joule thomson effect
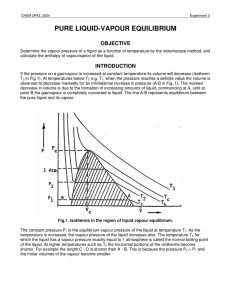
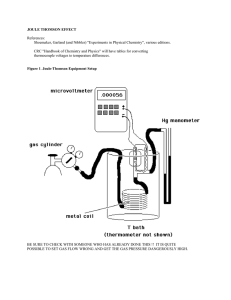
... What is the Joule-Thomson effect? When a non-ideal gas suddenly expands from a high pressure to a low pressure there is often a temperature change. Officially, the ratio of ∆T/∆P is known as the Joule-Thomson coefficient. Note that this is far from a reversible effect! It is however an adiabatic eff ...
... What is the Joule-Thomson effect? When a non-ideal gas suddenly expands from a high pressure to a low pressure there is often a temperature change. Officially, the ratio of ∆T/∆P is known as the Joule-Thomson coefficient. Note that this is far from a reversible effect! It is however an adiabatic eff ...
Chapter 1 Review of laser
... transitions raises the absorption causing a stronger heating. Upon heating even more carriers are produced reinforcing the absorption. This cascade-like effect is denominated thermal runaway and can be observed very well in the infrared where the lattice absorption is small [All87]. In addition to o ...
... transitions raises the absorption causing a stronger heating. Upon heating even more carriers are produced reinforcing the absorption. This cascade-like effect is denominated thermal runaway and can be observed very well in the infrared where the lattice absorption is small [All87]. In addition to o ...
Transition State of a Creatine Molecule during Dehydration
... The experiment began with the use of MacSpartan on a Power Macintosh. We completed our project using MacSpartan Pro. The transition state was determined using the SemiEmpirical method of AM-1. Due to the complexity of our molecule, the ab initio method (321G*) was impractical. We used the Semi ...
... The experiment began with the use of MacSpartan on a Power Macintosh. We completed our project using MacSpartan Pro. The transition state was determined using the SemiEmpirical method of AM-1. Due to the complexity of our molecule, the ab initio method (321G*) was impractical. We used the Semi ...
Viscosity activation energy
... in the Discussion part. Equation (11) is based only on the assumption that viscous flow is a thermally activated process. Therefore, the definition of the dimensionless fragility parameter α is universal. It accounts for the rate at which the activation energy changes with temperature. By means of E ...
... in the Discussion part. Equation (11) is based only on the assumption that viscous flow is a thermally activated process. Therefore, the definition of the dimensionless fragility parameter α is universal. It accounts for the rate at which the activation energy changes with temperature. By means of E ...
Many thermal and chemical reactions occur during the roasting
... and partially disordered (amorphous). The amorphous regions are highly accessible and react readily, but the crystalline regions with close packing and hydrogen bonding may be completely inaccessible. Native cellulose, or cellulose 1, is converted to polymorphs cellulose III and cellulose IV when ex ...
... and partially disordered (amorphous). The amorphous regions are highly accessible and react readily, but the crystalline regions with close packing and hydrogen bonding may be completely inaccessible. Native cellulose, or cellulose 1, is converted to polymorphs cellulose III and cellulose IV when ex ...
Spontaniety
... Elements have nonzero standard entropies. Standard molar entropies of pure substances are always positive quantities. Aqueous ions may have negative entropy values. As a group, gases tend to have higher entropies than liquids. An increase in the number of moles of a gas also leads to a higher entrop ...
... Elements have nonzero standard entropies. Standard molar entropies of pure substances are always positive quantities. Aqueous ions may have negative entropy values. As a group, gases tend to have higher entropies than liquids. An increase in the number of moles of a gas also leads to a higher entrop ...
Nugget
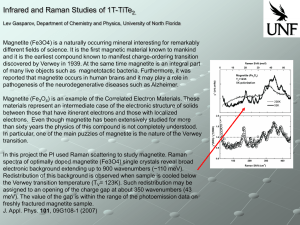
... Magnetite (Fe3O4) is a naturally occurring mineral interesting for remarkably different fields of science. It is the first magnetic material known to mankind and it is the earliest compound known to manifest charge-ordering transition discovered by Verwey in 1939. At the same time magnetite is an in ...
... Magnetite (Fe3O4) is a naturally occurring mineral interesting for remarkably different fields of science. It is the first magnetic material known to mankind and it is the earliest compound known to manifest charge-ordering transition discovered by Verwey in 1939. At the same time magnetite is an in ...
Communicating Research to the General Public
... One of the major themes of inorganic chemistry is the study of metals, in particular transition metals. Transition metals, highlighted in red in Figure 1.1 comprise a majority of the periodic table and can be considered the building blocks of inorganic chemistry just as carbon is considered the buil ...
... One of the major themes of inorganic chemistry is the study of metals, in particular transition metals. Transition metals, highlighted in red in Figure 1.1 comprise a majority of the periodic table and can be considered the building blocks of inorganic chemistry just as carbon is considered the buil ...
ppt - GeDet
... High-purity germanium detectors are used in neutrinoless doublebeta decay experiments like GERDA because they have very good energy resolutions and act as detectors and sources simultaneously. They are operated close to liquid nitrogen temperature. The mobility of the charge carriers is temperature ...
... High-purity germanium detectors are used in neutrinoless doublebeta decay experiments like GERDA because they have very good energy resolutions and act as detectors and sources simultaneously. They are operated close to liquid nitrogen temperature. The mobility of the charge carriers is temperature ...
In Praise of Entropy Gary D. Patterson Professor of Chemistry
... When crystals melt, the entropy of the system increases because liquids have a higher entropy than the corresponding solid at the same temperature ( the entropy change on melting is equal to the heat of melting divided by the melting temperature). Liquids are more disordered than crystalline solids ...
... When crystals melt, the entropy of the system increases because liquids have a higher entropy than the corresponding solid at the same temperature ( the entropy change on melting is equal to the heat of melting divided by the melting temperature). Liquids are more disordered than crystalline solids ...
Class 26: Calculating Electronic contribution to specific heat
... process much more elegantly and effectively than real space. Therefore, as a first step we have to understand what is reciprocal space, how is it defined, how are crystal structures represented in reciprocal space, and how diffraction is described in reciprocal space. This will be the subject of our ...
... process much more elegantly and effectively than real space. Therefore, as a first step we have to understand what is reciprocal space, how is it defined, how are crystal structures represented in reciprocal space, and how diffraction is described in reciprocal space. This will be the subject of our ...
Lecture 8
... - The rate of reaction generally depends on the concentration of reactants. Rate =k[A]n[B]m - where k is the rate constant and n and m are the orders of reaction with respect to reactants A and B. - Orders of reaction depend on the mechanism and are not necessarily equal to the stoichiometric coeffi ...
... - The rate of reaction generally depends on the concentration of reactants. Rate =k[A]n[B]m - where k is the rate constant and n and m are the orders of reaction with respect to reactants A and B. - Orders of reaction depend on the mechanism and are not necessarily equal to the stoichiometric coeffi ...
pure liquid-vapour equilibrium - Theoretical and Computational
... approximation Vvap = Vv. The molar volume of the liquid can be neglected compared to that of the vapour. Defining the compressibility factor of the vapour as ...
... approximation Vvap = Vv. The molar volume of the liquid can be neglected compared to that of the vapour. Defining the compressibility factor of the vapour as ...
Vapor Pressure of a Pure Liquid
... and enter the gas phase until the pressure of the vapor in the bulb reaches a definite value which is determined by the nature of the liquid and its temperature. This is called the vapor pressure of the liquid. In this experiment, the variation of vapor pressure with temperature will be measured and ...
... and enter the gas phase until the pressure of the vapor in the bulb reaches a definite value which is determined by the nature of the liquid and its temperature. This is called the vapor pressure of the liquid. In this experiment, the variation of vapor pressure with temperature will be measured and ...
Properties of Matter - Red Clay Secondary Science Wiki
... Which Standards are students learning in this unit? Standard 2.1.A All matter consists of particles too small to be seen with the naked eye. The arrangement, motion, and interaction of these particles determine the three states of matter (solid, liquid, and gas). Particles in all three states are in ...
... Which Standards are students learning in this unit? Standard 2.1.A All matter consists of particles too small to be seen with the naked eye. The arrangement, motion, and interaction of these particles determine the three states of matter (solid, liquid, and gas). Particles in all three states are in ...
Catalytic Mechanisms Acid-Base Catalysis Covalent Catalysis Metal
... Interactions that preferentially bind the transition state increase its concentration and proportionally increase the reaction rate Use of transition state theory leads to the prediction that enzymatic binding of a transition state by two hydrogen bonds that cannot form in the Michaelis complex shou ...
... Interactions that preferentially bind the transition state increase its concentration and proportionally increase the reaction rate Use of transition state theory leads to the prediction that enzymatic binding of a transition state by two hydrogen bonds that cannot form in the Michaelis complex shou ...
Glass transition
The glass–liquid transition or glass transition for short is the reversible transition in amorphous materials (or in amorphous regions within semicrystalline materials) from a hard and relatively brittle state into a molten or rubber-like state. An amorphous solid that exhibits a glass transition is called a glass. Supercooling a viscous liquid into the glass state is called vitrification, from the Latin vitreum, ""glass"" via French vitrifier.Despite the massive change in the physical properties of a material through its glass transition, the transition is not itself a phase transition of any kind; rather it is a laboratory phenomenon extending over a range of temperature and defined by one of several conventions. Such conventions include a constant cooling rate (20 K/min) and a viscosity threshold of 1012 Pa·s, among others. Upon cooling or heating through this glass-transition range, the material also exhibits a smooth step in the thermal-expansion coefficient and in the specific heat, with the location of these effects again being dependent on the history of the material. However, the question of whether some phase transition underlies the glass transition is a matter of continuing research.The glass-transition temperature Tg is always lower than the melting temperature, Tm, of the crystalline state of the material, if one exists.