Spring Benchmark Exam
... milliliters of distilled water while adding KCl crystals until no more KCl would dissolve. She then capped the clear solution and set it aside on the lab bench. After several hours she noticed the solution had become cloudy and some solid had settled to the bottom of the flask. Which statement best ...
... milliliters of distilled water while adding KCl crystals until no more KCl would dissolve. She then capped the clear solution and set it aside on the lab bench. After several hours she noticed the solution had become cloudy and some solid had settled to the bottom of the flask. Which statement best ...
Final Exam Review – Free Response Section Name: 1. A sample of
... 3. All binary compounds of the halogens (other than F) with metals are soluble, except those of Ag, Hg(I), and Pb. Pb halides are soluble in hot water.) 4. All sulfates are soluble, except those of barium, strontium, calcium, lead, silver, and mercury (I). The latter three are slightly ...
... 3. All binary compounds of the halogens (other than F) with metals are soluble, except those of Ag, Hg(I), and Pb. Pb halides are soluble in hot water.) 4. All sulfates are soluble, except those of barium, strontium, calcium, lead, silver, and mercury (I). The latter three are slightly ...
Solutions Foldable
... lone pairs of electrons on central atom) o CO2, CH4, SO3, C2H6, F2 Ionic compounds = positive and negative ions bonded (usually contains a metal and a nonmetal or a metal and a polyatomic ion) o Li2SO4, MgO, Na2O, Ca(OH)2 Now that we know what will mix to make a solution how do we know how MUCH s ...
... lone pairs of electrons on central atom) o CO2, CH4, SO3, C2H6, F2 Ionic compounds = positive and negative ions bonded (usually contains a metal and a nonmetal or a metal and a polyatomic ion) o Li2SO4, MgO, Na2O, Ca(OH)2 Now that we know what will mix to make a solution how do we know how MUCH s ...
Solubility Equilibria
... solubility of this type of compounds is useful) One useful principle used to study the extent of solubility of ionic compounds is the solubility product constant (Ksp). Dr. Al‐Saadi ...
... solubility of this type of compounds is useful) One useful principle used to study the extent of solubility of ionic compounds is the solubility product constant (Ksp). Dr. Al‐Saadi ...
matter and its reactivity. Objects in the universe are composed of
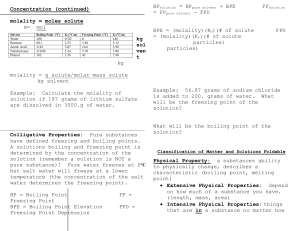
... color, odor, phase, density, solubility, heat and electrical conductivity, and boiling and freezing points. 3.1b Solubility can be affected by the nature of the solute and solvent, temperature, and pressure. The rate of solution can be affected by the size of the particles, stirring, temperature, an ...
... color, odor, phase, density, solubility, heat and electrical conductivity, and boiling and freezing points. 3.1b Solubility can be affected by the nature of the solute and solvent, temperature, and pressure. The rate of solution can be affected by the size of the particles, stirring, temperature, an ...
Page 1 of 4 FOSS California Mixtures and Solutions
... Carbohydrate: A group of carbon-based nutrients, such as sugars and starches. Carbon-14 dating: A process used to find the age of carbon-based matter. Carbon dioxide gas: A compound made from carbon and oxygen (CO2) Chemical equation: A model of a chemical reaction showing reactants and products. Ch ...
... Carbohydrate: A group of carbon-based nutrients, such as sugars and starches. Carbon-14 dating: A process used to find the age of carbon-based matter. Carbon dioxide gas: A compound made from carbon and oxygen (CO2) Chemical equation: A model of a chemical reaction showing reactants and products. Ch ...
Atomic number
... Which of these describes a pollution-producing process that involves only a physical change? a) Coal with a high sulfur content is burned, producing gases that cause acid rain. b) Chlorofluorocarbons are released, changing ozone in the upper atmosphere into oxygen. c) Hot wastewater is discharged i ...
... Which of these describes a pollution-producing process that involves only a physical change? a) Coal with a high sulfur content is burned, producing gases that cause acid rain. b) Chlorofluorocarbons are released, changing ozone in the upper atmosphere into oxygen. c) Hot wastewater is discharged i ...
Course Pack3 Phase Diagrams
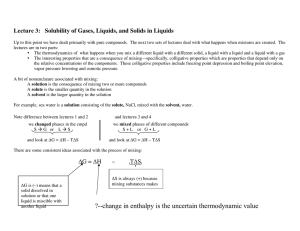
... ∆Hsoln is (+) for NaCl in H2O ∆Hsoln is (–) for Na2SO4 in H2O ∆Hsoln is (–) for O2 in H2O Consider the case that ∆Hmix is negative: since ∆Smix is positive then ∆Gsoln will have to be negative and the reaction happens. Now consider the case that ∆Hmix is positive: in this case the spontaneity of the ...
... ∆Hsoln is (+) for NaCl in H2O ∆Hsoln is (–) for Na2SO4 in H2O ∆Hsoln is (–) for O2 in H2O Consider the case that ∆Hmix is negative: since ∆Smix is positive then ∆Gsoln will have to be negative and the reaction happens. Now consider the case that ∆Hmix is positive: in this case the spontaneity of the ...
2nd Semester Final Exam Review
... 27. The melting of 1 mole of H2O takes 1.44 kcal of energy. Calculate the energy involved if only 3.15 grams of ice were melted. q= H x n 28. In the problem above did the entropy increase, decrease, or not change? Explain. 29. If 45.0 g of water is heated and the temp. rose from 20.6 oC to 30.0 oC. ...
... 27. The melting of 1 mole of H2O takes 1.44 kcal of energy. Calculate the energy involved if only 3.15 grams of ice were melted. q= H x n 28. In the problem above did the entropy increase, decrease, or not change? Explain. 29. If 45.0 g of water is heated and the temp. rose from 20.6 oC to 30.0 oC. ...
File
... Solvation • The process of a solute dissolving in a solvent • Solute is added to solvent solvent particles attract solute particles bonds holding solute together break down solute becomes surrounded by solvent molecules • if the attraction between particles of the solute is stronger than thos ...
... Solvation • The process of a solute dissolving in a solvent • Solute is added to solvent solvent particles attract solute particles bonds holding solute together break down solute becomes surrounded by solvent molecules • if the attraction between particles of the solute is stronger than thos ...
Mixtures
... suspensions. These mixtures are known as colloids. A colloid is a mixture in which the particles are dispersed throughout but are not heavy enough to settle out. The particles in a colloid are relatively small and are fairly well mixed. Solids, liquids, and gases can be used to make colloids. Unli ...
... suspensions. These mixtures are known as colloids. A colloid is a mixture in which the particles are dispersed throughout but are not heavy enough to settle out. The particles in a colloid are relatively small and are fairly well mixed. Solids, liquids, and gases can be used to make colloids. Unli ...
SCIENCE
... has different parts; it’s not all the same. 2. Homogenous mixture: a mixture where the molecules of each substance are equally mixed, and you can’t see the different parts of the mixture. Sugar that has been dissolved in water creates a homogenous mixture; you can’t see the sugar and the water, just ...
... has different parts; it’s not all the same. 2. Homogenous mixture: a mixture where the molecules of each substance are equally mixed, and you can’t see the different parts of the mixture. Sugar that has been dissolved in water creates a homogenous mixture; you can’t see the sugar and the water, just ...
Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. Examples
... Density is the mass per unit of volume. It is affected by a change in temperature. Formula: Density = mass D=m Volume V ...
... Density is the mass per unit of volume. It is affected by a change in temperature. Formula: Density = mass D=m Volume V ...
matter
... this mixture of solid materials so that the gravel ends in the G cup, the powder in the P cup, and the salt in the S cup. ...
... this mixture of solid materials so that the gravel ends in the G cup, the powder in the P cup, and the salt in the S cup. ...
Formation of Solutions
... Sodium Chloride dissolves by dissociation. This is how an Ionic Compound separates into ions. ...
... Sodium Chloride dissolves by dissociation. This is how an Ionic Compound separates into ions. ...
Second Semester Extra Review
... 6. A mixture of gases is at a pressure of 920.3 mmHg, what is the partial pressure of carbon dioxide gas in the mixture containing oxygen and carbon dioxide if the partial pressure of oxygen is 524.9 mmHg? 7. What is standard temperature and pressure? 8. An oxygen gas cylinder has a volume of 5.6 x ...
... 6. A mixture of gases is at a pressure of 920.3 mmHg, what is the partial pressure of carbon dioxide gas in the mixture containing oxygen and carbon dioxide if the partial pressure of oxygen is 524.9 mmHg? 7. What is standard temperature and pressure? 8. An oxygen gas cylinder has a volume of 5.6 x ...
Chemistry Vocab for Quiz 12/21 or 12/22 Atom – The smallest
... Physical change – A change that alters the form or appearance of a material but does not make the material into a different substance. Chemical change – A change in matter that produces a new substance. Solution – A well mixed mixture. Solubility – A measure of how well a solute can be dissolved at ...
... Physical change – A change that alters the form or appearance of a material but does not make the material into a different substance. Chemical change – A change in matter that produces a new substance. Solution – A well mixed mixture. Solubility – A measure of how well a solute can be dissolved at ...
Science Notes on Physical and Chemical Properties
... 4. Non-Reactivity – when something fails to react…example…platinum dropped in acid has no reaction…nothing happens. Even when held into a flame, platinum has no reaction ** Main Point to Remember about Chemical Reactions… ...
... 4. Non-Reactivity – when something fails to react…example…platinum dropped in acid has no reaction…nothing happens. Even when held into a flame, platinum has no reaction ** Main Point to Remember about Chemical Reactions… ...
Solubility
... In studio 5c, you dissolved salts to make hot and cold packs. For example: NaCl(s) → Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) Hrxn = 4 kJ/mol All of the salt you added to the water dissolved so these reactions could be described as going to completion. Could you just keep dissolving sodium chloride in water to generate a ...
... In studio 5c, you dissolved salts to make hot and cold packs. For example: NaCl(s) → Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) Hrxn = 4 kJ/mol All of the salt you added to the water dissolved so these reactions could be described as going to completion. Could you just keep dissolving sodium chloride in water to generate a ...
Metathesis Problems (and Some Solutions) Identified Through
... (bubbles that appear when heating water) • Most ionic solids are more soluble in water at higher temperatures – Some have very little change, like NaCl – Some are less soluble in higher temperatures • Heat of solution: heat absorbed or released when a solid is dissolved – Depends on combination of l ...
... (bubbles that appear when heating water) • Most ionic solids are more soluble in water at higher temperatures – Some have very little change, like NaCl – Some are less soluble in higher temperatures • Heat of solution: heat absorbed or released when a solid is dissolved – Depends on combination of l ...
Atomic number
... Which of these describes a pollution-producing process that involves only a physical change? a) Coal with a high sulfur content is burned, producing gases that cause acid rain. b) Chlorofluorocarbons are released, changing ozone in the upper atmosphere into oxygen. c) Hot wastewater is discharged i ...
... Which of these describes a pollution-producing process that involves only a physical change? a) Coal with a high sulfur content is burned, producing gases that cause acid rain. b) Chlorofluorocarbons are released, changing ozone in the upper atmosphere into oxygen. c) Hot wastewater is discharged i ...