Meiosis And Mitosis - Bloomfield Public Schools
... The process of Meiosis Meiosis is the process by which sex cells divide. Chromosomes make copies of themselves. They line up in the middle of the cell side by side. Then move to opposite ends of the cell. 2 new cells are formed. Again, they line up in the middle. Then they divide and ...
... The process of Meiosis Meiosis is the process by which sex cells divide. Chromosomes make copies of themselves. They line up in the middle of the cell side by side. Then move to opposite ends of the cell. 2 new cells are formed. Again, they line up in the middle. Then they divide and ...
Structure and function of cell components
... Provide structural support by resisting compression Have a role in organelle movement Separate chromatids during cell division Components of cilia, flagella and centrioles ...
... Provide structural support by resisting compression Have a role in organelle movement Separate chromatids during cell division Components of cilia, flagella and centrioles ...
Plant and Animal Cells
... information you have learned. You may use the other side if you need more space. Cheek cell ...
... information you have learned. You may use the other side if you need more space. Cheek cell ...
Study Guide for the Cells Test 2006 Textbook Chapter 1 pages 4-23
... 6. Do you understand the vocab and concepts? Ask questions before it’s too late! Section 1 Diversity of Cells pg. 4-10 Vocabulary Cells nucleus Cell membrane prokaryote Surface area to volume ratio Concepts ...
... 6. Do you understand the vocab and concepts? Ask questions before it’s too late! Section 1 Diversity of Cells pg. 4-10 Vocabulary Cells nucleus Cell membrane prokaryote Surface area to volume ratio Concepts ...
Unit 3 (Cells and Transport) Review Guide
... the scope of the information presented in lecture and your text. These review items are meant to be indicative of the possible material one might expect to see on the exam. With a set time limit of one class period, however, it is not possible to test your knowledge regarding all of the subject mate ...
... the scope of the information presented in lecture and your text. These review items are meant to be indicative of the possible material one might expect to see on the exam. With a set time limit of one class period, however, it is not possible to test your knowledge regarding all of the subject mate ...
TISSUES OF THE BODY
... They are made of many different types of cells surrounded by a NONLIVING substance called the EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX. This matrix is composed of various types of fibers including elastic, collagen, and reticular fibers. ...
... They are made of many different types of cells surrounded by a NONLIVING substance called the EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX. This matrix is composed of various types of fibers including elastic, collagen, and reticular fibers. ...
7th Grade Chapter 13 Study Guide Vocabulary: Section One Cell
... 2. Compare the levels of organization among eukaryotes with the types of organization found among prokaryotes. 3. Explain why cells in an embryo will grow no larger than a certain size before they divide. 4. How did Schwann and Schleiden contribute to science? Describe their contribution. 5. Why did ...
... 2. Compare the levels of organization among eukaryotes with the types of organization found among prokaryotes. 3. Explain why cells in an embryo will grow no larger than a certain size before they divide. 4. How did Schwann and Schleiden contribute to science? Describe their contribution. 5. Why did ...
Anatomy and development of the adult spinal cord neural stem cell
... “Anatomy & development of the adult spinal cord stem cell niche” Professor Kate Storey (co- supervisor Dr Paul Felts) Division of Cell & Developmental Biology College of Life Sciences, University of Dundee The aim of this project is to characterize the heterogeneous cell populations within the adult ...
... “Anatomy & development of the adult spinal cord stem cell niche” Professor Kate Storey (co- supervisor Dr Paul Felts) Division of Cell & Developmental Biology College of Life Sciences, University of Dundee The aim of this project is to characterize the heterogeneous cell populations within the adult ...
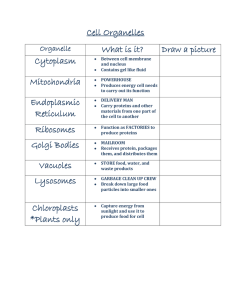
Cell organelles
... • Has enzymes that break down food, old materials, etc. • Garbage disposal of cell ...
... • Has enzymes that break down food, old materials, etc. • Garbage disposal of cell ...
Chloroplasts discovered
... Casts of real human blood vessels, made using a technique called ‘corrosion casting’, in which blood vessels are injected with a coloured plastic which sets hard. The body tissue is then chemically removed. As seen at ‘Bodies: the Exhibition’. ...
... Casts of real human blood vessels, made using a technique called ‘corrosion casting’, in which blood vessels are injected with a coloured plastic which sets hard. The body tissue is then chemically removed. As seen at ‘Bodies: the Exhibition’. ...
File
... Casts of real human blood vessels, made using a technique called ‘corrosion casting’, in which blood vessels are injected with a coloured plastic which sets hard. The body tissue is then chemically removed. As seen at ‘Bodies: the Exhibition’. ...
... Casts of real human blood vessels, made using a technique called ‘corrosion casting’, in which blood vessels are injected with a coloured plastic which sets hard. The body tissue is then chemically removed. As seen at ‘Bodies: the Exhibition’. ...
Life cycle of cell
... material around the body 4. cells of blood 1. red blood cells carry oxygen 2. white blood cells destroy pathogens – principle component of the immune system 3. platelets – prevent blood loss through clotting Hemopoietic tissue ...
... material around the body 4. cells of blood 1. red blood cells carry oxygen 2. white blood cells destroy pathogens – principle component of the immune system 3. platelets – prevent blood loss through clotting Hemopoietic tissue ...
Regulation of the Cell Cycle
... Cells stop growing when when there is no more surface area for them. This is called Contact inhibition of growth, and the cells are said to have anchorage dependence. ...
... Cells stop growing when when there is no more surface area for them. This is called Contact inhibition of growth, and the cells are said to have anchorage dependence. ...
topic 5 -part 3 guided notes -plant vs animal cells - student
... TOPIC 5: CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION PART 3: PLANT VS. ANIMAL CELLS Plants and animals differ in their cell makeup. Structures Common to Both Plant and Animal Cells 1. cell membrane 2. nucleus 3. nuclear envelope 4. DNA 5. nucleolus 6. ribosomes ...
... TOPIC 5: CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION PART 3: PLANT VS. ANIMAL CELLS Plants and animals differ in their cell makeup. Structures Common to Both Plant and Animal Cells 1. cell membrane 2. nucleus 3. nuclear envelope 4. DNA 5. nucleolus 6. ribosomes ...
The Cell Cycle - Haiku Learning
... What are the 3 phases of the cell cycle? What are the 4 phases of Mitosis? What is differentiation? ...
... What are the 3 phases of the cell cycle? What are the 4 phases of Mitosis? What is differentiation? ...
What Part of the Cell am I?
... I’m strong and stiff and getting through me is tough; I’m found only in plants, but I guess that’s enough. What am I? Cell Wall ...
... I’m strong and stiff and getting through me is tough; I’m found only in plants, but I guess that’s enough. What am I? Cell Wall ...
Microbodies
... large molecules and detoxify hazardous substances It contains oxidative enzymes and catalysts. ...
... large molecules and detoxify hazardous substances It contains oxidative enzymes and catalysts. ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).