File - The Physics Doctor
... Calculate the density of the hot air in a balloon floating at a fixed height close to the ground. The density of the cold air is 1.4kgm-3. The total mass of the balloon’s fabric gondola, fuel, burners and occupants is 700kg and it’s volume is 2500m3 ...
... Calculate the density of the hot air in a balloon floating at a fixed height close to the ground. The density of the cold air is 1.4kgm-3. The total mass of the balloon’s fabric gondola, fuel, burners and occupants is 700kg and it’s volume is 2500m3 ...
Introduction to fluid dynamics and simulations in COMSOL
... where dV indicates the volume integral and dA is the surface integral. The internal forces acting through surface are now composed of two terms: normal (represented by scalar function p – the pressure) and shear/tangential (represented by matrix function – the stress tensor). It can be also proved ...
... where dV indicates the volume integral and dA is the surface integral. The internal forces acting through surface are now composed of two terms: normal (represented by scalar function p – the pressure) and shear/tangential (represented by matrix function – the stress tensor). It can be also proved ...
Three-dimensional numerical analysis to predict behavior of driftage carried by tsunami
... cross-sectional area and volume equal to that of the actual cylinder (driftage). Figure 8 shows the results of a comparison between the vertical 2D trajectory of the driftage obtained by the computation and that obtained in the experiment. In this figure, the trajectories of the centroid of the fron ...
... cross-sectional area and volume equal to that of the actual cylinder (driftage). Figure 8 shows the results of a comparison between the vertical 2D trajectory of the driftage obtained by the computation and that obtained in the experiment. In this figure, the trajectories of the centroid of the fron ...
Min-218 Fundamentals of Fluid Flow
... upon by a source of energy (for example, pressure or heat) which is used by the molecules to overcome attractive forces that bind them together. This can be made clear by assuming the fluid consists of layers parallel to each other and letting a force act upon one of the layers in a direction parall ...
... upon by a source of energy (for example, pressure or heat) which is used by the molecules to overcome attractive forces that bind them together. This can be made clear by assuming the fluid consists of layers parallel to each other and letting a force act upon one of the layers in a direction parall ...
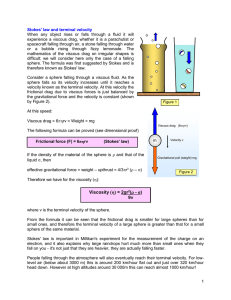
Stokes` law - schoolphysics
... electron, and it also explains why large raindrops hurt much more than small ones when they fall on you - it's not just that they are heavier, they are actually falling faster. People falling through the atmosphere will also eventually reach their terminal velocity. For lowlevel air (below about 300 ...
... electron, and it also explains why large raindrops hurt much more than small ones when they fall on you - it's not just that they are heavier, they are actually falling faster. People falling through the atmosphere will also eventually reach their terminal velocity. For lowlevel air (below about 300 ...
Chapter 5.2: Convection and the Mantle (continued) Learning Target
... KEY CONCEPT: Heating and cooling of a fluid, changes in the fluid’s density and the force of gravity combine to set convection currents in motion. Convection is the transfer of heat by the movement of particles in ___________. This movement is called convection currents. A convection current sta ...
... KEY CONCEPT: Heating and cooling of a fluid, changes in the fluid’s density and the force of gravity combine to set convection currents in motion. Convection is the transfer of heat by the movement of particles in ___________. This movement is called convection currents. A convection current sta ...
PowerPoint - UMD Physics
... upon by a net upward force as the result of any effect that causes the fluid to change its direction as it flows past the object ...
... upon by a net upward force as the result of any effect that causes the fluid to change its direction as it flows past the object ...
Chang Right Angle Cannula for Hydrodissection
... internal fluid wave cleaves the epinucleus apart from the firmer endonucleus. There are three separate goals for hydrodissection: 1) endonucleus rotation, 2) epinucleus rotation, and 3) loosening of the cortex. ...
... internal fluid wave cleaves the epinucleus apart from the firmer endonucleus. There are three separate goals for hydrodissection: 1) endonucleus rotation, 2) epinucleus rotation, and 3) loosening of the cortex. ...
MMV211, March 9, 2005 P1. The figure below shows a vane with a
... Consider a control volume (CV) that is fixed to the moving vane, which means that the flow through CV can be considered to be stationary; liquid flow means incompressible flow. Let coordinate x be in the direction of movement. The lower surface of CV is between the wheels and the horizontal ground, ...
... Consider a control volume (CV) that is fixed to the moving vane, which means that the flow through CV can be considered to be stationary; liquid flow means incompressible flow. Let coordinate x be in the direction of movement. The lower surface of CV is between the wheels and the horizontal ground, ...
Document
... Stream 1a has a velocity v0 and a cross-sectional area (1/3)A1, and Stream 1b has a velocity (1/2)v0 and a cross-sectional area (2/3)A1. Plane 2 is chosen far enough downstream so that the two streams have mixed and the velocity is almost uniform at v2. The flow is turbulent and the velocity profile ...
... Stream 1a has a velocity v0 and a cross-sectional area (1/3)A1, and Stream 1b has a velocity (1/2)v0 and a cross-sectional area (2/3)A1. Plane 2 is chosen far enough downstream so that the two streams have mixed and the velocity is almost uniform at v2. The flow is turbulent and the velocity profile ...
BAL Collection in Cows and Calves - University of Wisconsin School
... inserted into the end of the BAL tube and 240-ml of sterile saline is infused using 60-ml syringes. Immediately after the 240 ml infusion, negative pressure is applied to aspirate fluid, a process that can yield up to 120 ml of mildly turbid, foamy fluid. Mucus and purulent flecks may be visualized ...
... inserted into the end of the BAL tube and 240-ml of sterile saline is infused using 60-ml syringes. Immediately after the 240 ml infusion, negative pressure is applied to aspirate fluid, a process that can yield up to 120 ml of mildly turbid, foamy fluid. Mucus and purulent flecks may be visualized ...
The Normal Pleura
... Pleural effusion : The Normal Pleura The lung is covered with visceral pleura The adjacent surfaces of the mediastinum, chest wall, and diaphragm are lined by parietal pleura. These layers are in continuity both at the hilum and below, where they form the pulmonary ligament. The visceral and ...
... Pleural effusion : The Normal Pleura The lung is covered with visceral pleura The adjacent surfaces of the mediastinum, chest wall, and diaphragm are lined by parietal pleura. These layers are in continuity both at the hilum and below, where they form the pulmonary ligament. The visceral and ...
Fluid thread breakup
Fluid thread breakup is the process by which a single mass of fluid breaks into several smaller fluid masses. The process is characterized by the elongation of the fluid mass forming thin, thread-like regions between larger nodules of fluid. The thread-like regions continue to thin until they break, forming individual droplets of fluid.Thread breakup occurs where two fluids or a fluid in a vacuum form a free surface with surface energy. If more surface area is present than the minimum required to contain the volume of fluid, the system has an excess of surface energy. A system not at the minimum energy state will attempt to rearrange so as to move toward the lower energy state, leading to the breakup of the fluid into smaller masses to minimize the system surface energy by reducing the surface area. The exact outcome of the thread breakup process is dependent on the surface tension, viscosity, density, and diameter of the thread undergoing breakup.