Pumping myocytes 1. What enzyme is used to dissolve heart tissue into individual cells? 2. How do cell physiologists measure how ion channels work? Apoptosis 3. How do cells “commit suicide”? Microbiology: HIV infection 4. Wha ...
Document
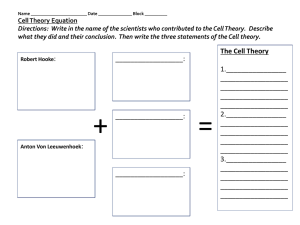
... his hypothesis that all living things are composed of cells? (A) He tried to grow an organism from a single cell. (B) He studied literature on the development of cell theory. (C) He built a model of a cell he saw in one type of organism. (D) He used microscopes to examine the tissues of many differe ...
... his hypothesis that all living things are composed of cells? (A) He tried to grow an organism from a single cell. (B) He studied literature on the development of cell theory. (C) He built a model of a cell he saw in one type of organism. (D) He used microscopes to examine the tissues of many differe ...
Slide 1
... – To identify cell parts – To compare and contrast various cell types• Plant and animal cells ...
... – To identify cell parts – To compare and contrast various cell types• Plant and animal cells ...
Cell membrane Cell wall Cellulose fibers Chloroplast Cytoplasm
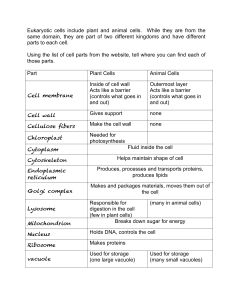
... Eukaryotic cells include plant and animal cells. While they are from the same domain, they are part of two different kingdoms and have different parts to each cell. Using the list of cell parts from the website, tell where you can find each of those parts. Part ...
... Eukaryotic cells include plant and animal cells. While they are from the same domain, they are part of two different kingdoms and have different parts to each cell. Using the list of cell parts from the website, tell where you can find each of those parts. Part ...
Cells, Tissues, Organs, Organ Systems
... What are some advantages of being multi-celled? Disadvantages? ...
... What are some advantages of being multi-celled? Disadvantages? ...
answers - Biology Resources
... chromosomes. (b) Only plant cells have a cell wall, central vacuole and cell sap. 5 The most likely sequence is as shown below. ...
... chromosomes. (b) Only plant cells have a cell wall, central vacuole and cell sap. 5 The most likely sequence is as shown below. ...
cells-study-guide
... Advantages of being multicellular (p. 76): 1. _________________________________________________ 2. ________________________________________________ 3. __________________________________________________ Understand how these relate to each other Organism > Organ System > Organ > Tissue > Cell ...
... Advantages of being multicellular (p. 76): 1. _________________________________________________ 2. ________________________________________________ 3. __________________________________________________ Understand how these relate to each other Organism > Organ System > Organ > Tissue > Cell ...
Structures found in Eukaryotes Continued 4. • Formed by • Vesicles
... -harvest __________________from organic compounds and transfer it to________. ...
... -harvest __________________from organic compounds and transfer it to________. ...
The Magic Universe of Cells Directions
... draw, label, and define the parts of an animal cell and a plant cell. You need to include at least: nucleus, nucleolus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrion, cell membrane, cell wall, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, cytoplasm, vacuoles, centrioles, lysosomes, nuclear envelope, and chromatin. If there is ...
... draw, label, and define the parts of an animal cell and a plant cell. You need to include at least: nucleus, nucleolus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrion, cell membrane, cell wall, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, cytoplasm, vacuoles, centrioles, lysosomes, nuclear envelope, and chromatin. If there is ...
Cell Surface 1.Cell wall: of the plant cells
... -protect plant cells -maintain its shape -prevent excessive uptake of water -hold the plant up against the gravity force ...
... -protect plant cells -maintain its shape -prevent excessive uptake of water -hold the plant up against the gravity force ...
hw1017-tour-cell
... It’s time to jump into the heart of biology – taking a good look at the building block that living organisms are composed. A Tour of the Cell – Bozeman Science ...
... It’s time to jump into the heart of biology – taking a good look at the building block that living organisms are composed. A Tour of the Cell – Bozeman Science ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).