184
... The average absolute error of the additivity assumptions in the G2 level of theory is only 0.30 kcal/mol.11 Because the geometry and frequencies of some transition states are sensitive to the level of theory, in the present work we use the zeropoint energy calculated at the MP2/6-31G(d) scaled by 0. ...
... The average absolute error of the additivity assumptions in the G2 level of theory is only 0.30 kcal/mol.11 Because the geometry and frequencies of some transition states are sensitive to the level of theory, in the present work we use the zeropoint energy calculated at the MP2/6-31G(d) scaled by 0. ...
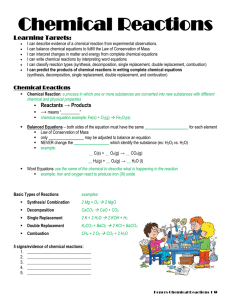
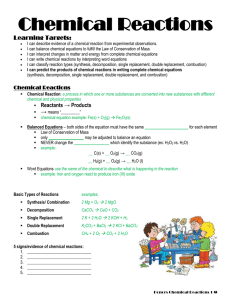
Stoichiometry – Chapter 9
... Stoichiometry ? the name given to the study of quantitative relationships that can be derived from formulas and equations. It is from the Greek words stoicheion, meaning ?element? and metron, meaning ?measure?. There are two types: composition stoichiometry (formulas) and reaction stoichiometry ...
... Stoichiometry ? the name given to the study of quantitative relationships that can be derived from formulas and equations. It is from the Greek words stoicheion, meaning ?element? and metron, meaning ?measure?. There are two types: composition stoichiometry (formulas) and reaction stoichiometry ...
CHAPTER-7 EQUILIBRIUM Equilibrium state- When
... The acid-base pair thatdiffers only by one proton is called a conjugateacidbase pair. IfBrönsted acid is a strong acid then itsconjugate base is a weak base and viceversa. Ionic product of water.Kw = [H+][OH–] pH = -log [H+] ; here[H+] is molar concentration of hydrogen ion. pH + pOH =14 p ...
... The acid-base pair thatdiffers only by one proton is called a conjugateacidbase pair. IfBrönsted acid is a strong acid then itsconjugate base is a weak base and viceversa. Ionic product of water.Kw = [H+][OH–] pH = -log [H+] ; here[H+] is molar concentration of hydrogen ion. pH + pOH =14 p ...
2 Chemical equilibrium occurs when a reaction and its reverse
... The ratio of [NO2]2 to [N2O4] remains constant (within error) at this temperature no matter what the initial concentrations of NO2 and N2O4 are. ...
... The ratio of [NO2]2 to [N2O4] remains constant (within error) at this temperature no matter what the initial concentrations of NO2 and N2O4 are. ...
Loeblein chemistry clicker questions2013
... •Describe a molecular model of gas pressure •Describe what happens to the measurable quantities if changes to the gas system are made. •Make sense of the measurable quantities of gases by analyzing examples of macroscopic things that are similar •Explain using physics what is happening on a molecula ...
... •Describe a molecular model of gas pressure •Describe what happens to the measurable quantities if changes to the gas system are made. •Make sense of the measurable quantities of gases by analyzing examples of macroscopic things that are similar •Explain using physics what is happening on a molecula ...
Experimental and Computational Evidence of Metal‑O2 Activation
... Initial rates of O2 consumption were determined with a Clarktype O2 (YSI) electrode. In contrast to the kinetic behavior of wild-type CuAGAO,60 CoAGAO exhibited a significant induction or lag phase. Maximal rates were estimated from the linear portion of time traces corresponding to the steepest slop ...
... Initial rates of O2 consumption were determined with a Clarktype O2 (YSI) electrode. In contrast to the kinetic behavior of wild-type CuAGAO,60 CoAGAO exhibited a significant induction or lag phase. Maximal rates were estimated from the linear portion of time traces corresponding to the steepest slop ...
Metal disordering Cu(II) supramolecular polymers constructed from
... sharing the edges closely, leading to metal–carboxylate (MC) layer along the ab plane. All the atoms in the layer exhibit a good planarity, which is rare even for rigid BTC ligand. Water and pyridine molecules coordinate to metal atoms lying perpendicular to the layer. As a result, alternating U1-MC ...
... sharing the edges closely, leading to metal–carboxylate (MC) layer along the ab plane. All the atoms in the layer exhibit a good planarity, which is rare even for rigid BTC ligand. Water and pyridine molecules coordinate to metal atoms lying perpendicular to the layer. As a result, alternating U1-MC ...
Formic acid oxidation reaction on a PdxNiy bimetallic nanoparticle
... Palladium (Pd) at nanoscale size has demonstrated its unique ability to catalyze the oxidation of formic acid in fuel cells in 1987 [5]. Recently, many methods to synthesize Pd NPs have been reported. For example, Wang et al. [6] reported a facile method to synthesize Pd NPs supported on graphene ri ...
... Palladium (Pd) at nanoscale size has demonstrated its unique ability to catalyze the oxidation of formic acid in fuel cells in 1987 [5]. Recently, many methods to synthesize Pd NPs have been reported. For example, Wang et al. [6] reported a facile method to synthesize Pd NPs supported on graphene ri ...
Problem 1: A brief history of life in the universe
... When molecules with non-zero dipole moments rotate, electromagnetic radiation can be absorbed or emitted. The spectroscopy related to molecular rotation is called microwave spectroscopy, because the electromagnetic radiation involved is in the microwave region. The rotational energy level of a diato ...
... When molecules with non-zero dipole moments rotate, electromagnetic radiation can be absorbed or emitted. The spectroscopy related to molecular rotation is called microwave spectroscopy, because the electromagnetic radiation involved is in the microwave region. The rotational energy level of a diato ...
No Slide Title
... concentrations for the reaction? First, calculate y, the change in concentration. • PCl5 (g) ⇌ PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) • y = 0.087 or -0.687 Choose 0.087 to get a result in which all the concentrations are positive. ...
... concentrations for the reaction? First, calculate y, the change in concentration. • PCl5 (g) ⇌ PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) • y = 0.087 or -0.687 Choose 0.087 to get a result in which all the concentrations are positive. ...
Supramolecular catalysis

Supramolecular catalysis is not a well-defined field but it generally refers to an application of supramolecular chemistry, especially molecular recognition and guest binding, toward catalysis. This field was originally inspired by enzymatic system which, unlike classical organic chemistry reactions, utilizes non-covalent interactions such as hydrogen bonding, cation-pi interaction, and hydrophobic forces to dramatically accelerate rate of reaction and/or allow highly selective reactions to occur. Because enzymes are structurally complex and difficult to modify, supramolecular catalysts offer a simpler model for studying factors involved in catalytic efficiency of the enzyme. Another goal that motivates this field is the development of efficient and practical catalysts that may or may not have an enzyme equivalent in nature.A closely related field of study is asymmetric catalysis which requires molecular recognition to differentiate two chiral starting material or chiral transition states and thus it could be categorized as an area of supramolecular catalysis, but supramolecular catalysis however does not necessarily have to involve asymmetric reaction. As there is another Wikipedia article already written about small molecule asymmetric catalysts, this article focuses primarily on large catalytic host molecules. Non-discrete and structurally poorly defined system such as micelle and dendrimers are not included.