CH 13
... Slow Steps- A step that is much slower than any other in a reaction mechanism. Rate-determining step - The rate of the overall reaction can be taken to be that of the slow step Step 1: Step 2: Step 3: ...
... Slow Steps- A step that is much slower than any other in a reaction mechanism. Rate-determining step - The rate of the overall reaction can be taken to be that of the slow step Step 1: Step 2: Step 3: ...
vce chemistry trial exam 1
... C is correct. HPLC allows the separation of organic compounds such as esters. NMR spectroscopy allows the estimation of the structure of organic compounds based on their 13C and 1H spectra. A is incorrect because neither UV-visible spectroscopy nor NMR spectroscopy allow the separation of compounds. ...
... C is correct. HPLC allows the separation of organic compounds such as esters. NMR spectroscopy allows the estimation of the structure of organic compounds based on their 13C and 1H spectra. A is incorrect because neither UV-visible spectroscopy nor NMR spectroscopy allow the separation of compounds. ...
Isopropanol oxidation by pure metal oxide
... and NH3 . CO2 and NH3 do not measure all the surface sites. CO2 only adsorbs on basic OH groups on the surface and NH3 only adsorbs on Lewis and Bronsted acid sites. Furthermore, the above methods are unable to distinguish between surface acidic and redox sites. The adsorption and reaction of alcoho ...
... and NH3 . CO2 and NH3 do not measure all the surface sites. CO2 only adsorbs on basic OH groups on the surface and NH3 only adsorbs on Lewis and Bronsted acid sites. Furthermore, the above methods are unable to distinguish between surface acidic and redox sites. The adsorption and reaction of alcoho ...
Methane Activation by Transition-Metal Oxides, MOx
... methane activation, the combined system MoO3/HZSM-5 yields conversions as high as 10% with 80% selectivity toward benzene.1 This catalyst has an induction period and appears to be poisoned by coke formation.1 There is general agreement that this system forms a bifunctional catalyst with the metal re ...
... methane activation, the combined system MoO3/HZSM-5 yields conversions as high as 10% with 80% selectivity toward benzene.1 This catalyst has an induction period and appears to be poisoned by coke formation.1 There is general agreement that this system forms a bifunctional catalyst with the metal re ...
Stoich chem reactions practice Answer Section
... 3. To balance a chemical equation, it may be necessary to adjust the a. coefficients. c. formulas of the products. b. subscripts. d. number of products. 4. Which word equation represents the reaction that produces water from hydrogen and oxygen? a. Water is produced from hydrogen and oxygen. b. Hydr ...
... 3. To balance a chemical equation, it may be necessary to adjust the a. coefficients. c. formulas of the products. b. subscripts. d. number of products. 4. Which word equation represents the reaction that produces water from hydrogen and oxygen? a. Water is produced from hydrogen and oxygen. b. Hydr ...
South Pasadena • AP Chemistry Name
... The heat of combustion of propane, C3H8 , is -2220 kJ·mol-1. Use this information to calculate the Hf of C3H8. 1. Calculate the ΔH for the reaction: C2H4(g) + H2(g) → C2H6(g), from the following Data. C2H4(g) + 3 O2(g) → 2 CO2(g)+ 2 H2O(l) ΔH = -1411.kJ ...
... The heat of combustion of propane, C3H8 , is -2220 kJ·mol-1. Use this information to calculate the Hf of C3H8. 1. Calculate the ΔH for the reaction: C2H4(g) + H2(g) → C2H6(g), from the following Data. C2H4(g) + 3 O2(g) → 2 CO2(g)+ 2 H2O(l) ΔH = -1411.kJ ...
Photogeneration of Hydride Donors and Their Use Toward CO2
... located above the pyridine ring of bpy. indicate that a π-stacked dimer is a key intermediate in the photoreduction of [1]2+. The chiral recognition reaction via stereospecific dimerization of a racemic mixture of monomers, followed by disproportionation, may open new directions for photochemical st ...
... located above the pyridine ring of bpy. indicate that a π-stacked dimer is a key intermediate in the photoreduction of [1]2+. The chiral recognition reaction via stereospecific dimerization of a racemic mixture of monomers, followed by disproportionation, may open new directions for photochemical st ...
Unit 2:
... (a) Write the expression for the solubility-product constant, Ksp, and calculate its value at 18ºC. (b) Calculate the equilibrium concentration of Mg2+ in 1.000 liter of saturated MgF2 solution at 18ºC to which 0.100 mole of solid KF has been added. The KF dissolves completely. Assume the volume cha ...
... (a) Write the expression for the solubility-product constant, Ksp, and calculate its value at 18ºC. (b) Calculate the equilibrium concentration of Mg2+ in 1.000 liter of saturated MgF2 solution at 18ºC to which 0.100 mole of solid KF has been added. The KF dissolves completely. Assume the volume cha ...
Summary - Clydebank High School
... 1. In an ............................................... reaction heat energy is released to the surroundings. In an ............................................... reaction heat energy is absorbed from the surroundings. 2. In an exothermic reaction the reactants have ........................... sto ...
... 1. In an ............................................... reaction heat energy is released to the surroundings. In an ............................................... reaction heat energy is absorbed from the surroundings. 2. In an exothermic reaction the reactants have ........................... sto ...
1 Discussion questions 22.1 Consult literature sources and list the
... k′ = 1.4 × 1011 dm3 mol-1 s-1, Ea = 53.3 kJ mol-1 for the reverse reaction. Compute ΔfH_, Sm_, and ΔfG_ of C2H5 at 298 K. ...
... k′ = 1.4 × 1011 dm3 mol-1 s-1, Ea = 53.3 kJ mol-1 for the reverse reaction. Compute ΔfH_, Sm_, and ΔfG_ of C2H5 at 298 K. ...
Problem 1: “A brief history” of life in the universe
... elemental mass. The rest is mostly helium with small amounts of other elements. Hydrogen is not only abundant. It is the building block of all other elements. Hydrogen is abundant in stars such as the sun. Thus the Milky Way galaxy, consisting of over 100 billion stars, is rich in hydrogen. The dist ...
... elemental mass. The rest is mostly helium with small amounts of other elements. Hydrogen is not only abundant. It is the building block of all other elements. Hydrogen is abundant in stars such as the sun. Thus the Milky Way galaxy, consisting of over 100 billion stars, is rich in hydrogen. The dist ...
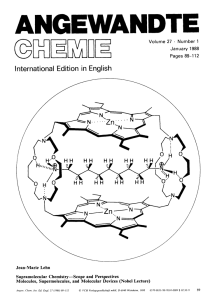
Supramolecular Chemistry—Scope and Perspectives Molecules
... coordination. Supramolecular catalysis by receptors bearing reactive groups effects bond cleavage reactions as well as synthetic bond formation via cocatalysis. Lipophilic receptor molecules act as selective carriers for various substrates and make it possible to set up coupled transport processes l ...
... coordination. Supramolecular catalysis by receptors bearing reactive groups effects bond cleavage reactions as well as synthetic bond formation via cocatalysis. Lipophilic receptor molecules act as selective carriers for various substrates and make it possible to set up coupled transport processes l ...
2 C2H6 (g)
... D. 2 Fe2O3 (s) + 3 C (s) + heat 4 Fe (s) + 3 CO2 (g) E. C (graphite) + O2 (g) CO2 (g) + heat F. CH4 (g) + O2 (g) CO2 (g) + H2O (l) + heat Question 27 of 28 Based on their descriptions, classify these chemical changes as endothermic or exothermic. A. A chemical change takes place in a container ...
... D. 2 Fe2O3 (s) + 3 C (s) + heat 4 Fe (s) + 3 CO2 (g) E. C (graphite) + O2 (g) CO2 (g) + heat F. CH4 (g) + O2 (g) CO2 (g) + H2O (l) + heat Question 27 of 28 Based on their descriptions, classify these chemical changes as endothermic or exothermic. A. A chemical change takes place in a container ...
Unit 5 Chemical Kinetics Section 5.1 Rates of Chemical Reaction
... The most significant method to make reactions go faster is to heat the reactants. An increase in temperature increases the number of reactant particles having energy greater than the activation energy of the reaction, thus producing more fruitful collisions. Moreover, the increase in temperature als ...
... The most significant method to make reactions go faster is to heat the reactants. An increase in temperature increases the number of reactant particles having energy greater than the activation energy of the reaction, thus producing more fruitful collisions. Moreover, the increase in temperature als ...
Revised Syllabus - M. Sc. First Year - Chemistry
... Home assignment: (a) Corresponding distribution laws, (Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution law) (b) Heat capacity behaviour of solids – chemical equilibria constant in terms of partition functions. (C) ...
... Home assignment: (a) Corresponding distribution laws, (Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution law) (b) Heat capacity behaviour of solids – chemical equilibria constant in terms of partition functions. (C) ...
program
... make a connection between bond types, lattice type, and the properties of a substance: • melting point and boiling point; • hardness and brittleness; • absence or presence of electrical conductivity in the solid, liquid, and/or dissolved ...
... make a connection between bond types, lattice type, and the properties of a substance: • melting point and boiling point; • hardness and brittleness; • absence or presence of electrical conductivity in the solid, liquid, and/or dissolved ...
Intermolecular forces and molecules
... boiling point. Do electronegativity differences account for this difference? Due to the molecule geometry, the bond dipoles in each cancel. In this case, differences in molar mass (polarizability) account for the variation in boiling point. Having noted that molar mass affects van der Waals forces, ...
... boiling point. Do electronegativity differences account for this difference? Due to the molecule geometry, the bond dipoles in each cancel. In this case, differences in molar mass (polarizability) account for the variation in boiling point. Having noted that molar mass affects van der Waals forces, ...
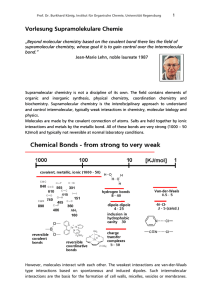
Supramolecular catalysis

Supramolecular catalysis is not a well-defined field but it generally refers to an application of supramolecular chemistry, especially molecular recognition and guest binding, toward catalysis. This field was originally inspired by enzymatic system which, unlike classical organic chemistry reactions, utilizes non-covalent interactions such as hydrogen bonding, cation-pi interaction, and hydrophobic forces to dramatically accelerate rate of reaction and/or allow highly selective reactions to occur. Because enzymes are structurally complex and difficult to modify, supramolecular catalysts offer a simpler model for studying factors involved in catalytic efficiency of the enzyme. Another goal that motivates this field is the development of efficient and practical catalysts that may or may not have an enzyme equivalent in nature.A closely related field of study is asymmetric catalysis which requires molecular recognition to differentiate two chiral starting material or chiral transition states and thus it could be categorized as an area of supramolecular catalysis, but supramolecular catalysis however does not necessarily have to involve asymmetric reaction. As there is another Wikipedia article already written about small molecule asymmetric catalysts, this article focuses primarily on large catalytic host molecules. Non-discrete and structurally poorly defined system such as micelle and dendrimers are not included.