Chapter 14 (13) Exchange Rate Determination
... • Risk of holding asset • Liquidity of an asset: or ease of using the asset to buy goods and services – We assume risk and liquidity of currency deposits in foreign exchange markets are essentially the same, regardless of their currency denomination. – Importers and exporters may be concerned about ...
... • Risk of holding asset • Liquidity of an asset: or ease of using the asset to buy goods and services – We assume risk and liquidity of currency deposits in foreign exchange markets are essentially the same, regardless of their currency denomination. – Importers and exporters may be concerned about ...
PANEL
... Firstly, the US external position has at times been affected by adverse cyclical movements at home and abroad, as for example in the years 1958-59. Secondly, there has been an adverse effect at times from domestic excess demand, particularly evident during the period of the Vietnam war 0 ...
... Firstly, the US external position has at times been affected by adverse cyclical movements at home and abroad, as for example in the years 1958-59. Secondly, there has been an adverse effect at times from domestic excess demand, particularly evident during the period of the Vietnam war 0 ...
Results of World War I
... collective security system (League of Nations) undermined at starting point due to isolationism stopping wilsonianism in US Congress Washington Naval Conference (1921-1922) – complementing European peace settlements (UK, USA - 5, Japan - 3, France, Italy - 1.67 ratios for capital ships – recognition ...
... collective security system (League of Nations) undermined at starting point due to isolationism stopping wilsonianism in US Congress Washington Naval Conference (1921-1922) – complementing European peace settlements (UK, USA - 5, Japan - 3, France, Italy - 1.67 ratios for capital ships – recognition ...
[INSERT TITLE HERE] Running head: [INSERT TITLE HERE
... overstating the damage that currency fixing is doing to our economy? Is it a political issue or a real economic one? Be sure to back up your thoughts in a two page paper in APA format with at least two cited scholarly reference. Please utilize LIRN to help you get started with your search. You may v ...
... overstating the damage that currency fixing is doing to our economy? Is it a political issue or a real economic one? Be sure to back up your thoughts in a two page paper in APA format with at least two cited scholarly reference. Please utilize LIRN to help you get started with your search. You may v ...
1.1.1 - LPS Business DEPT
... The additional trade creation also encourages greater competition within euro member states, which can help reduce prices and promote efficiency ...
... The additional trade creation also encourages greater competition within euro member states, which can help reduce prices and promote efficiency ...
international investment process
... In our ETF only portfolios, we will use ETFs exclusively. In using third-party ETFs, the portfolio managers are limited in their ability to execute their dynamic hedging strategy by the ETF products that are currently on the market. 2. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE TOOLS • Quantitative: Over the long ...
... In our ETF only portfolios, we will use ETFs exclusively. In using third-party ETFs, the portfolio managers are limited in their ability to execute their dynamic hedging strategy by the ETF products that are currently on the market. 2. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE TOOLS • Quantitative: Over the long ...
12-3
... Currently the CA deficit is hovering around 3-4% because the recession has caused depreciation of the USD and Oil prices are substantially lower. ...
... Currently the CA deficit is hovering around 3-4% because the recession has caused depreciation of the USD and Oil prices are substantially lower. ...
optimum currency areas - YSU
... with free trade, free flows of financial assets, and free migration of people—in addition to fixed exchange rates or a common currency—was believed to foster economic growth and economic well-being. 3. To make Europe politically stable and peaceful. ...
... with free trade, free flows of financial assets, and free migration of people—in addition to fixed exchange rates or a common currency—was believed to foster economic growth and economic well-being. 3. To make Europe politically stable and peaceful. ...
F S B C
... elsewhere in the region. But it would still give a welcome boost to world demand and might marginally help those who have borrowed in yen. The optimal response by Japan would be a policy mix of monetary and fiscal expansion with offsetting exchange rate effects. Given the dollar and yen debts incurr ...
... elsewhere in the region. But it would still give a welcome boost to world demand and might marginally help those who have borrowed in yen. The optimal response by Japan would be a policy mix of monetary and fiscal expansion with offsetting exchange rate effects. Given the dollar and yen debts incurr ...
Chapter 17 International Finance Name
... 8. A change in the supply or demand changes the money’s ( ) ( ). 9. After the Lord of the Rings, if there was a sudden demand by Americans for travel to New Zealand, the equilibrium price of the NZ dollar would ( ). The US dollar becomes worth ( ) in terms of the NZ dollar, and the NZ dollar become ...
... 8. A change in the supply or demand changes the money’s ( ) ( ). 9. After the Lord of the Rings, if there was a sudden demand by Americans for travel to New Zealand, the equilibrium price of the NZ dollar would ( ). The US dollar becomes worth ( ) in terms of the NZ dollar, and the NZ dollar become ...
Lecture 3: Int`l Finance
... – Govt must use its foreign exchange reserves to buy up the local currency. Problem: foreign reserves are exhaustible. – When this happens, govt must use monetary policy to increase demand for its currency: raise domestic interest rates to attract capital inflows – But high interest rates have damag ...
... – Govt must use its foreign exchange reserves to buy up the local currency. Problem: foreign reserves are exhaustible. – When this happens, govt must use monetary policy to increase demand for its currency: raise domestic interest rates to attract capital inflows – But high interest rates have damag ...
Appreciation
... •The Case for Fixed Exchange Rates • Facilitates trade by creating certainty about the exchange rate ...
... •The Case for Fixed Exchange Rates • Facilitates trade by creating certainty about the exchange rate ...
Presentation
... opened, accumulating hard currency as much as possible, even allowing some “sacrifice”. • System arrangement – The control of capital account – The control of exchange rate (fixed or manageable floating exchange regime for the purpose to devaluating domestic currency) – No debt, but accumulating har ...
... opened, accumulating hard currency as much as possible, even allowing some “sacrifice”. • System arrangement – The control of capital account – The control of exchange rate (fixed or manageable floating exchange regime for the purpose to devaluating domestic currency) – No debt, but accumulating har ...
solution
... 10. No. Looking simply at countries that are currently industrialized and finding convergence is not a valid way to test convergence. Countries that are currently well off may have started from a variety of circumstances, but by only choosing countries that are currently wealthy, we are forcing a fi ...
... 10. No. Looking simply at countries that are currently industrialized and finding convergence is not a valid way to test convergence. Countries that are currently well off may have started from a variety of circumstances, but by only choosing countries that are currently wealthy, we are forcing a fi ...
Commission on Currency Exchange
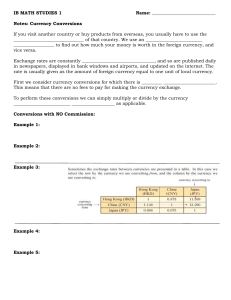
... Exchange rates are constantly ________________________________, and so are published daily in newspapers, displayed in bank windows and airports, and updated on the internet. The rate is usually given as the amount of foreign currency equal to one unit of local currency. First we consider currency c ...
... Exchange rates are constantly ________________________________, and so are published daily in newspapers, displayed in bank windows and airports, and updated on the internet. The rate is usually given as the amount of foreign currency equal to one unit of local currency. First we consider currency c ...
Exchange Rates
... Consider the spot foreign exchange market. • Price of US$: S is the price of US$ in terms of DCU. • Supply of US$: Foreign people who want to acquire DCU to buy domestic goods or assets. – When US$ becomes expensive, domestic goods or assets get cheap and foreign investors are attracted to domestic ...
... Consider the spot foreign exchange market. • Price of US$: S is the price of US$ in terms of DCU. • Supply of US$: Foreign people who want to acquire DCU to buy domestic goods or assets. – When US$ becomes expensive, domestic goods or assets get cheap and foreign investors are attracted to domestic ...
FRBSF E L CONOMIC ETTER
... labor from agriculture to nonagriculture accounted for over one-third of China’s average annual increase in output per capita (that is, 2.0 percentage points of total labor productivity growth of 5.2%), while productivity growth in the public sector and private nonagricultural sector contributed 1.6 ...
... labor from agriculture to nonagriculture accounted for over one-third of China’s average annual increase in output per capita (that is, 2.0 percentage points of total labor productivity growth of 5.2%), while productivity growth in the public sector and private nonagricultural sector contributed 1.6 ...
Real Exchange Rate
... identical good, if the good is tradable, if there is free trade and there are no transactions /transportation costs, then the price should be the same in both countries. In the shirt example, U.S consumers would buy Indian shirts, buy more rupees, causing an appreciation of the Indian rupee and maki ...
... identical good, if the good is tradable, if there is free trade and there are no transactions /transportation costs, then the price should be the same in both countries. In the shirt example, U.S consumers would buy Indian shirts, buy more rupees, causing an appreciation of the Indian rupee and maki ...
AP Macroeconomics Section 8 Practice Test 1. An open economy is
... B. uncertainty about the value of goods traded internationally. C. increased discipline brought on monetary policy. D. distorted incentives imposed on the normal flow of imports and exports. E. inability of domestic citizens to afford international travel. 15. When a government wishes to target its ...
... B. uncertainty about the value of goods traded internationally. C. increased discipline brought on monetary policy. D. distorted incentives imposed on the normal flow of imports and exports. E. inability of domestic citizens to afford international travel. 15. When a government wishes to target its ...
China Going Global Policy-
... Decentralized 3.3 billion foreign currency purchase quota approval for investing abroad Self earned foreign currency—subject to approval Domestic foreign currency loan—subject to scrutiny Increase of investment amount (equity)—same as above approval Not possible to get cash ...
... Decentralized 3.3 billion foreign currency purchase quota approval for investing abroad Self earned foreign currency—subject to approval Domestic foreign currency loan—subject to scrutiny Increase of investment amount (equity)—same as above approval Not possible to get cash ...
Currency war

Currency war, also known as competitive devaluation, is a condition in international affairs where countries compete against each other to achieve a relatively low exchange rate for their own currency. As the price to buy a country's currency falls so too does the price of exports. Imports to the country become more expensive. So domestic industry, and thus employment, receives a boost in demand from both domestic and foreign markets. However, the price increase for imports can harm citizens' purchasing power. The policy can also trigger retaliatory action by other countries which in turn can lead to a general decline in international trade, harming all countries.Competitive devaluation has been rare through most of history as countries have generally preferred to maintain a high value for their currency. Countries have generally allowed market forces to work, or have participated in systems of managed exchanges rates. An exception occurred when currency war broke out in the 1930s. As countries abandoned the Gold Standard during the Great Depression, they used currency devaluations to stimulate their economies. Since this effectively pushes unemployment overseas, trading partners quickly retaliated with their own devaluations. The period is considered to have been an adverse situation for all concerned, as unpredictable changes in exchange rates reduced overall international trade.According to Guido Mantega, the Brazilian Minister for Finance, a global currency war broke out in 2010. This view was echoed by numerous other government officials and financial journalists from around the world. Other senior policy makers and journalists suggested the phrase ""currency war"" overstated the extent of hostility. With a few exceptions, such as Mantega, even commentators who agreed there had been a currency war in 2010 generally concluded that it had fizzled out by mid-2011.States engaging in possible competitive devaluation since 2010 have used a mix of policy tools, including direct government intervention, the imposition of capital controls, and, indirectly, quantitative easing. While many countries experienced undesirable upward pressure on their exchange rates and took part in the ongoing arguments, the most notable dimension of the 2010–11 episode was the rhetorical conflict between the United States and China over the valuation of the yuan. In January 2013, measures announced by Japan which were expected to devalue its currency sparked concern of a possible second 21st century currency war breaking out, this time with the principal source of tension being not China versus the US, but Japan versus the Eurozone. By late February, concerns of a new outbreak of currency war had been mostly allayed, after the G7 and G20 issued statements committing to avoid competitive devaluation. After the European Central Bank launched a fresh programme of quantitative easing in January 2015, there was once again an intensification of discussion about currency war.


![[INSERT TITLE HERE] Running head: [INSERT TITLE HERE](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/011305355_1-cb5f3e9bbbed3a09c4eda803f7fd7eb3-300x300.png)