Modeling, Simulating and Rendering Fluids
... • Pressure follows a diffusion process – Fluid moves from high-pressure areas to low-pressure areas ...
... • Pressure follows a diffusion process – Fluid moves from high-pressure areas to low-pressure areas ...
Middle Ear Fluid and Tubes
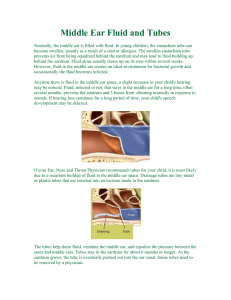
... Normally, the middle ear is filled with fluid. In young children, the eustachian tube can become swollen, usually as a result of a cold or allergies. The swollen eustachian tube prevents air from being equalized behind the eardrum and may lead to fluid building up behind the eardrum. Fluid alone usu ...
... Normally, the middle ear is filled with fluid. In young children, the eustachian tube can become swollen, usually as a result of a cold or allergies. The swollen eustachian tube prevents air from being equalized behind the eardrum and may lead to fluid building up behind the eardrum. Fluid alone usu ...
Introduction to Fluid Mechanics
... 6. Viscosity is a measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow. Most simple fluids are represented well by Newton’s law of viscosity. The exceptions (non-Newtonian fluids) are generally complex mixtures, some of which are of great practical significance. Kinematic viscosity is viscosity divided by densit ...
... 6. Viscosity is a measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow. Most simple fluids are represented well by Newton’s law of viscosity. The exceptions (non-Newtonian fluids) are generally complex mixtures, some of which are of great practical significance. Kinematic viscosity is viscosity divided by densit ...
ch14
... •A fluid, in contrast to a solid, is a substance that can flow. •Fluids conform to the boundaries of any container in which we put them. They do so because a fluid cannot sustain a force that is tangential to its surface. That is, a fluid is a substance that flows because it cannot withstand a shear ...
... •A fluid, in contrast to a solid, is a substance that can flow. •Fluids conform to the boundaries of any container in which we put them. They do so because a fluid cannot sustain a force that is tangential to its surface. That is, a fluid is a substance that flows because it cannot withstand a shear ...
Halliday-ch14
... An open-tube manometer measures the gauge pressure pg of a gas. It consists of a U-tube containing a liquid, with one end of the tube connected to the vessel whose gauge pressure we wish to measure and the other end open to the atmosphere. If po is the atmospheric pressure, p is the pressure at leve ...
... An open-tube manometer measures the gauge pressure pg of a gas. It consists of a U-tube containing a liquid, with one end of the tube connected to the vessel whose gauge pressure we wish to measure and the other end open to the atmosphere. If po is the atmospheric pressure, p is the pressure at leve ...
Fluids, Shear Zones and Continental Rheology
... strengthening of the rock mass once more. As a result, from the perspective of a relatively small rock mass, deformation will be sporadic as rock strengths alternate between those of wet and dry rock in a relatively uniform stress field. In this situation, rheology is a time-dependent variable. View ...
... strengthening of the rock mass once more. As a result, from the perspective of a relatively small rock mass, deformation will be sporadic as rock strengths alternate between those of wet and dry rock in a relatively uniform stress field. In this situation, rheology is a time-dependent variable. View ...
Fluid Mechanics Concepts
... An object submerged in a fluid will experience a volume stress. The magnitude of this stress will depend on the pressure of the fluid, the force that the fluid exerts on a unit area of a given surface: The SI unit for pressure is the pascal (Pa): Consider a liquid at rest in a container. If we made ...
... An object submerged in a fluid will experience a volume stress. The magnitude of this stress will depend on the pressure of the fluid, the force that the fluid exerts on a unit area of a given surface: The SI unit for pressure is the pascal (Pa): Consider a liquid at rest in a container. If we made ...
Fluid Mechanics Primer
... the action of the force. Its shape will change continuously as long as the force is applied. A solid can resist a deformation force while at rest. While a force may cause some displacement, the solid does not move indefinitely. ...
... the action of the force. Its shape will change continuously as long as the force is applied. A solid can resist a deformation force while at rest. While a force may cause some displacement, the solid does not move indefinitely. ...
Cone-Plate Viscometer
... which the experiments are performed as the outer cylinder, and placing a rotating inner cylinder centrally within it. ...
... which the experiments are performed as the outer cylinder, and placing a rotating inner cylinder centrally within it. ...
Fluid thread breakup
Fluid thread breakup is the process by which a single mass of fluid breaks into several smaller fluid masses. The process is characterized by the elongation of the fluid mass forming thin, thread-like regions between larger nodules of fluid. The thread-like regions continue to thin until they break, forming individual droplets of fluid.Thread breakup occurs where two fluids or a fluid in a vacuum form a free surface with surface energy. If more surface area is present than the minimum required to contain the volume of fluid, the system has an excess of surface energy. A system not at the minimum energy state will attempt to rearrange so as to move toward the lower energy state, leading to the breakup of the fluid into smaller masses to minimize the system surface energy by reducing the surface area. The exact outcome of the thread breakup process is dependent on the surface tension, viscosity, density, and diameter of the thread undergoing breakup.