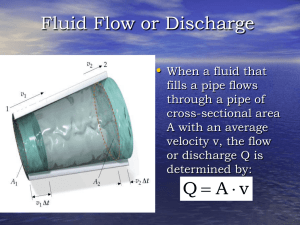
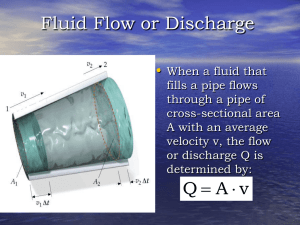
the fluid mechanics course, CHE 204, Transport Phenomena I
... to recover their recent states, they will exhibit elasticity in addition to viscosity. Other fluids, such as drilling mud or toothpaste, behave essentially as solids and will not flow when subject to small shear forces, but will flow readily under the influence of high shear forces. Fluids can also ...
... to recover their recent states, they will exhibit elasticity in addition to viscosity. Other fluids, such as drilling mud or toothpaste, behave essentially as solids and will not flow when subject to small shear forces, but will flow readily under the influence of high shear forces. Fluids can also ...
Fluid mechanics
... In short, a fluid continues in motion under the application of a shear stress and can not sustain any shear stress when at rest. Fluid as a continuum In the definition of the fluid the molecular structure of the fluid was not mentioned. As we know the fluids are composed of molecules in constant mot ...
... In short, a fluid continues in motion under the application of a shear stress and can not sustain any shear stress when at rest. Fluid as a continuum In the definition of the fluid the molecular structure of the fluid was not mentioned. As we know the fluids are composed of molecules in constant mot ...
Basic Equations - Earth and Space Sciences at the University of
... fe = ρ e E′ + j × B where j = ρ e u is the electric current density. The second term in this relation is called the Lorentz force. When the fluid conductivity is very large as it is in the Earth’s core and in space plasmas, B depends on u and µ 0 j = ∇ × B, where µ 0 is the permeability of free spac ...
... fe = ρ e E′ + j × B where j = ρ e u is the electric current density. The second term in this relation is called the Lorentz force. When the fluid conductivity is very large as it is in the Earth’s core and in space plasmas, B depends on u and µ 0 j = ∇ × B, where µ 0 is the permeability of free spac ...
Engineering Thermodynamics
... • The term natural convection is used if this motion and mixing is caused by density variations resulting from temperature differences within the fluid. • The term forced convection is used if this motion and mixing is caused by an outside force, such as a pump. • Heat transfer by convection is more ...
... • The term natural convection is used if this motion and mixing is caused by density variations resulting from temperature differences within the fluid. • The term forced convection is used if this motion and mixing is caused by an outside force, such as a pump. • Heat transfer by convection is more ...
151-0902-00 Micro- and Nano-Particle (MNP) Technology FS09
... b) What would be the edge length of a cube of the same material falling in the same fluid at the same steady state settling velocity? ...
... b) What would be the edge length of a cube of the same material falling in the same fluid at the same steady state settling velocity? ...
Euler`s equation
... The buoyancy force is equal the weight of the mass of fluid displaced, M = ρ0 V , and points in the direction opposite to gravity. If the fluid is only partially submerged, then we need to split it into parts above and below the water surface, and apply Archimedes’ theorem to the lower section only. ...
... The buoyancy force is equal the weight of the mass of fluid displaced, M = ρ0 V , and points in the direction opposite to gravity. If the fluid is only partially submerged, then we need to split it into parts above and below the water surface, and apply Archimedes’ theorem to the lower section only. ...
American Journal of Physics, Vol. 71, Nº 1, 46-48 (2003).
... Three different methods have been described to solve the profile of velocities of an incompressible fluid moving in a permanent laminar regime inside a hollow tube. In one approach we have made use of the Navier-Stokes equation to solve the velocity profile of the fluid inside the hollow tube. We ha ...
... Three different methods have been described to solve the profile of velocities of an incompressible fluid moving in a permanent laminar regime inside a hollow tube. In one approach we have made use of the Navier-Stokes equation to solve the velocity profile of the fluid inside the hollow tube. We ha ...
Fluid thread breakup
Fluid thread breakup is the process by which a single mass of fluid breaks into several smaller fluid masses. The process is characterized by the elongation of the fluid mass forming thin, thread-like regions between larger nodules of fluid. The thread-like regions continue to thin until they break, forming individual droplets of fluid.Thread breakup occurs where two fluids or a fluid in a vacuum form a free surface with surface energy. If more surface area is present than the minimum required to contain the volume of fluid, the system has an excess of surface energy. A system not at the minimum energy state will attempt to rearrange so as to move toward the lower energy state, leading to the breakup of the fluid into smaller masses to minimize the system surface energy by reducing the surface area. The exact outcome of the thread breakup process is dependent on the surface tension, viscosity, density, and diameter of the thread undergoing breakup.