Lecture 14c - TTU Physics
... • Viscosity is a measure of the amount of internal friction in the fluid. • This internal friction or VISCOUS FORCE, comes from the resistance that two adjacent layers of fluid have to moving relative to each other. ...
... • Viscosity is a measure of the amount of internal friction in the fluid. • This internal friction or VISCOUS FORCE, comes from the resistance that two adjacent layers of fluid have to moving relative to each other. ...
Popping Sound - Back To Chiropractic
... and carbon dioxide gases. When a joint is adjusted the joint capsule is stretched and the joint volume is increased by as much as 15-20%. This creates a partial vacuum and the gas rapidly releases due to the pressure change. (Similar to Boyle's Law, 1662). The gas takes about 20 minutes to return to ...
... and carbon dioxide gases. When a joint is adjusted the joint capsule is stretched and the joint volume is increased by as much as 15-20%. This creates a partial vacuum and the gas rapidly releases due to the pressure change. (Similar to Boyle's Law, 1662). The gas takes about 20 minutes to return to ...
The four phses of matter are solid, liquid, gas, and plasma
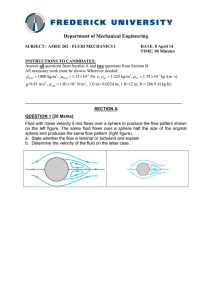
... Look up the density of ice; what part of an ice cube will be under water when dropped in a glass full of water? Note: A hydrometer indicates SG of a liquid by how far it sinks. Note: In a helium filled balloon, the buoyant force equals the weight of displaced air. The balloon floats if this is great ...
... Look up the density of ice; what part of an ice cube will be under water when dropped in a glass full of water? Note: A hydrometer indicates SG of a liquid by how far it sinks. Note: In a helium filled balloon, the buoyant force equals the weight of displaced air. The balloon floats if this is great ...
Buoyancy - UBC Math
... In these notes, we use the divergence theorem to show that when you immerse a body in a fluid the net effect of fluid pressure acting on the surface of the body is a vertical force (called the buoyant force) whose magnitude equals the weight of fluid displaced by the body. This is known as Archimede ...
... In these notes, we use the divergence theorem to show that when you immerse a body in a fluid the net effect of fluid pressure acting on the surface of the body is a vertical force (called the buoyant force) whose magnitude equals the weight of fluid displaced by the body. This is known as Archimede ...
L15 - University of Iowa Physics
... • The ball is moving but from the ball’s perspective the air moves relative to the ball • The streamlines are bunched at the top and ...
... • The ball is moving but from the ball’s perspective the air moves relative to the ball • The streamlines are bunched at the top and ...
Document
... Physical meaning of fluid stress components σxy and σxx ? (a) σxy is the shear stress acting on the surface element perpendicular to the x-axis. σxy is parallel to the surface and points to the y direction .σxx is the normal stress pointing to the x direction and acting on the surface element perpen ...
... Physical meaning of fluid stress components σxy and σxx ? (a) σxy is the shear stress acting on the surface element perpendicular to the x-axis. σxy is parallel to the surface and points to the y direction .σxx is the normal stress pointing to the x direction and acting on the surface element perpen ...
Gravity waves on water - UMD Physics
... to ignore surface tension must be proportional to gλ, while those √ with wavelength much longer than the depth have speed proportional to gh. In this supplement we’ll derive the speed for the general case. ...
... to ignore surface tension must be proportional to gλ, while those √ with wavelength much longer than the depth have speed proportional to gh. In this supplement we’ll derive the speed for the general case. ...
1 The basic equations of fluid dynamics
... at the level of “fluid elements”, defined in Sec. 1.1. In any domain, the flow equations must be solved subject to a set of conditions that act at the domain boundary, Sec. 1.5. If the flow leads to compression of the fluid, we must also consider thermodynamics: • conservation of energy. However we ...
... at the level of “fluid elements”, defined in Sec. 1.1. In any domain, the flow equations must be solved subject to a set of conditions that act at the domain boundary, Sec. 1.5. If the flow leads to compression of the fluid, we must also consider thermodynamics: • conservation of energy. However we ...
Fluid thread breakup
Fluid thread breakup is the process by which a single mass of fluid breaks into several smaller fluid masses. The process is characterized by the elongation of the fluid mass forming thin, thread-like regions between larger nodules of fluid. The thread-like regions continue to thin until they break, forming individual droplets of fluid.Thread breakup occurs where two fluids or a fluid in a vacuum form a free surface with surface energy. If more surface area is present than the minimum required to contain the volume of fluid, the system has an excess of surface energy. A system not at the minimum energy state will attempt to rearrange so as to move toward the lower energy state, leading to the breakup of the fluid into smaller masses to minimize the system surface energy by reducing the surface area. The exact outcome of the thread breakup process is dependent on the surface tension, viscosity, density, and diameter of the thread undergoing breakup.