international financing and international financial markets
... b. Important funding source: Japanese banks for U.S. firms ...
... b. Important funding source: Japanese banks for U.S. firms ...
UGBA 178: Introduction to International Business
... South, East, and Southeast Asia, and particularly China, are now seeing an increase of FDI inflows ...
... South, East, and Southeast Asia, and particularly China, are now seeing an increase of FDI inflows ...
Chapter 3
... • The Gold Standard (1876 – 1913) – Gold has been a medium of exchange since 3000 BC – “Rules of the game” were simple, each country set the rate at which its currency unit could be converted to a weight of gold – Currency exchange rates were in effect “fixed” – Expansionary monetary policy was limi ...
... • The Gold Standard (1876 – 1913) – Gold has been a medium of exchange since 3000 BC – “Rules of the game” were simple, each country set the rate at which its currency unit could be converted to a weight of gold – Currency exchange rates were in effect “fixed” – Expansionary monetary policy was limi ...
Dan Peck -- Chinese Currency: Manipulation?
... The Impacts of Manipulation The Claims against China Virtual Subsidy Counter Arguments ...
... The Impacts of Manipulation The Claims against China Virtual Subsidy Counter Arguments ...
Section One - Pearson Education
... naturally occurring minerals in the UK. After extraction by the UK subsidiary the semi-processed material is shipped on to the German subsidiary where it is further processed and refined. It is then transported to a specialist distribution subsidiary in Denmark. The three subsidiaries have no other ...
... naturally occurring minerals in the UK. After extraction by the UK subsidiary the semi-processed material is shipped on to the German subsidiary where it is further processed and refined. It is then transported to a specialist distribution subsidiary in Denmark. The three subsidiaries have no other ...
Fundamental Analysis
... Every major economic indicator released from major economies impact their respective currencies. Positive economic data strengthens the currency and negative data weakens the ...
... Every major economic indicator released from major economies impact their respective currencies. Positive economic data strengthens the currency and negative data weakens the ...
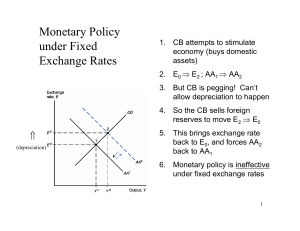
Fixed Exchange Rates and Macroeconomic Policy
... the exchange rate for which the output market is in short-run equilibrium (aggregate demand = aggregate output). • It slopes upward because a rise in the exchange rate (depreciation) causes output, Y, to rise – If P and P* are fixed in the short run, a depreciation of the domestic currency increases ...
... the exchange rate for which the output market is in short-run equilibrium (aggregate demand = aggregate output). • It slopes upward because a rise in the exchange rate (depreciation) causes output, Y, to rise – If P and P* are fixed in the short run, a depreciation of the domestic currency increases ...
Mr. Mayer AP Macroeconomics
... – Ex. a preference for Japanese goods creates an increase in the supply of dollars in the currency exchange market which leads to depreciation of the Dollar and an appreciation of Yen ...
... – Ex. a preference for Japanese goods creates an increase in the supply of dollars in the currency exchange market which leads to depreciation of the Dollar and an appreciation of Yen ...
Lecture 11 - Guoxiong ZHANG
... • Appreciation: a currency rises in value relative to another currency • Depreciation: a currency falls in value relative to another currency • When a country’s currency appreciates, the country’s goods abroad become more expensive and foreign goods in that country become less expensive and vice ver ...
... • Appreciation: a currency rises in value relative to another currency • Depreciation: a currency falls in value relative to another currency • When a country’s currency appreciates, the country’s goods abroad become more expensive and foreign goods in that country become less expensive and vice ver ...
Argentina Crisis
... attempt to restore market confidence, attract foreign capital and ultimately get the Argentinean market back on track. ...
... attempt to restore market confidence, attract foreign capital and ultimately get the Argentinean market back on track. ...
Week 5 Lecture Notes
... Individual dealers within the commercial banks communicate with one another electronically, buying and selling currencies and thus setting market prices • Spot transactions are settled within 2 days • Forward transactions guarantee a certain rate at some point in the future • Speculation by dealers ...
... Individual dealers within the commercial banks communicate with one another electronically, buying and selling currencies and thus setting market prices • Spot transactions are settled within 2 days • Forward transactions guarantee a certain rate at some point in the future • Speculation by dealers ...
The Baltic Paradox
... It is commonly supposed that the main cause of inflation and price rise is the unbacked issue of money and its depreciation linked with it. However, this maxim has not been confirmed by the development of Baltic economies. No Baltic State pursues an inflationary monetary policy. Lithuanian and Eston ...
... It is commonly supposed that the main cause of inflation and price rise is the unbacked issue of money and its depreciation linked with it. However, this maxim has not been confirmed by the development of Baltic economies. No Baltic State pursues an inflationary monetary policy. Lithuanian and Eston ...
Document
... – Ex. a preference for Japanese goods creates an increase in the supply of dollars in the currency exchange market which leads to depreciation of the Dollar and an appreciation of Yen ...
... – Ex. a preference for Japanese goods creates an increase in the supply of dollars in the currency exchange market which leads to depreciation of the Dollar and an appreciation of Yen ...
EconomicHistory(ASRIMarch2016)
... • The Glass-Steagall Act had provided for a strict separation of investment banking and commercial banking • Under the Glass-Steagall Act depositors money could not be used by commercial banks to invest in high risk securities (this would have been the preserve of investment bank who were taking ris ...
... • The Glass-Steagall Act had provided for a strict separation of investment banking and commercial banking • Under the Glass-Steagall Act depositors money could not be used by commercial banks to invest in high risk securities (this would have been the preserve of investment bank who were taking ris ...
Macro practice FRQs
... The FED and Monetary policy • Always affects the money market • Money market has vertical supply curve • Increase in money supply lowers interest rates – increases investment and consumption and AD • Lower interest rates cause $ to depreciate – exports increase, imports decrease • Decrease in money ...
... The FED and Monetary policy • Always affects the money market • Money market has vertical supply curve • Increase in money supply lowers interest rates – increases investment and consumption and AD • Lower interest rates cause $ to depreciate – exports increase, imports decrease • Decrease in money ...
Economics R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O`Brien, 2e.
... If the economy is currently below potential GDP, then, holding all other factors constant including prices at home and abroad, depreciation of the domestic currency should increase net exports, aggregate demand, and real GDP. An appreciation in the domestic currency should have the opposite effect: ...
... If the economy is currently below potential GDP, then, holding all other factors constant including prices at home and abroad, depreciation of the domestic currency should increase net exports, aggregate demand, and real GDP. An appreciation in the domestic currency should have the opposite effect: ...
Foreign currency
... -Non monetary items other than inventories and fixed assets- rate prevalent at the date of the transaction. -Fixed assets- rate prevalent at the date of the transaction as adjusted for exchange difference arising on settlement or restatement of liabilities incurred for acquiring those assets. -Balan ...
... -Non monetary items other than inventories and fixed assets- rate prevalent at the date of the transaction. -Fixed assets- rate prevalent at the date of the transaction as adjusted for exchange difference arising on settlement or restatement of liabilities incurred for acquiring those assets. -Balan ...
Argentina_en.pdf
... On the fiscal side, government policy in the first nine months of the year had a countercyclical bias, manifested in a rate of primary spending growth (44%) that outstripped growth in revenues (42.1%) and nominal output (about 30%). Within the primary spending category, current expenditure rose by 4 ...
... On the fiscal side, government policy in the first nine months of the year had a countercyclical bias, manifested in a rate of primary spending growth (44%) that outstripped growth in revenues (42.1%) and nominal output (about 30%). Within the primary spending category, current expenditure rose by 4 ...
Vulnerability Index – Guessing the Probability of a Currency Crisis
... appreciation of the currency, weak domestic economic growth, rising unemployment, an adverse terms-of-trade shock, a deteriorating current account balance, excessive domestic credit expansion, banking-system difficulties, unsustainably large government budget deficits, overly expansionary monetary p ...
... appreciation of the currency, weak domestic economic growth, rising unemployment, an adverse terms-of-trade shock, a deteriorating current account balance, excessive domestic credit expansion, banking-system difficulties, unsustainably large government budget deficits, overly expansionary monetary p ...
Document
... treasure bills nominated in bolivianos (the local currency) and nominated in foreign currency (dollars). So we need three data series. For each one, follow the following procedure: Select the country (Bolivia, US) and the data concept (“treasure bill rate” for US and Bolivia and “treasure bill rate ...
... treasure bills nominated in bolivianos (the local currency) and nominated in foreign currency (dollars). So we need three data series. For each one, follow the following procedure: Select the country (Bolivia, US) and the data concept (“treasure bill rate” for US and Bolivia and “treasure bill rate ...
Todays CA - WordPress.com
... levels it’s believed to enter over-valued zone and vice versa.The RBI calculates REER for India CURRENCY OVERVALUATION is condition that occurs when the supply of a currency is disrupted by overdemand resulting in an increase in its value beyond the accepted market exchange rate. +VES 1) Downward pr ...
... levels it’s believed to enter over-valued zone and vice versa.The RBI calculates REER for India CURRENCY OVERVALUATION is condition that occurs when the supply of a currency is disrupted by overdemand resulting in an increase in its value beyond the accepted market exchange rate. +VES 1) Downward pr ...
Weekly Market Commentary November 25, 2013
... abolished and replaced by an automated system that would increase money supply at a steady, pre-set rate. He believed such a system would better control inflation, making spending and investment decisions more certain. The Economist article said: "In theory, then, the system ought to keep a lid on i ...
... abolished and replaced by an automated system that would increase money supply at a steady, pre-set rate. He believed such a system would better control inflation, making spending and investment decisions more certain. The Economist article said: "In theory, then, the system ought to keep a lid on i ...
INTERNATIONAL FINANCE
... discussed (forwards, options, money market hedges) are most appropriate for covering transaction exposure. ...
... discussed (forwards, options, money market hedges) are most appropriate for covering transaction exposure. ...
Currency war

Currency war, also known as competitive devaluation, is a condition in international affairs where countries compete against each other to achieve a relatively low exchange rate for their own currency. As the price to buy a country's currency falls so too does the price of exports. Imports to the country become more expensive. So domestic industry, and thus employment, receives a boost in demand from both domestic and foreign markets. However, the price increase for imports can harm citizens' purchasing power. The policy can also trigger retaliatory action by other countries which in turn can lead to a general decline in international trade, harming all countries.Competitive devaluation has been rare through most of history as countries have generally preferred to maintain a high value for their currency. Countries have generally allowed market forces to work, or have participated in systems of managed exchanges rates. An exception occurred when currency war broke out in the 1930s. As countries abandoned the Gold Standard during the Great Depression, they used currency devaluations to stimulate their economies. Since this effectively pushes unemployment overseas, trading partners quickly retaliated with their own devaluations. The period is considered to have been an adverse situation for all concerned, as unpredictable changes in exchange rates reduced overall international trade.According to Guido Mantega, the Brazilian Minister for Finance, a global currency war broke out in 2010. This view was echoed by numerous other government officials and financial journalists from around the world. Other senior policy makers and journalists suggested the phrase ""currency war"" overstated the extent of hostility. With a few exceptions, such as Mantega, even commentators who agreed there had been a currency war in 2010 generally concluded that it had fizzled out by mid-2011.States engaging in possible competitive devaluation since 2010 have used a mix of policy tools, including direct government intervention, the imposition of capital controls, and, indirectly, quantitative easing. While many countries experienced undesirable upward pressure on their exchange rates and took part in the ongoing arguments, the most notable dimension of the 2010–11 episode was the rhetorical conflict between the United States and China over the valuation of the yuan. In January 2013, measures announced by Japan which were expected to devalue its currency sparked concern of a possible second 21st century currency war breaking out, this time with the principal source of tension being not China versus the US, but Japan versus the Eurozone. By late February, concerns of a new outbreak of currency war had been mostly allayed, after the G7 and G20 issued statements committing to avoid competitive devaluation. After the European Central Bank launched a fresh programme of quantitative easing in January 2015, there was once again an intensification of discussion about currency war.