Lecture 14
... • Chs. 5 - 13: Methods to analyze dynamics of objects in Translational & Rotational Motion using Newton’s Laws! Chs. 5 & 6: Newton’s Laws using Forces (translational motion) Chs. 7 & 8: Newton’s Laws using Energy & Work (translational motion) Ch. 9: Newton’s Laws using Momentum (translational motion ...
... • Chs. 5 - 13: Methods to analyze dynamics of objects in Translational & Rotational Motion using Newton’s Laws! Chs. 5 & 6: Newton’s Laws using Forces (translational motion) Chs. 7 & 8: Newton’s Laws using Energy & Work (translational motion) Ch. 9: Newton’s Laws using Momentum (translational motion ...
Tissue Fluid and Lymph
... • Here the hydrostatic pressure of the blood is high. This will encourage the filtration of the fluid content of the blood through small gaps between the endothelial cells of the walls of the capillary. Blood cells and plasma proteins are too large to be filtered. • However, as the blood has a low ( ...
... • Here the hydrostatic pressure of the blood is high. This will encourage the filtration of the fluid content of the blood through small gaps between the endothelial cells of the walls of the capillary. Blood cells and plasma proteins are too large to be filtered. • However, as the blood has a low ( ...
Department of Mechanical Engineering
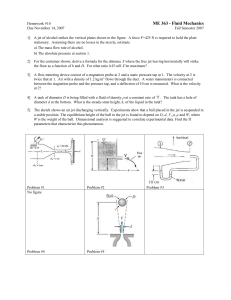
... 1] A jet of alcohol strikes the vertical plates shown in the figure. A force F=425 N is required to hold the plate stationary. Assuming there are no losses in the nozzle, estimate a) The mass flow rate of alcohol. b) The absolute pressure at section 1. 2] For the container shown, derive a formula fo ...
... 1] A jet of alcohol strikes the vertical plates shown in the figure. A force F=425 N is required to hold the plate stationary. Assuming there are no losses in the nozzle, estimate a) The mass flow rate of alcohol. b) The absolute pressure at section 1. 2] For the container shown, derive a formula fo ...
There are several equations useful in understanding hydraulics and
... Ch-3. There are several equations useful in understanding hydraulics and sediments deposits. Reynolds Number Froude Number ...
... Ch-3. There are several equations useful in understanding hydraulics and sediments deposits. Reynolds Number Froude Number ...
Physics--Chapter 9: Fluid Mechanics
... b. Mass density = mass/volume; we'll measure it in kg/m 3 c. Equation for mass density (): = m/V d. The density of solids and liquids changes very little with pressure and temperature changes so a standard density can be given e. The density of gases changes significantly with temperature and pre ...
... b. Mass density = mass/volume; we'll measure it in kg/m 3 c. Equation for mass density (): = m/V d. The density of solids and liquids changes very little with pressure and temperature changes so a standard density can be given e. The density of gases changes significantly with temperature and pre ...
Fluid thread breakup
Fluid thread breakup is the process by which a single mass of fluid breaks into several smaller fluid masses. The process is characterized by the elongation of the fluid mass forming thin, thread-like regions between larger nodules of fluid. The thread-like regions continue to thin until they break, forming individual droplets of fluid.Thread breakup occurs where two fluids or a fluid in a vacuum form a free surface with surface energy. If more surface area is present than the minimum required to contain the volume of fluid, the system has an excess of surface energy. A system not at the minimum energy state will attempt to rearrange so as to move toward the lower energy state, leading to the breakup of the fluid into smaller masses to minimize the system surface energy by reducing the surface area. The exact outcome of the thread breakup process is dependent on the surface tension, viscosity, density, and diameter of the thread undergoing breakup.