Chapter 17 - Cengage Learning
... The collision model says that in order for molecules to react with each other, they must first collide. Increases in the temperature and concentration of reactants bring about more collisions, and the rate of reaction increases. The collision model explains many observations about reactions. Not all ...
... The collision model says that in order for molecules to react with each other, they must first collide. Increases in the temperature and concentration of reactants bring about more collisions, and the rate of reaction increases. The collision model explains many observations about reactions. Not all ...
Supporting Information Biomimetic Polymeric
... catalyst cm −2 of ZIF-9/glassy carbon electrode (blue line) in 0.1 M potassium phosphate buffer (pH = 7.0) at a scanning rate of 5mV/s.The catalyst was uniformly cast onto a 5 mm glassy carbon electrode with a total loading of ca. 200 μg catalyst cm−2. During the measurements, the working electrode ...
... catalyst cm −2 of ZIF-9/glassy carbon electrode (blue line) in 0.1 M potassium phosphate buffer (pH = 7.0) at a scanning rate of 5mV/s.The catalyst was uniformly cast onto a 5 mm glassy carbon electrode with a total loading of ca. 200 μg catalyst cm−2. During the measurements, the working electrode ...
Advanced Kinetic Analysis Using a LAMBDA Series Spectrometer
... 1.2 Kinetic Reactions in Enzyme Systems Chemical reactions in living systems would be extremely slow without the catalytic activity of enzymes. Biological processes use reaction chains and reaction cycles where several reactions are combined in sequence and the product of the first reaction is used ...
... 1.2 Kinetic Reactions in Enzyme Systems Chemical reactions in living systems would be extremely slow without the catalytic activity of enzymes. Biological processes use reaction chains and reaction cycles where several reactions are combined in sequence and the product of the first reaction is used ...
Document
... If 4.0 mol N2 and 1.0 mol O2 are mixed in a 5.0 L container, what are all equilibrium concentrations? ...
... If 4.0 mol N2 and 1.0 mol O2 are mixed in a 5.0 L container, what are all equilibrium concentrations? ...
Activation of Nitrous Oxide and Selective Epoxidation of Alkenes
... Nitrous oxide is usually considered to be inert1 and a poor ligand toward transition metals.2 However, there is incentive to use N2O as an oxygen donor because it contains 36 wt % oxygen, and the byproduct of an oxidation reaction would be N2. In practice, there are only a few catalytic systems that ...
... Nitrous oxide is usually considered to be inert1 and a poor ligand toward transition metals.2 However, there is incentive to use N2O as an oxygen donor because it contains 36 wt % oxygen, and the byproduct of an oxidation reaction would be N2. In practice, there are only a few catalytic systems that ...
Adsorption studies of cyanide onto activated carbon
... and as for the fourth process, it is limited to certain climate conditions. The next best process used, is the oxidation with hydrogen peroxide where the cyanide concentration is reduced to low enough levels, but this process requires an expensive reagent which cannot be reused [10-16]. Activated ca ...
... and as for the fourth process, it is limited to certain climate conditions. The next best process used, is the oxidation with hydrogen peroxide where the cyanide concentration is reduced to low enough levels, but this process requires an expensive reagent which cannot be reused [10-16]. Activated ca ...
Supramolecular catalysis

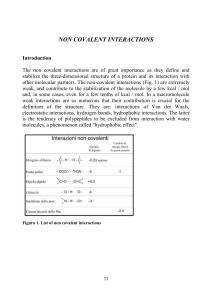
Supramolecular catalysis is not a well-defined field but it generally refers to an application of supramolecular chemistry, especially molecular recognition and guest binding, toward catalysis. This field was originally inspired by enzymatic system which, unlike classical organic chemistry reactions, utilizes non-covalent interactions such as hydrogen bonding, cation-pi interaction, and hydrophobic forces to dramatically accelerate rate of reaction and/or allow highly selective reactions to occur. Because enzymes are structurally complex and difficult to modify, supramolecular catalysts offer a simpler model for studying factors involved in catalytic efficiency of the enzyme. Another goal that motivates this field is the development of efficient and practical catalysts that may or may not have an enzyme equivalent in nature.A closely related field of study is asymmetric catalysis which requires molecular recognition to differentiate two chiral starting material or chiral transition states and thus it could be categorized as an area of supramolecular catalysis, but supramolecular catalysis however does not necessarily have to involve asymmetric reaction. As there is another Wikipedia article already written about small molecule asymmetric catalysts, this article focuses primarily on large catalytic host molecules. Non-discrete and structurally poorly defined system such as micelle and dendrimers are not included.